1. The document discusses multistage separation processes and different types of distillation operations including simple distillation, flash distillation, and multistage distillation.
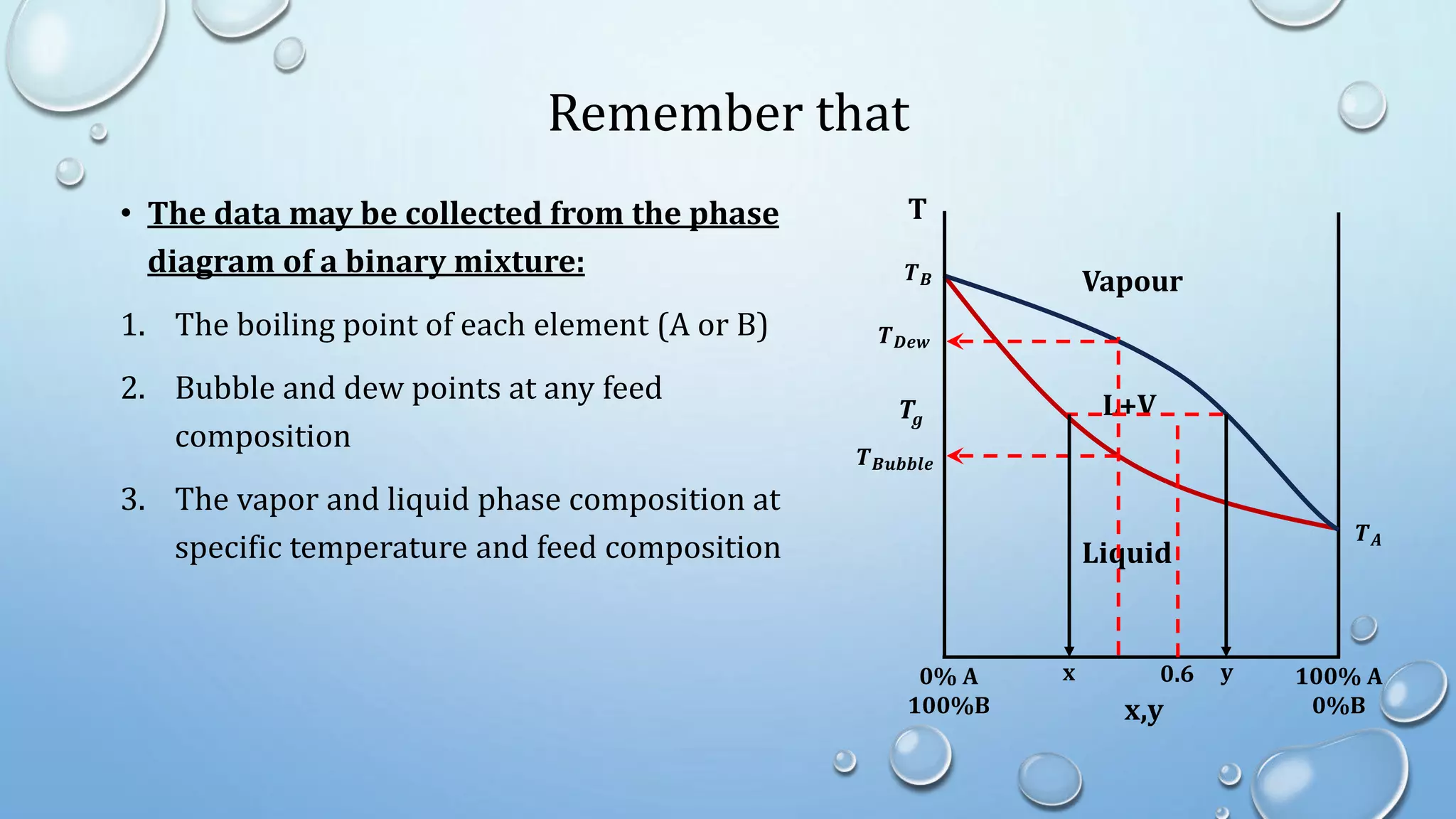
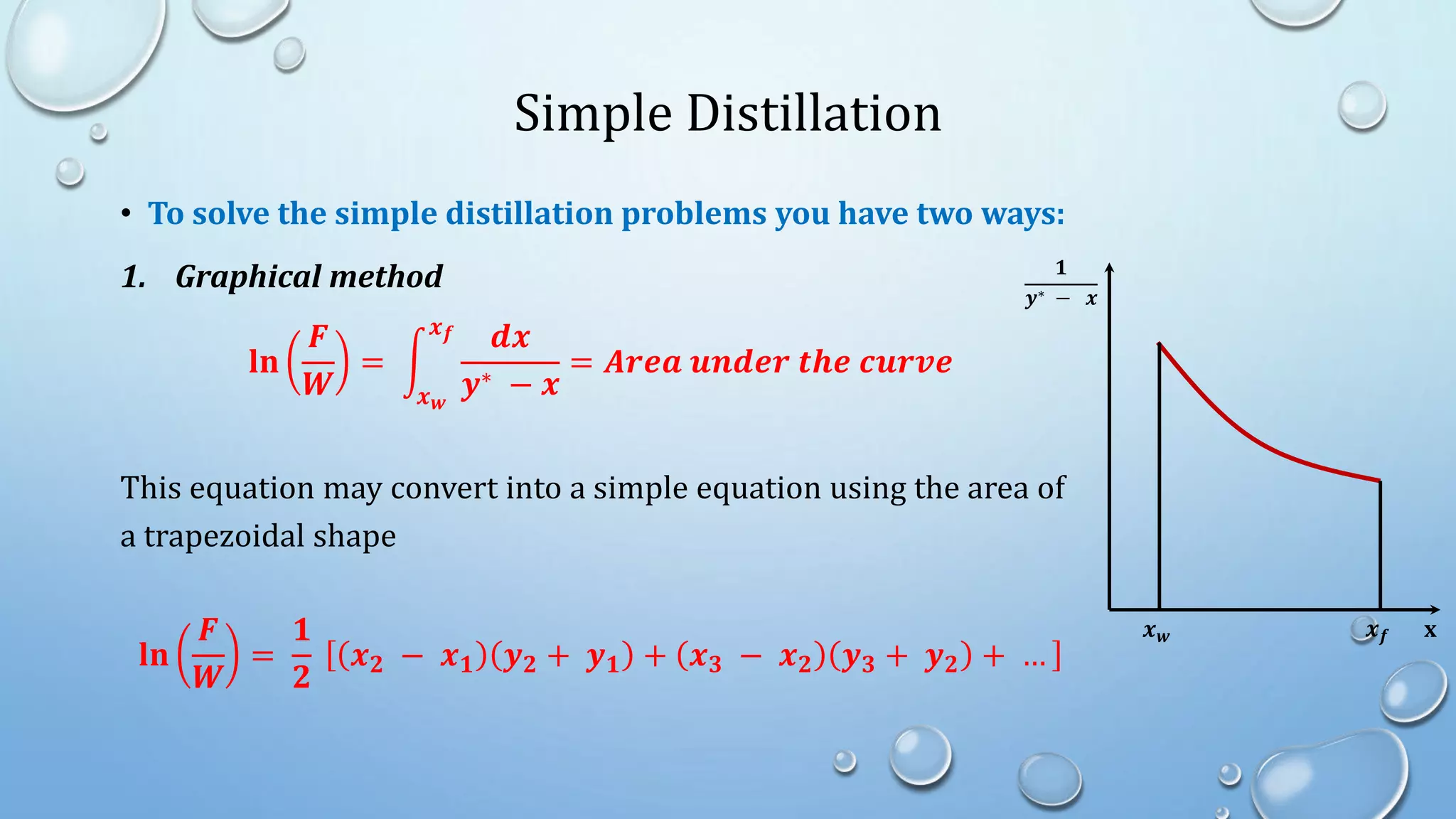
2. Simple distillation involves a feed, distillate, and residue stream, and can be solved graphically or algebraically using material balances.
