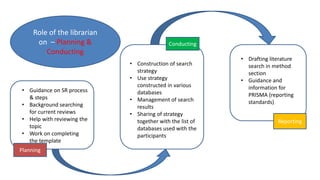
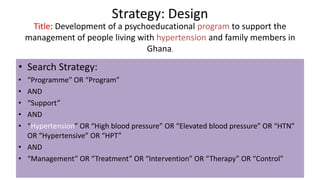
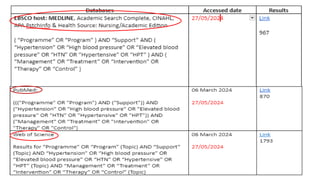
The document discusses evidence synthesis research, focusing on scoping and systematic reviews in nursing science. It outlines the definitions, differences, and key steps involved in conducting a scoping review, including identifying research questions, selecting relevant studies, and employing tools for organization. Additionally, the role of librarians in planning and conducting search strategies is highlighted, along with examples of scoping reviews related to healthcare.