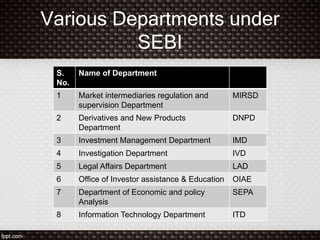
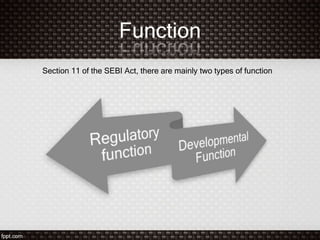
SEBI was established in 1988 as a non-statutory body and was given statutory powers through an amendment in 1995. It was constituted as the regulator of the Indian capital market through a 1998 government resolution. SEBI aims to protect investors, promote the securities market, and ensure fair practices through regulatory and developmental functions like registering and monitoring intermediaries and promoting research and education. It consists of a chairman and other government and private members and has powers like inspection, investigation, and issuing directions to achieve its objectives of developing the market and protecting investors.