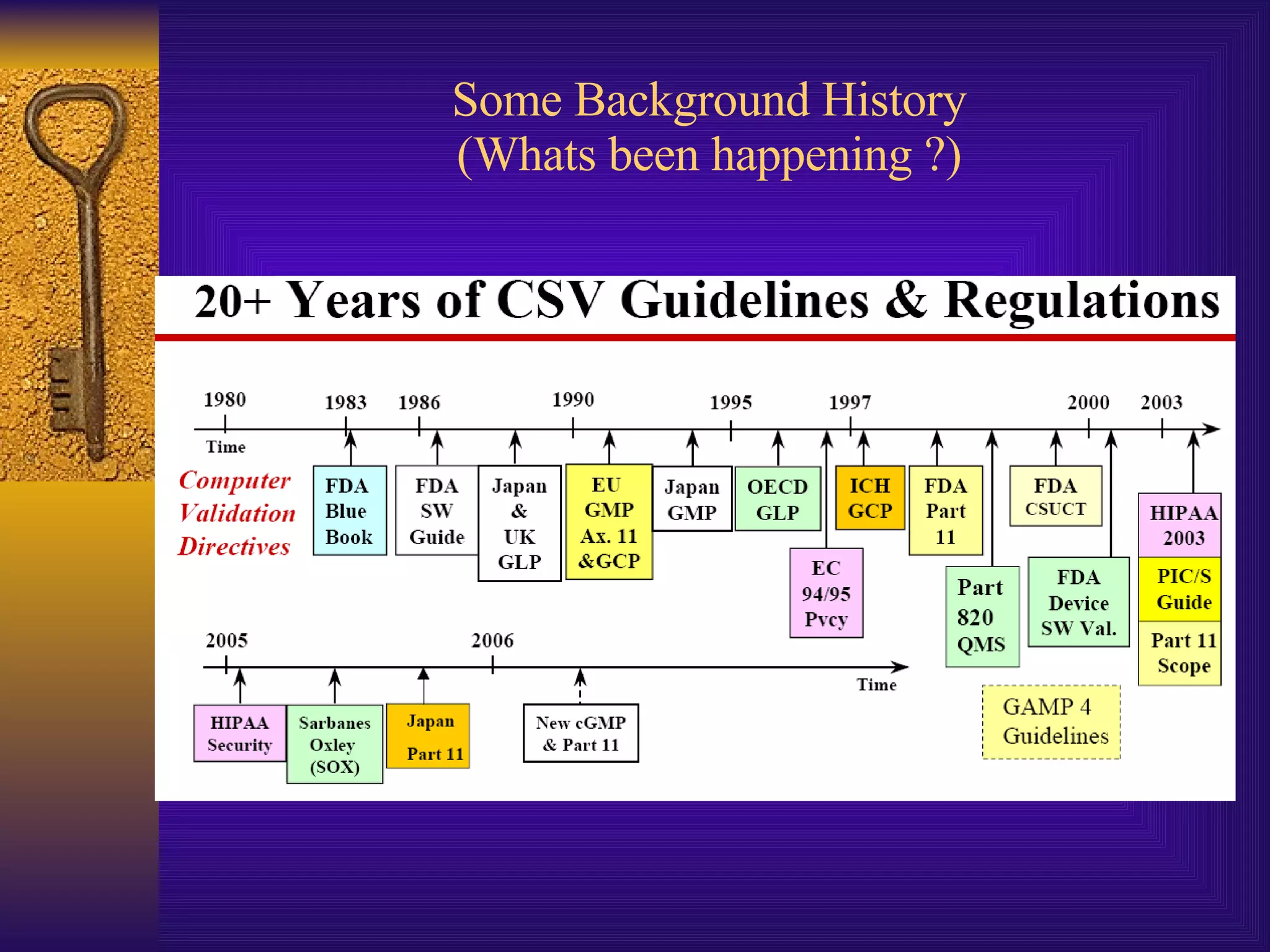
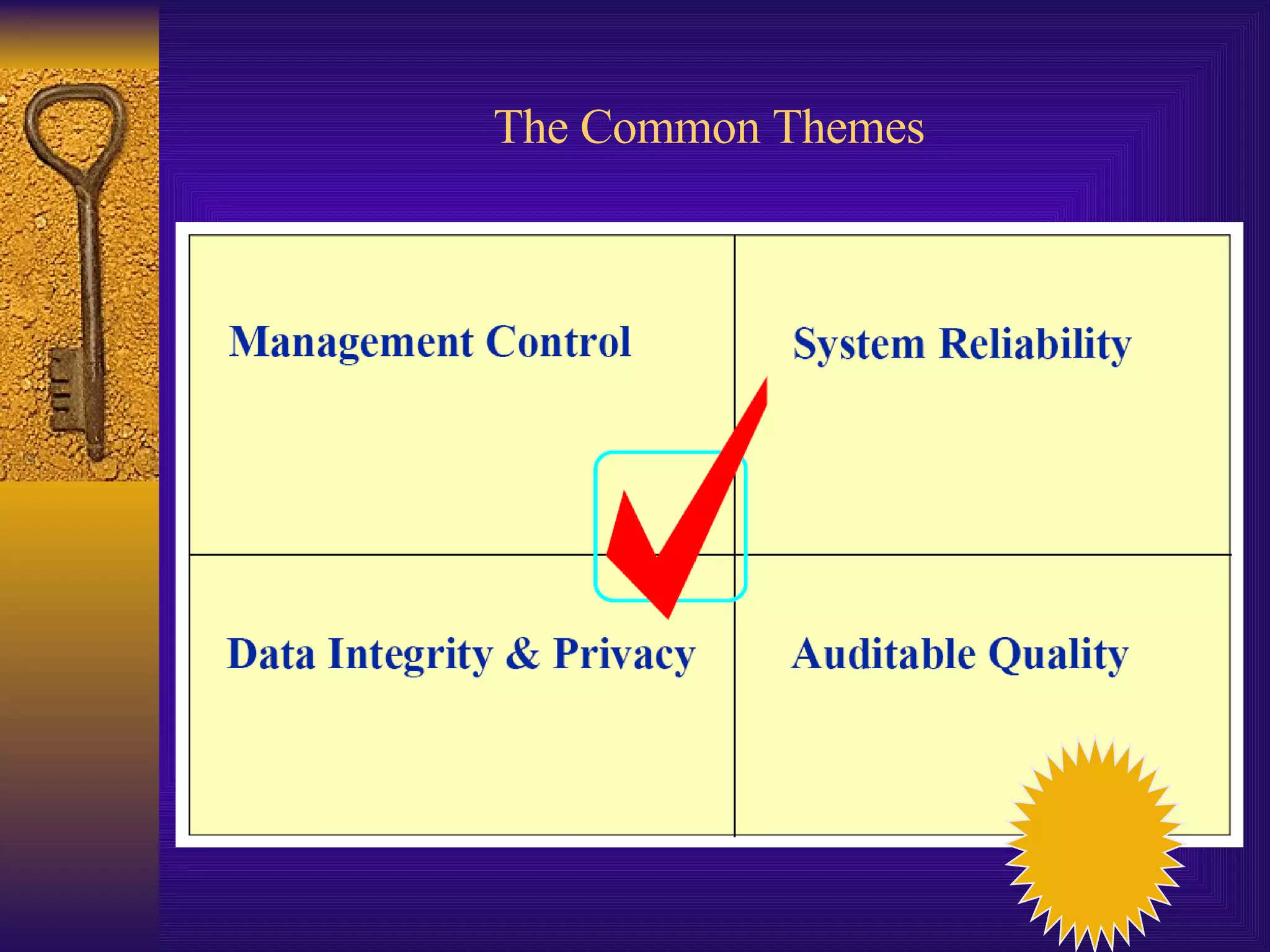
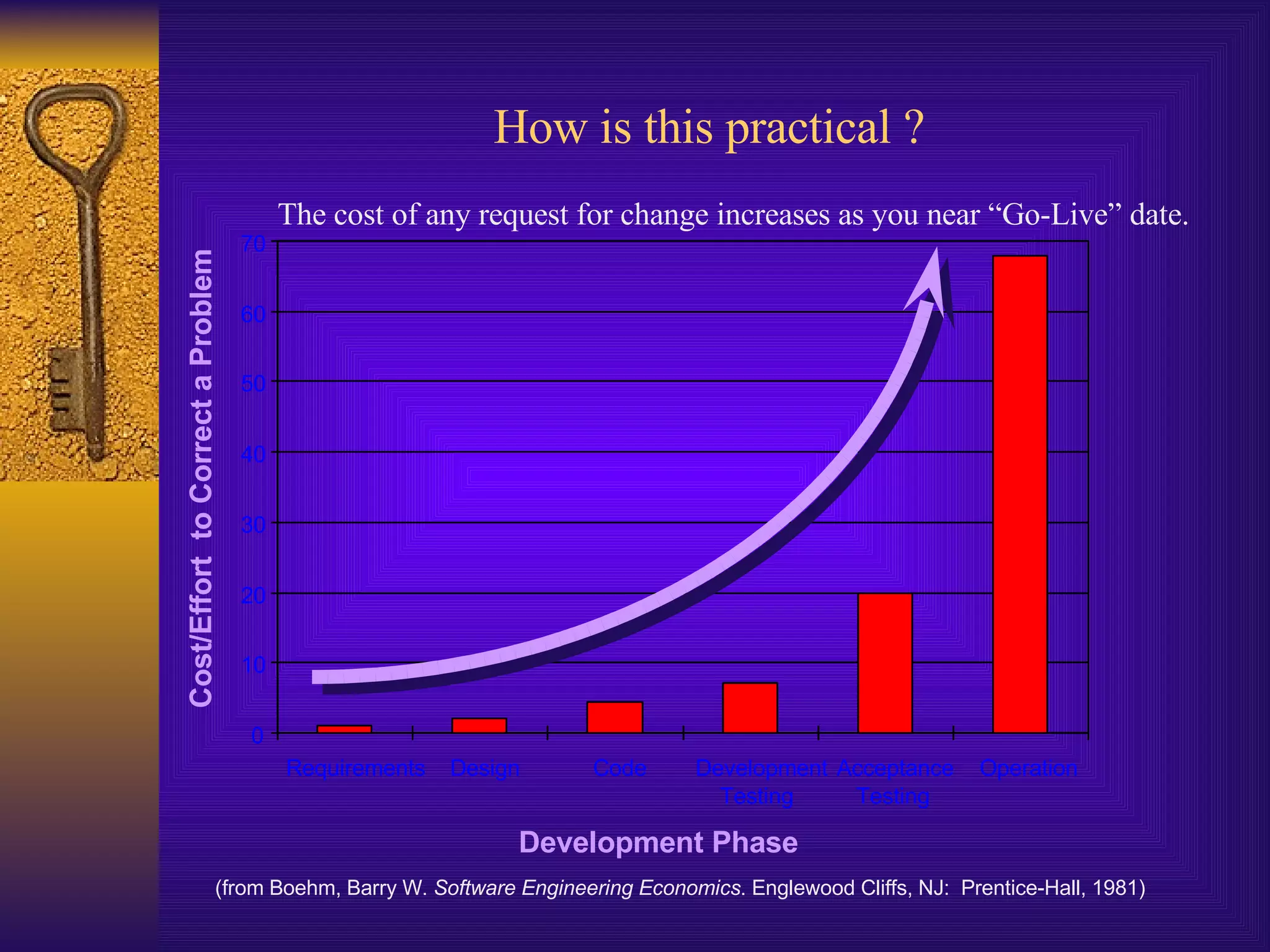
The document discusses computer system validation and change control. It outlines four common themes in regulations around management control of processes, system reliability, data integrity, and providing documented evidence. It notes the importance of computer systems to business processes and maintaining validated states as the environment changes. It proposes restarting IT steering meetings as a Change Control Board to approve change requests with documentation and signoff from relevant departments. Failing to properly manage validation and change control could lead to audit failures and loss of business.