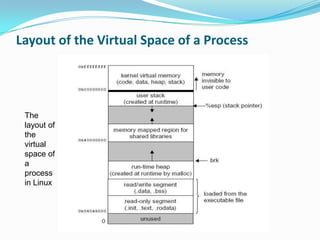
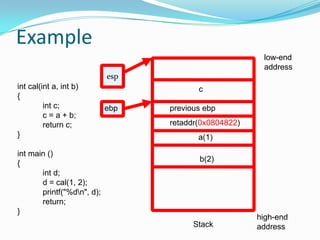
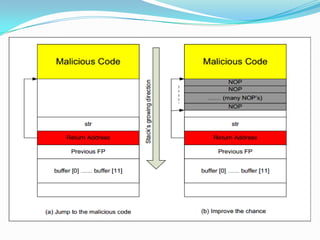
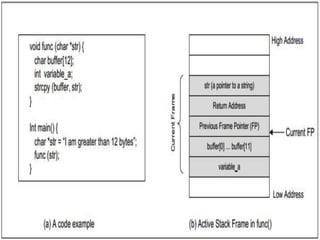
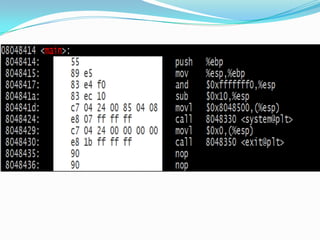
The document discusses buffer overflow attacks used to execute malicious code with unauthorized privileges, manipulating the process stack layout. It explains the mechanics of shellcode, its role in exploiting programs, and highlights prevention strategies such as stack guards and non-executable stacks. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of security measures against such vulnerabilities in both local and remote contexts.