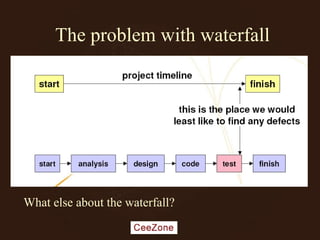
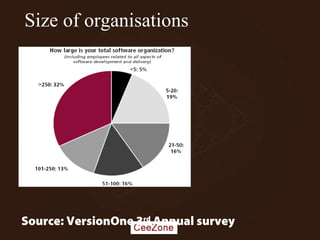
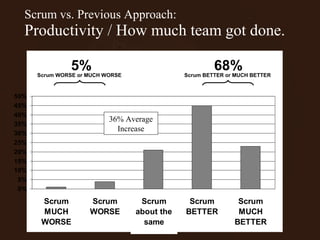
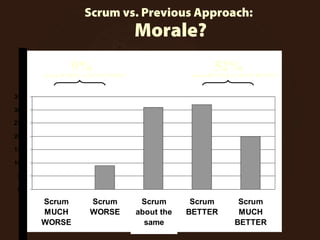
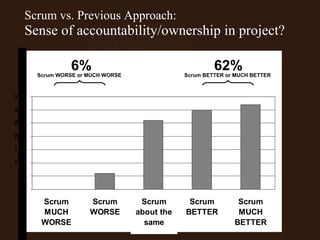
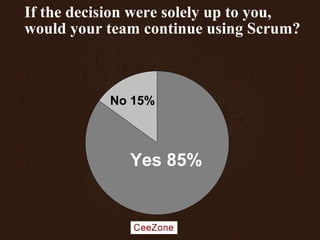
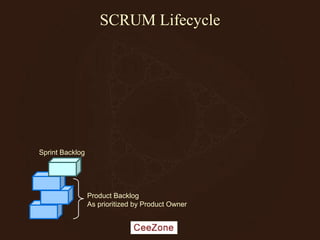
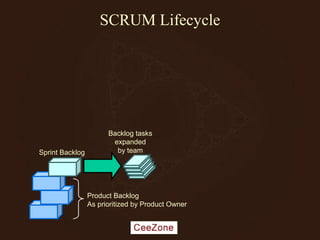
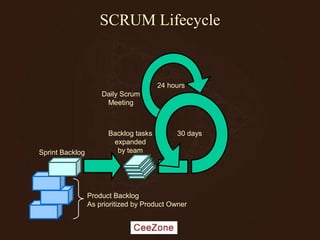
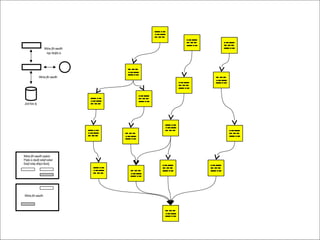
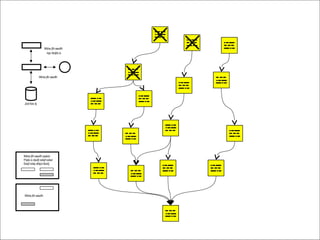
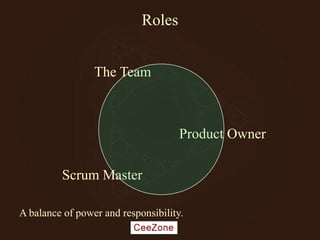
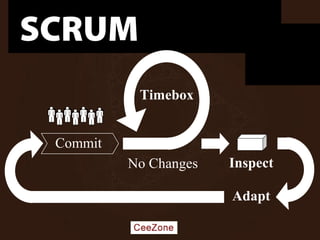
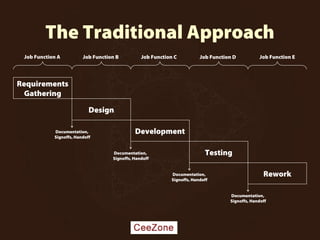
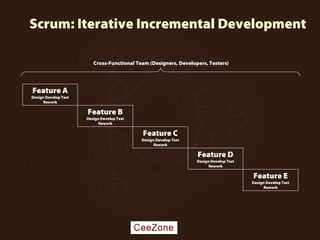
The document outlines the principles and advantages of Scrum as a software development framework, highlighting its iterative and people-centric approach compared to traditional waterfall methods. It includes case studies showcasing successful Scrum implementations in various organizations and emphasizes the need for effective teamwork, communication, and prioritization for optimal results. Additionally, it notes the challenges associated with adopting Scrum, including potential dysfunction and the necessity for commitment to change.