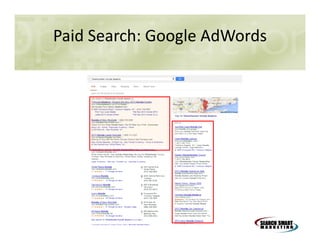
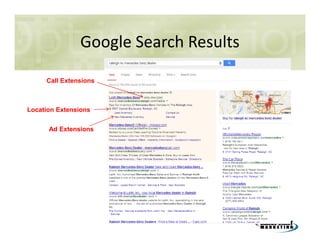
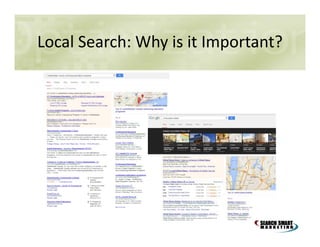
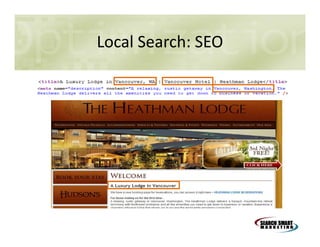
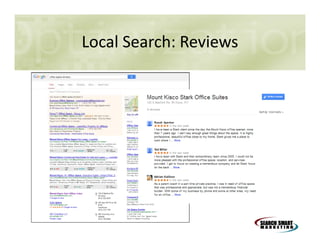
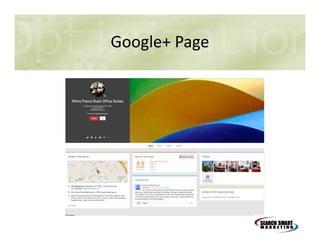
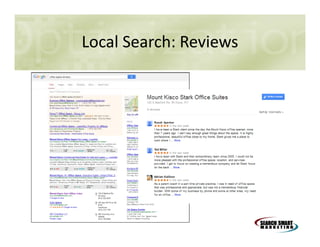
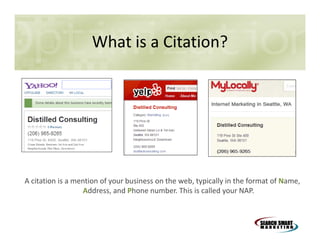
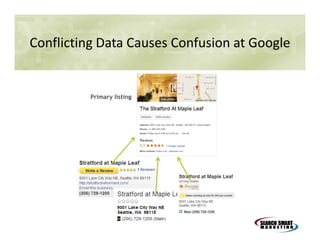
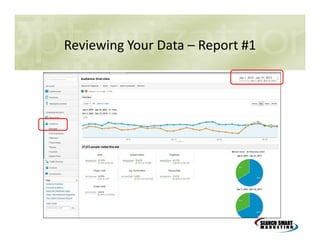
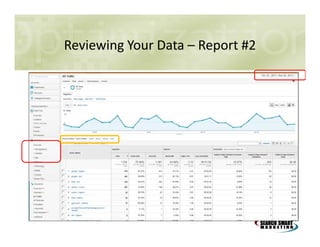
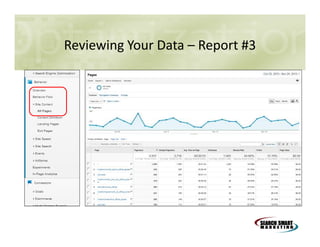
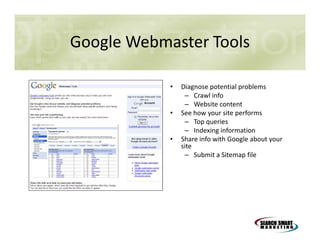
This document discusses search engine marketing strategies. It covers organic search engine optimization techniques like on-page optimization of titles, descriptions, content and coding as well as off-page optimization through link building. It also discusses paid search advertising on search engines like Google through pay-per-click campaigns and local search optimization through listings, citations and reviews. Finally, it discusses measuring search marketing success through analytics tools like Google Analytics.