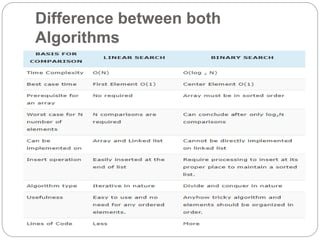
The document discusses linear and binary search algorithms.
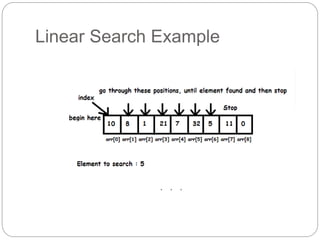
Linear search is the simplest algorithm that sequentially compares each element of an array to the target element. It has a worst case time complexity of O(N).
Binary search works on a sorted array by comparing the middle element to the target. It eliminates half of the remaining elements with each comparison. It has a worst case time complexity of O(log n), which is faster than linear search for large data sets.
Pseudocode and C programs are provided as examples to implement linear and binary search.


![Linear Search Algorithm
Linear Search ( Array A, Value x)
Step 1: Set i to 1
Step 2: if i > n then go to step 7
Step 3: if A[i] = x then go to step 6
Step 4: Set i to i + 1
Step 5: Go to Step 2
Step 6: Print Element x Found at index i and go to step 8
Step 7: Print element not found
Step 8: Exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programs-190408074204/85/Searching-3-320.jpg)

![Program for Linear Search in C
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[20],i,x,n;
printf("How many elements?");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter array elements:n");
for(i=0;i<n;++i)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
printf("nEnter element to search:");
scanf("%d",&x);
for(i=0;i<n;++i)
if(a[i]==x)
break;
if(i<n)
printf("Element found at index %d",i);
else
printf("Element not found");
return 0;
}
Output
How many elements?4
Enter array elements:
6 8 9 1
Enter element to
search:9
Element found at index
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programs-190408074204/85/Searching-6-320.jpg)


![Pseudo code for Binary Search
Procedure binary_search
A ← sorted array
n ← size of array
x ← value to be searched
Set lowerBound = 1
Set upperBound = n
while x not found
if upperBound < lowerBound
EXIT: x does not exists.
set midPoint = lowerBound + ( upperBound - lowerBound ) / 2
if A[midPoint] < x set lowerBound = midPoint + 1
if A[midPoint] > x set upperBound = midPoint - 1
if A[midPoint] = x EXIT: x found at location midPoint
end while
end procedure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programs-190408074204/85/Searching-9-320.jpg)

![#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{ int c, first, last, middle, n, search, array[100];
printf("Enter number of elementsn");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter %d integersn", n);
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
scanf("%d",&array[c]);
printf("Enter value to findn");
scanf("%d", &search);
first = 0; last = n - 1;
middle = (first+last)/2;
while (first <= last) {
if (array[middle] < search)
first = middle + 1;
else if (array[middle] == search) {
printf("%d found at location %d.n", search, middle+1);
break; }
else
last = middle - 1;
middle = (first + last)/2; }
if (first > last)
printf("Not found! %d isn't present in the list.n", search);
return 0; }
Program for Binary Search in
C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programs-190408074204/85/Searching-11-320.jpg)