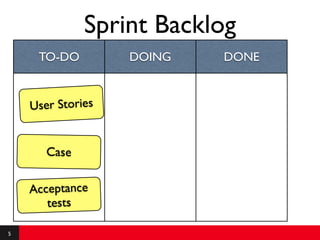
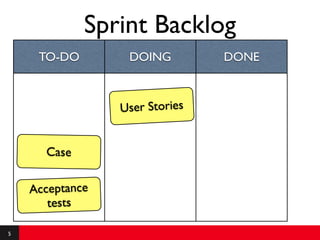
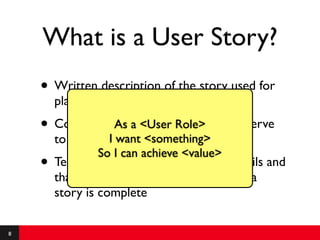
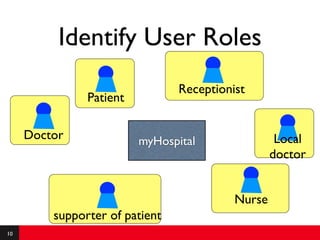
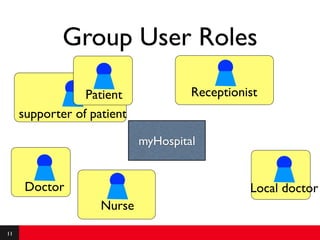
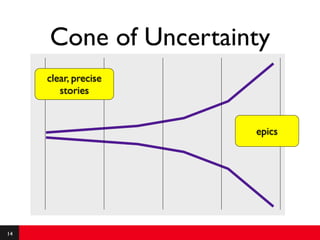
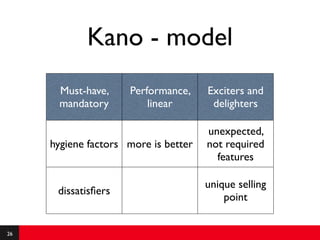
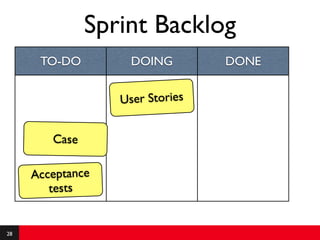
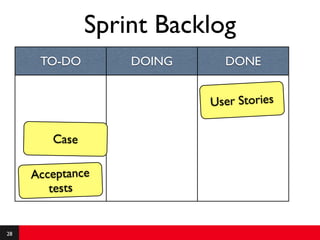
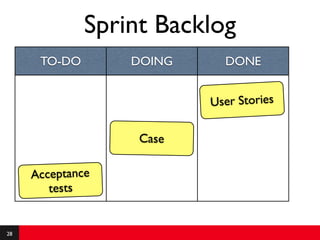
This document provides an introduction to agile requirements and user stories. It discusses key concepts such as the agile manifesto, user roles, personas, and developing user stories using the INVEST criteria. The document also covers acceptance tests and how they are used to determine if a user story is complete. It emphasizes that agile requirements focus on interaction, conversation, and confirmation rather than documentation.