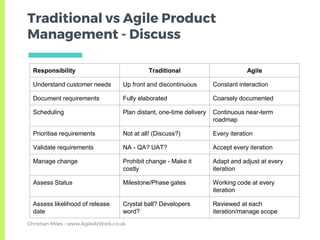
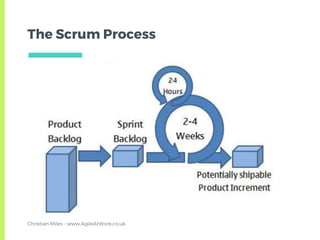
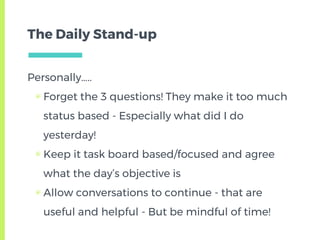
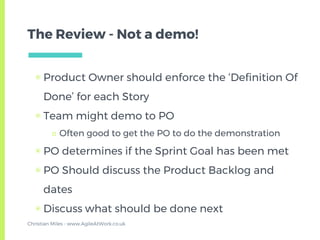
The document provides an overview of the Scrum framework. It discusses that Scrum was created in the early 1990s and published in 1995 by Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland. It then describes the core components of Scrum including roles like the Product Owner and Scrum Master, ceremonies such as sprint planning, daily stand-ups, and retrospectives, and artifacts like the product backlog. The document aims to give a quick introduction to Scrum and notes that the author has altered some parts to reflect what has worked best in their experience.