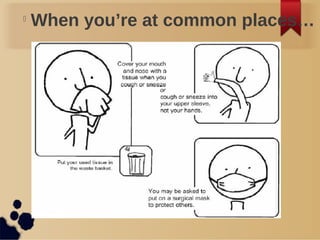
This document discusses commonly used disinfectants and their relative effectiveness against bacteria. It describes what disinfectants are, their purpose, and different levels of disinfection including low, intermediate, and high levels. Examples of specific disinfectants are provided such as alcohols, phenols, chlorine, iodine, quaternary ammonium compounds, and formaldehyde/glutaraldehyde. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of disinfecting to stay healthy by killing harmful bacteria.