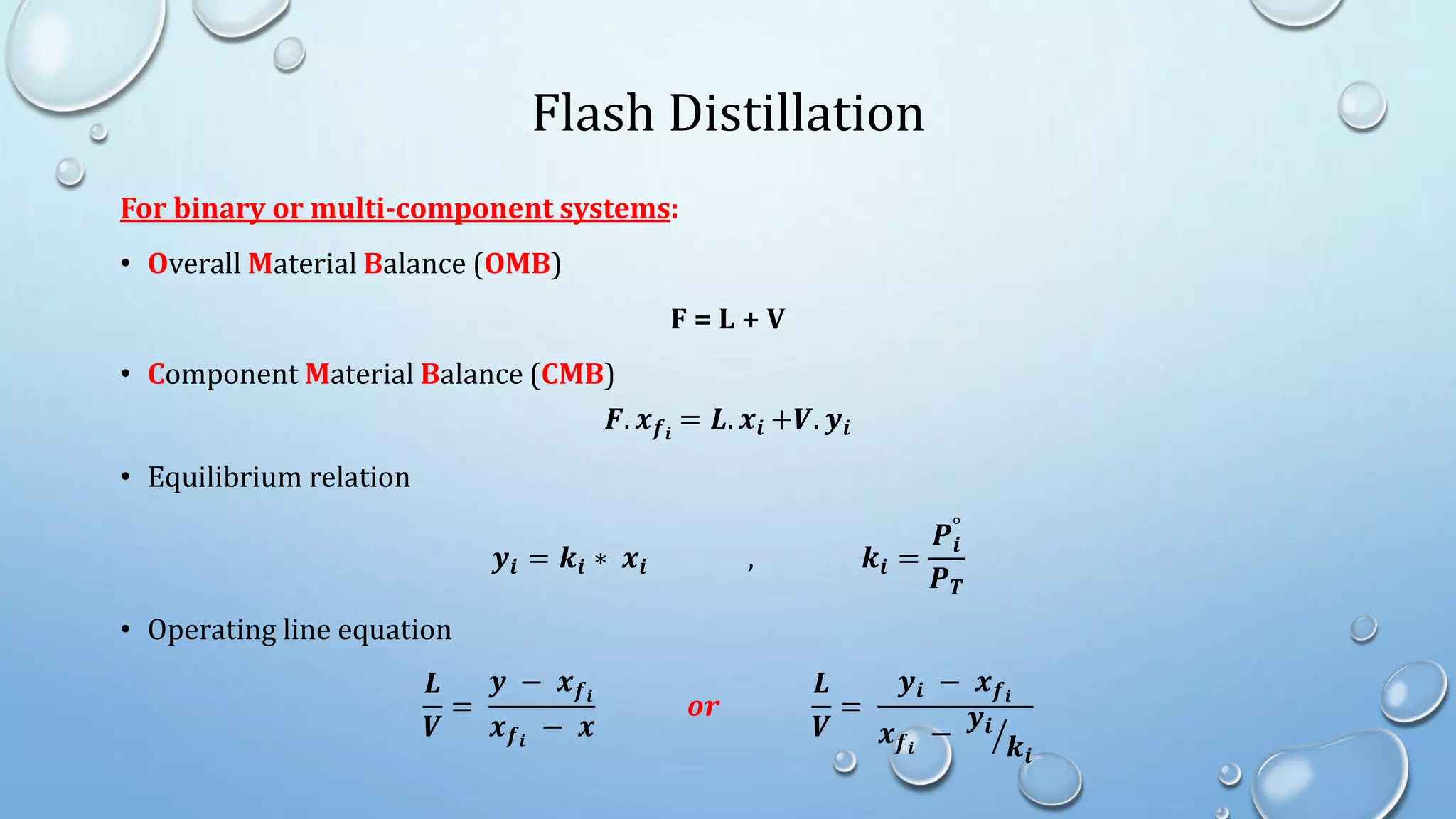
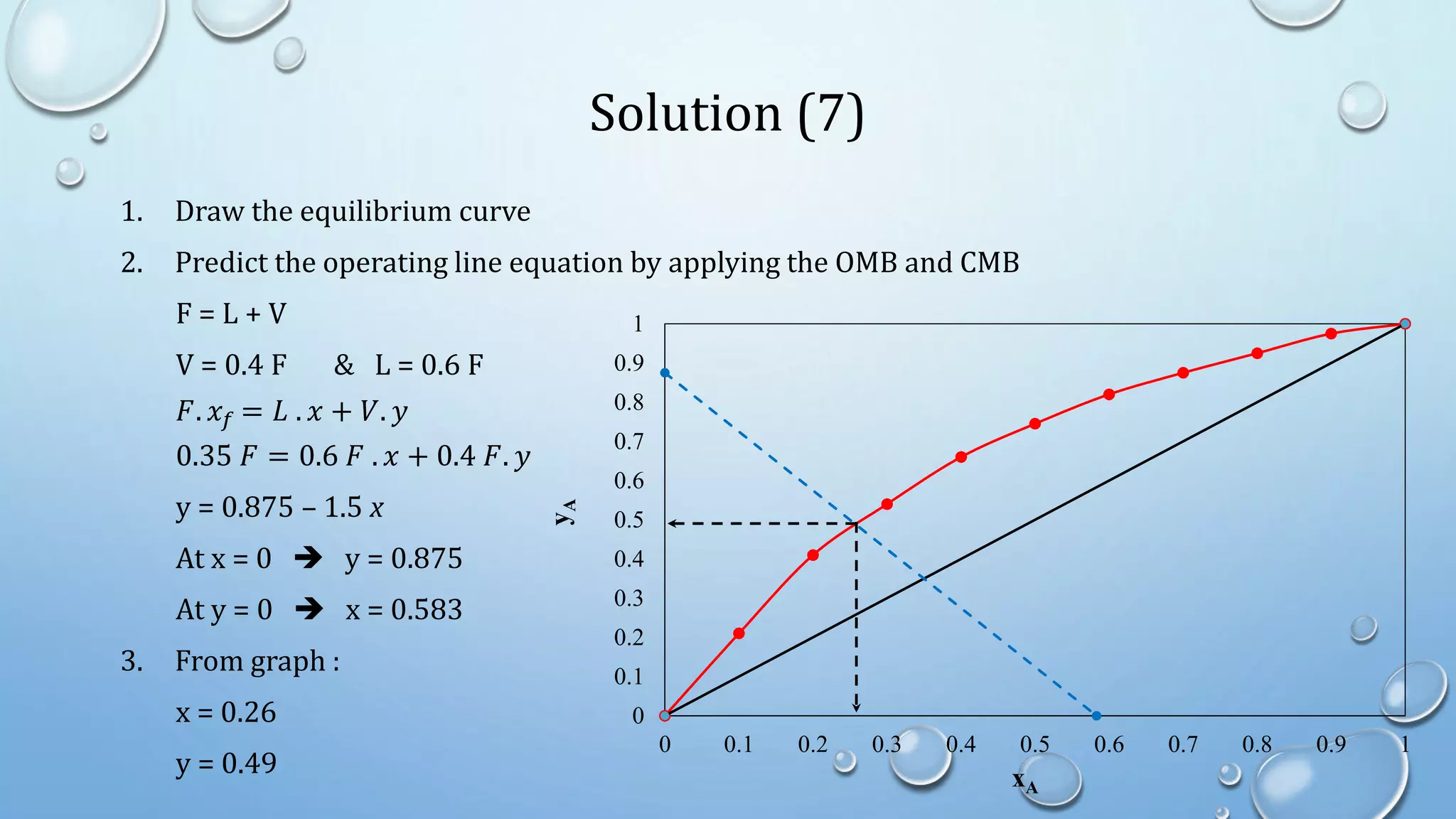
