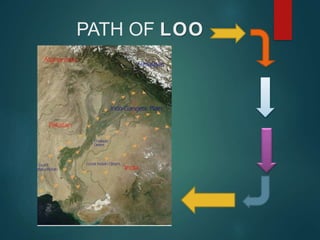
The document discusses the different seasons in India: winter, summer, rainy season, and retreating monsoon. Winter is the cold weather season from November to February when rabi crops like wheat and mustard are grown. Summer is the hot weather season from March to May. The rainy season or kharif season allows crops like rice, maize, and millet to be grown from onset of monsoon until September-October. A short zaid season in between allows crops like melons and vegetables to be grown from March to June. The hot, dry Loo winds blow during May and June, causing high temperatures over North India.