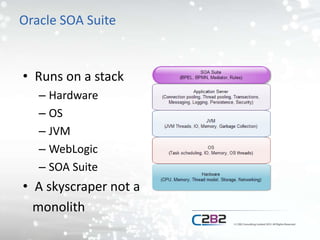
The document outlines the importance and methods of monitoring Oracle SOA Suite, highlighting key metrics to capture and the tools available for effective monitoring. It emphasizes early problem detection, capacity planning, and understanding system performance to enhance business operations and reduce costs. Best practices and recommendations for alerting and monitoring tool selection are also discussed.