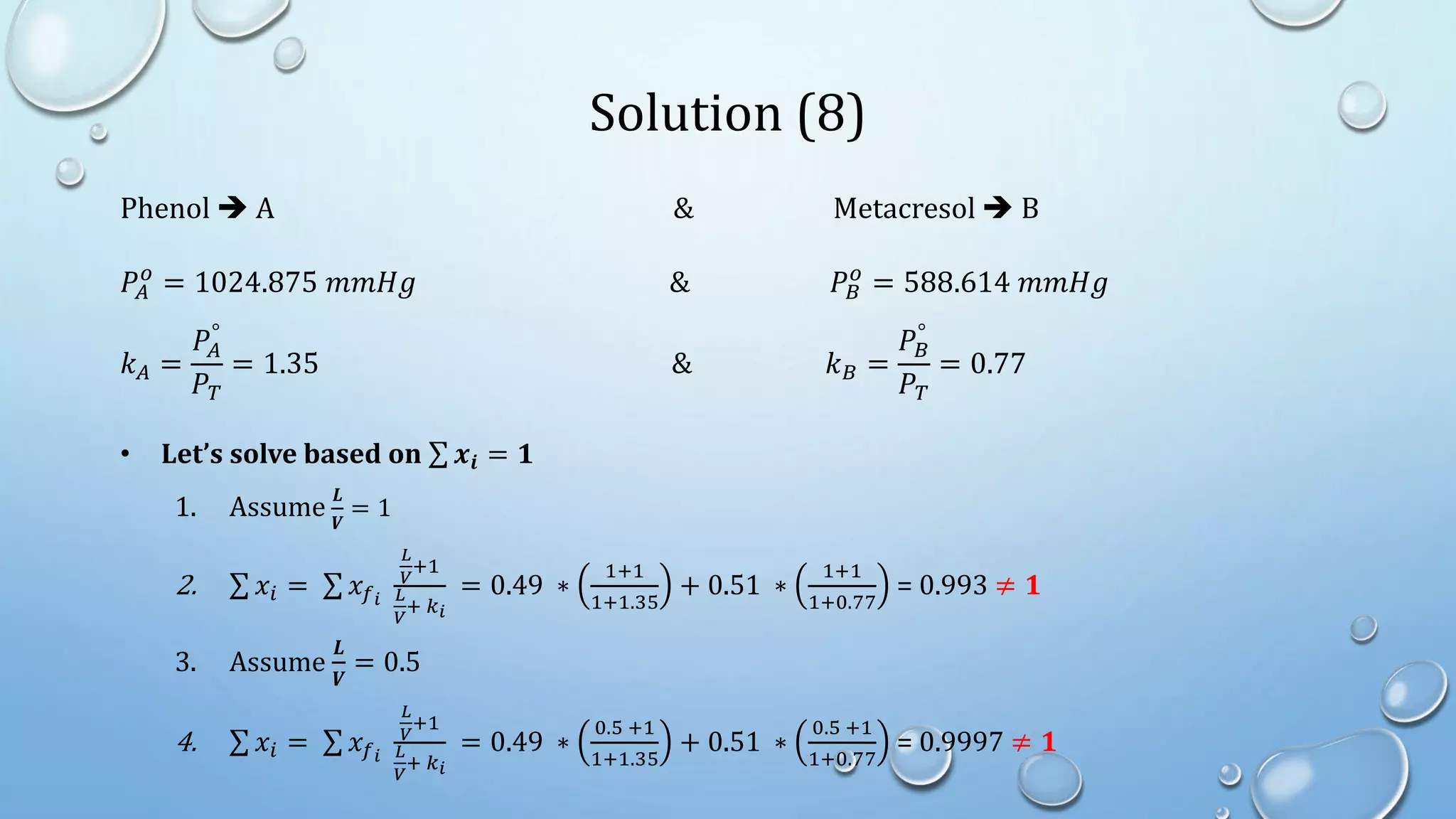
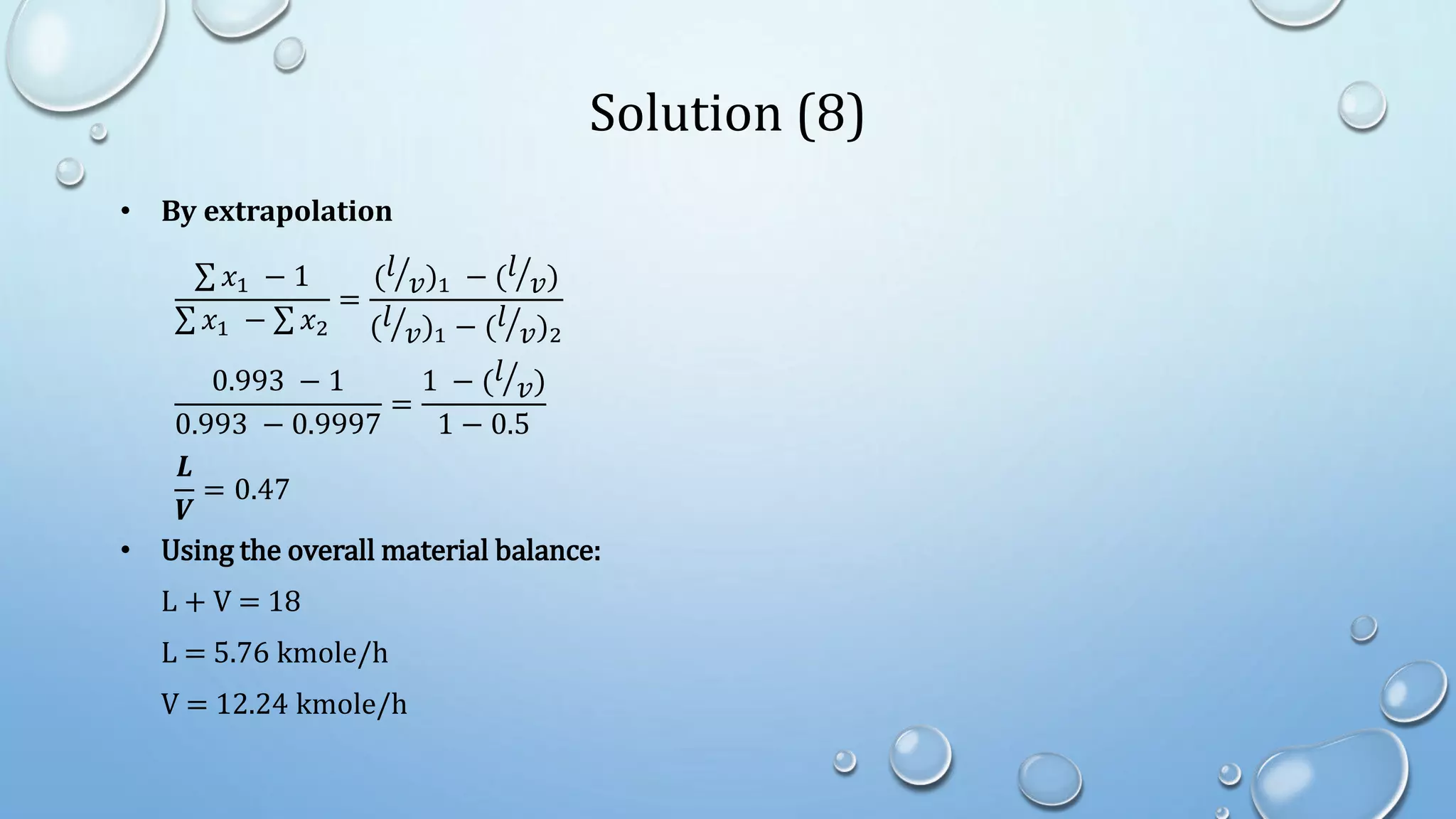
3. Flash distillation separates a feed stream into a vapor and liquid product using equilibrium relationships, and the compositions are solved using operating line equations.
