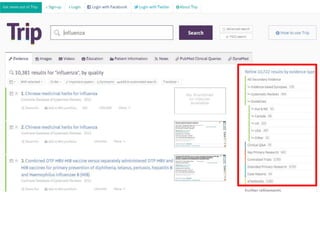
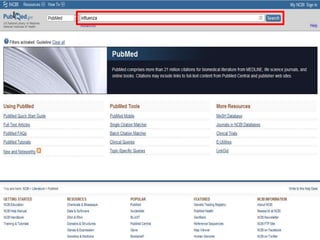
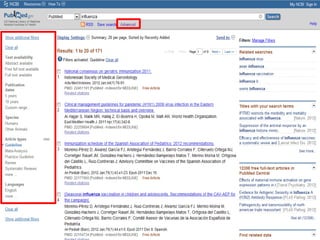
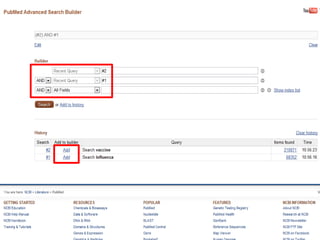
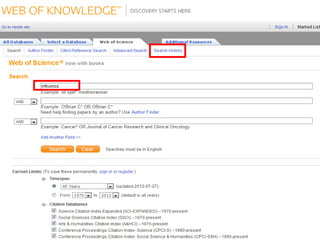
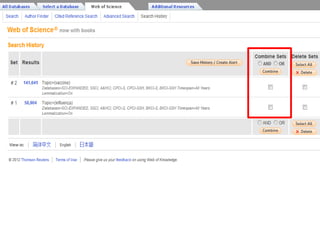
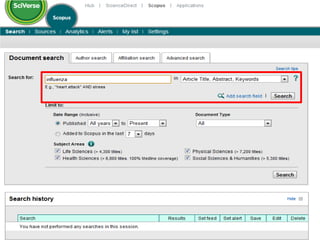
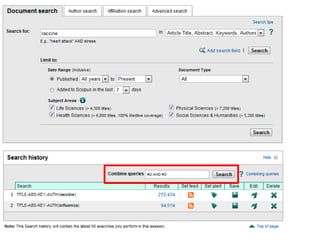
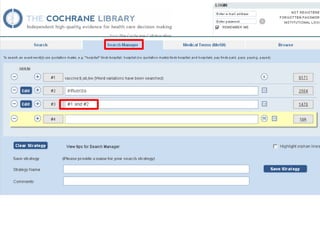
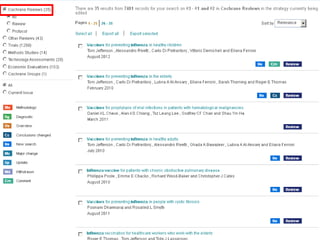
This document provides information on searching for health-related information online. It recommends using specialized search engines that filter results to high-quality sources. It describes several tools for searching medical literature databases, including Medline Plus, Evidence Search, TRIP, PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus. It also discusses strategies for broadening and narrowing searches, such as using Boolean operators, phrase searching, and subject headings. The goal is to help users efficiently find trustworthy information from curated sources.