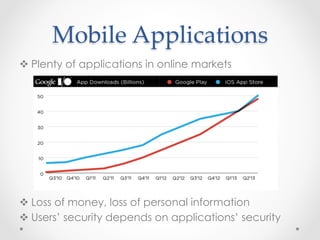
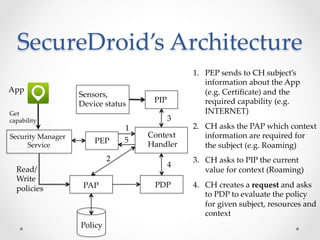
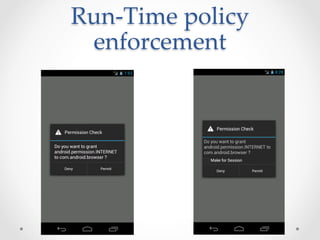
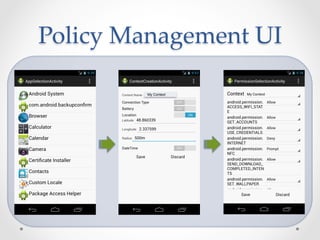
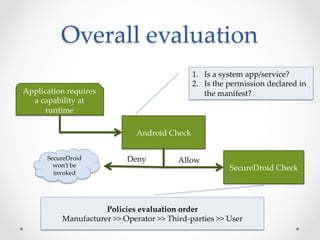
SecureDroid is an Android security framework extension that allows context-aware policy enforcement at runtime. It extends the standard Android security framework to check custom policies after an app is installed, using context information like location as constraints. Multiple parties like manufacturers, carriers, and users can set policies that are evaluated in a specific order. SecureDroid's architecture includes a policy enforcement point, context handler, policy administration and information points, and a policy decision point to determine access based on the app, permissions, context, and applicable policies.