- SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) is the regulator for securities markets in India, established in 1988 and given statutory powers in 1992 through the SEBI Act.
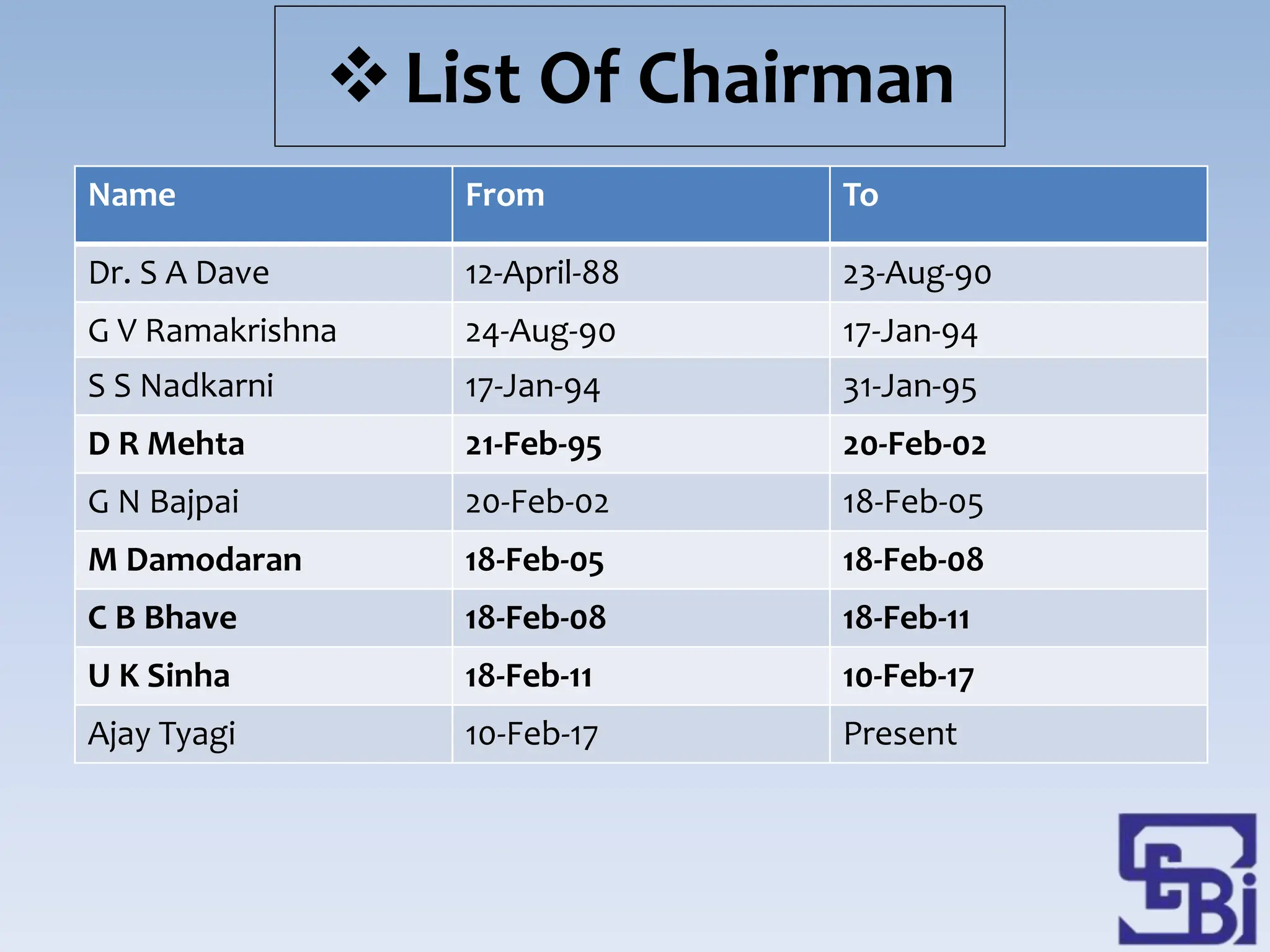
- SEBI is headquartered in Mumbai and has regional offices across India. It was established to regulate the stock market and protect investors due to issues like price rigging in stock exchanges.
