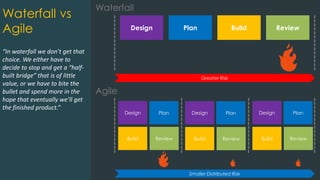
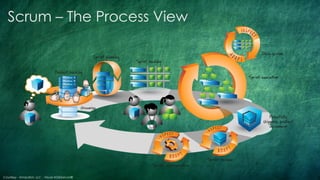
The document provides an introduction to the Scrum framework as part of the Agile methodology, emphasizing its focus on collaboration, adaptability, and iterative development. It outlines key Scrum components such as the product backlog, sprint planning, and the roles of the product owner, development team, and Scrum master. The content highlights the importance of evolving processes to remain competitive in a rapidly changing business environment.