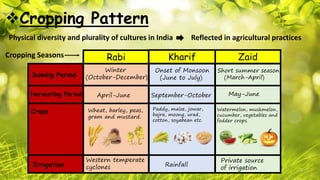
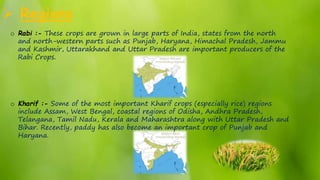
The document discusses cropping patterns and major crops in India. It outlines three cropping seasons - Rabi, Kharif, and Zaid - and their typical sowing and harvesting periods. Rabi crops like wheat and mustard are grown in winter. Kharif crops like rice, maize, and cotton are grown during the monsoon. Zaid crops such as melons and vegetables are grown in summer. It also identifies the main regions for producing Rabi and Kharif crops. The two most important crops in India are rice and wheat, with rice being a major Kharif crop grown in eastern states and wheat a primary Rabi crop in northern states.