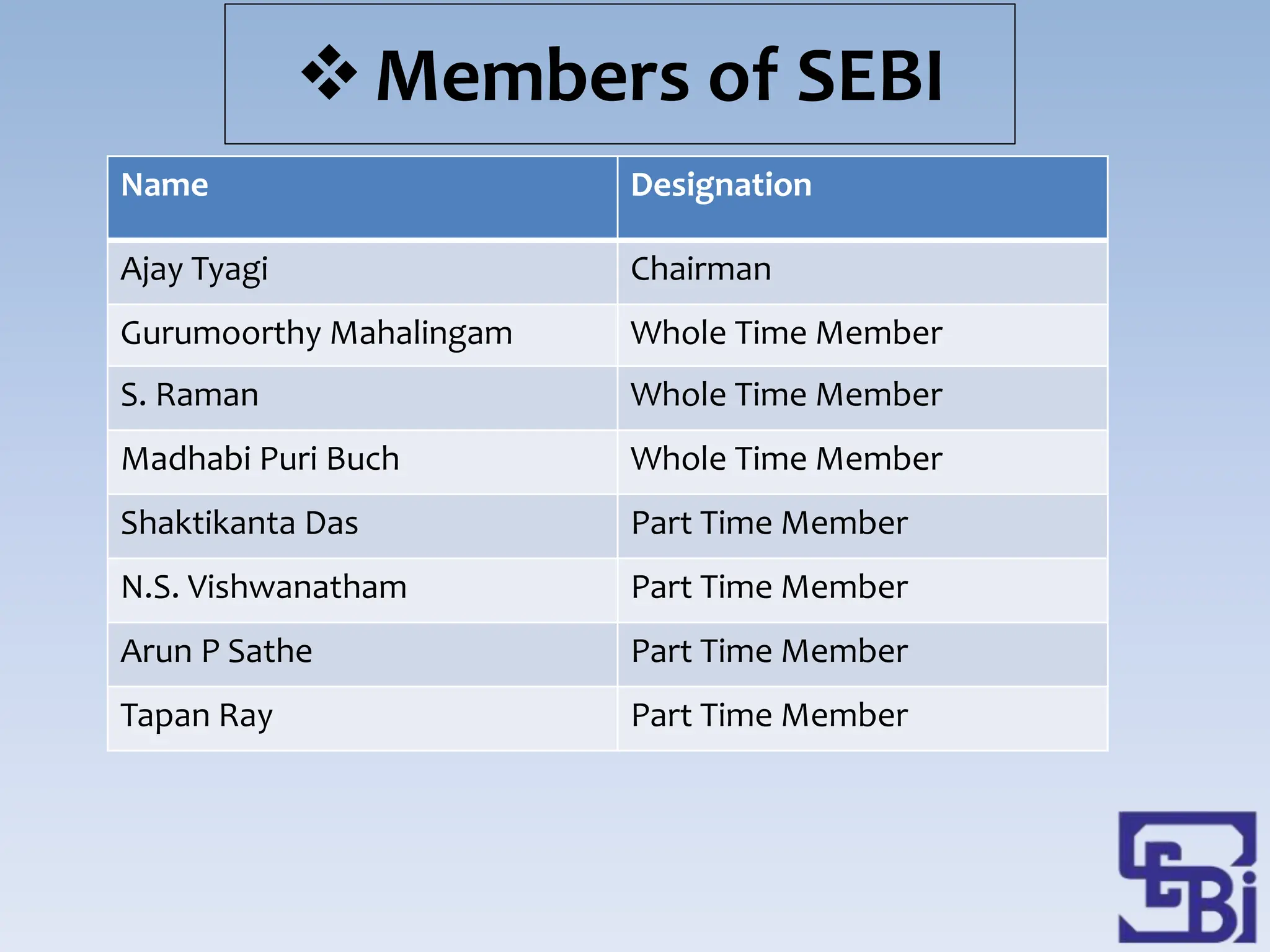
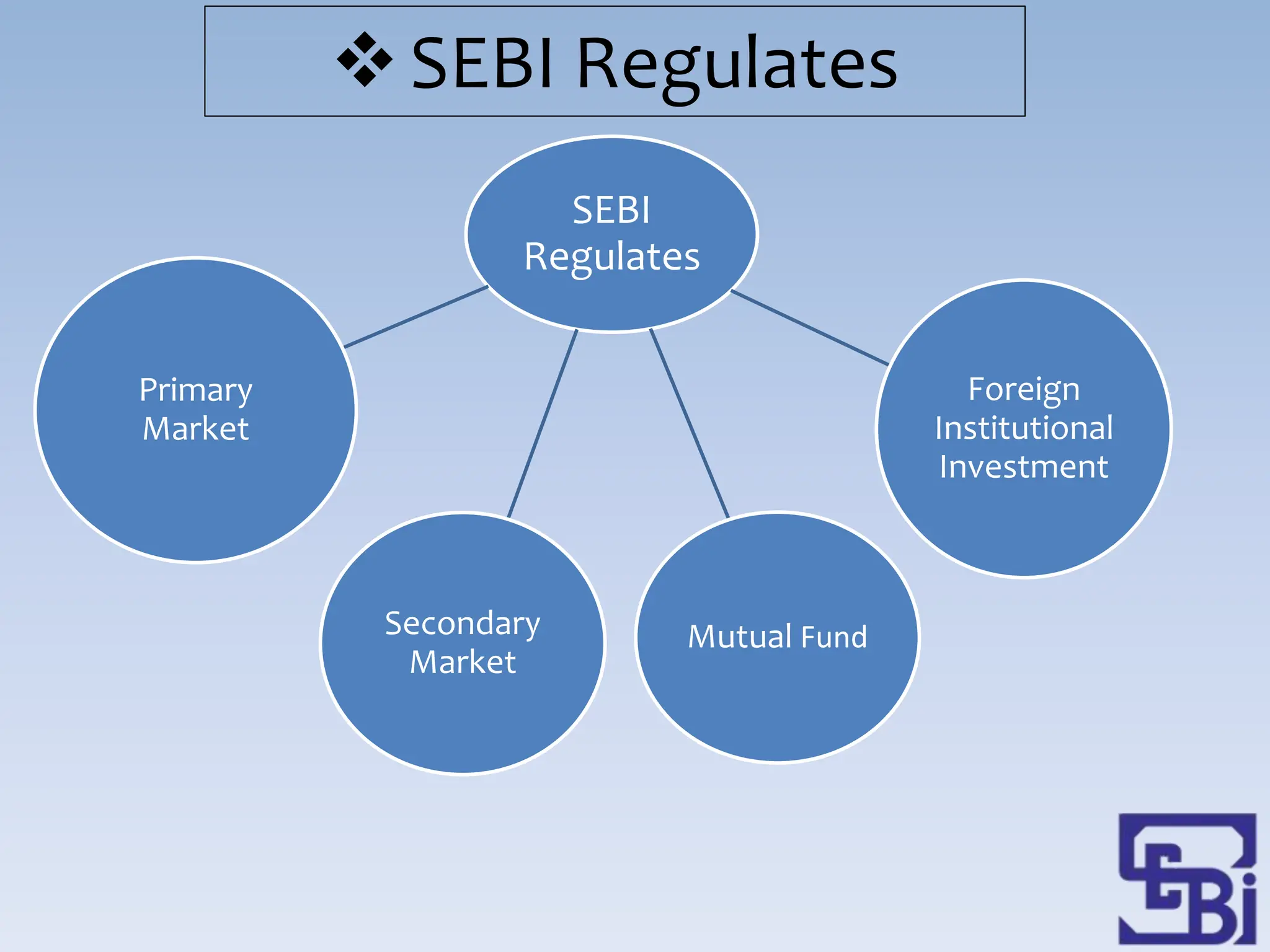
- SEBI's objectives include regulating stock exchanges, protecting investor interests, developing rules for market intermediaries, and balancing self-regulation with statutory regulation.
- To meet its objectives, SEBI performs protective, developmental, and regulatory functions like prohibiting insider trading, promoting stock exchange activities, and registering and regulating market participants.