This document discusses two algorithms for searching arrays: linear search and binary search. Linear search simply checks each element of the array sequentially to find a target value, while binary search relies on the array being sorted and checks elements in a divide-and-conquer manner by repeatedly dividing the search space in half. The document provides pseudocode to illustrate how binary search works and compares the advantages of each approach.





![INFO 106 – Computer Programming
7
Program
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a[10],i,target;
printf("Enter array value n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
printf("Which value to be search ->");
scanf("%d",&target);
/* Linear Search logic */
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
if(target==a[i])
{
printf(“Value found at %d”,i);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/searching-170327061929/85/Searching-in-Arrays-7-320.jpg)


![Binary Search
[ 0 ] [ 1 ]
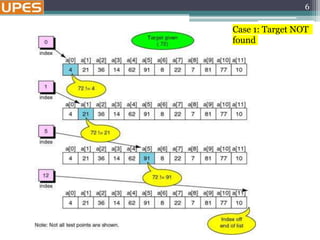
Example: sorted array of integer keys. Target=7.
3 6 7 11 32 33 53
[ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] [ 6 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/searching-170327061929/85/Searching-in-Arrays-10-320.jpg)
![INFO 106 – Computer Programming
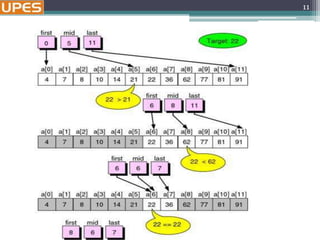
Binary Search Pseudocode
…
if(size == 0)
found = false;
else {
middle = index of approximate midpoint of array segment;
if(target == a[middle])
target has been found!
else if(target < a[middle])
search for target in area before midpoint;
else
search for target in area after midpoint;
}
…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/searching-170327061929/85/Searching-in-Arrays-12-320.jpg)
![INFO 106 – Computer Programming
Program
int result=-1;
int low=0;
int high=length-1;
int mid;
while( result==-1 && low<=high )
{ mid= low + ((high - low) / 2);
if( list[mid] == target )
result = mid;
else if( list[mid] < target)
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid - 1;
}
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/searching-170327061929/85/Searching-in-Arrays-13-320.jpg)
