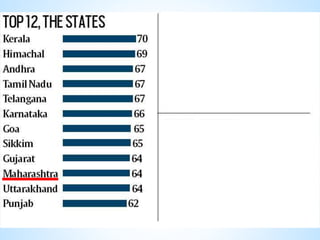
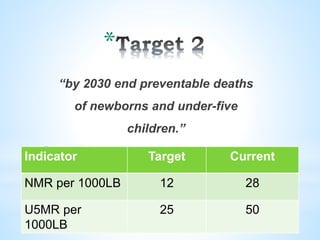
The document presents an overview of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), established on September 25, 2015, with 17 goals and 169 targets aimed at addressing global challenges by 2030. It highlights India's role in implementing these goals, particularly Goal 3 which focuses on ensuring healthy lives and well-being for all. Key challenges include improving health metrics, addressing maternal and child mortality, and combating communicable diseases, all of which require integrated approaches and significant funding.