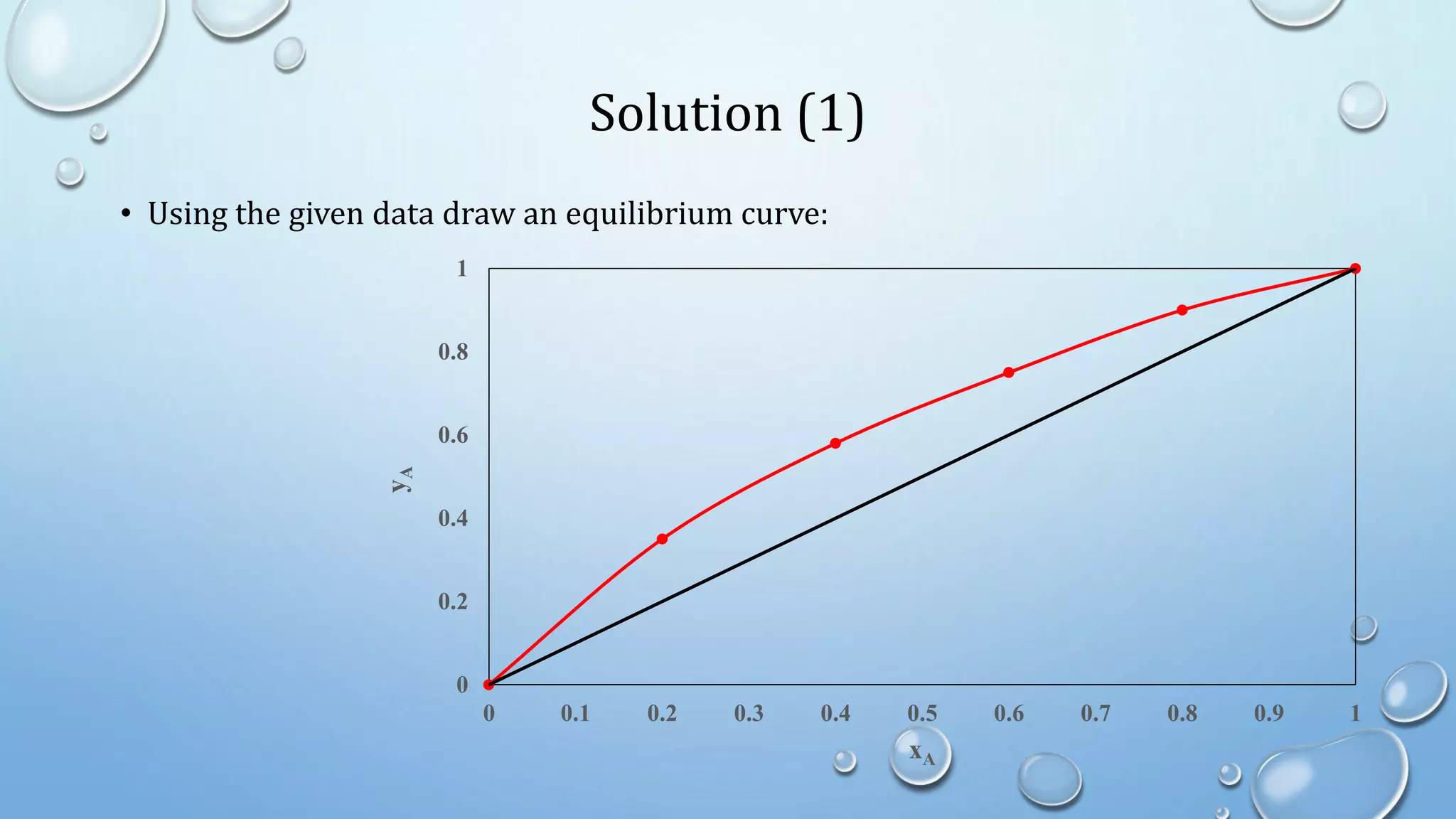
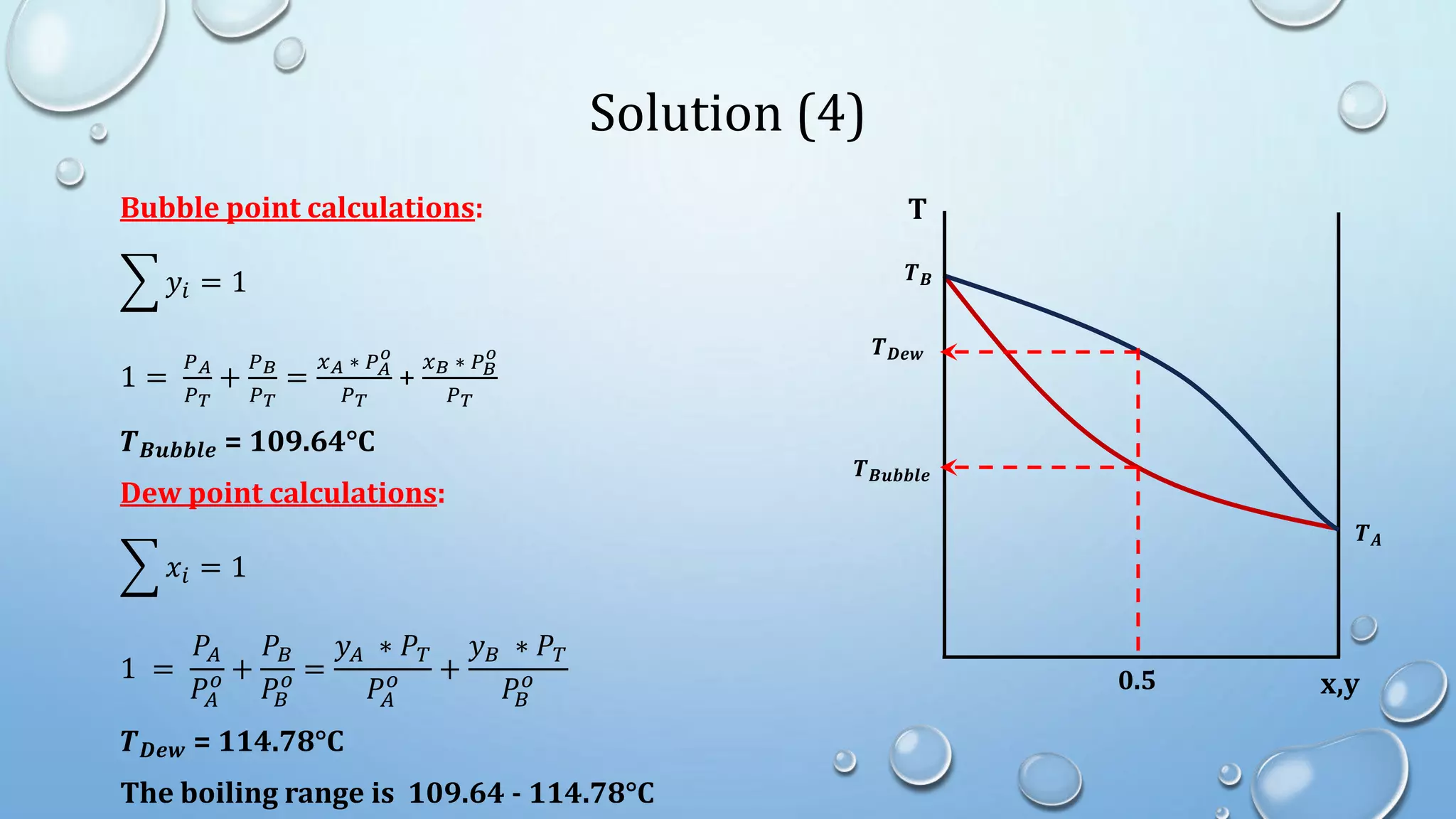
4. Examples show how to apply material balances and equilibrium relationships to calculate stream compositions for simple and flash distillation problems.