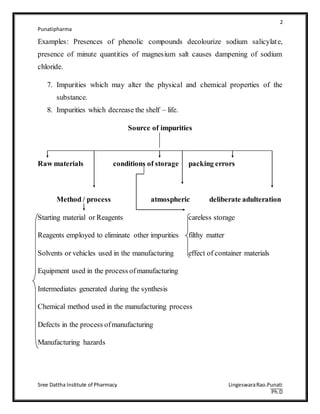
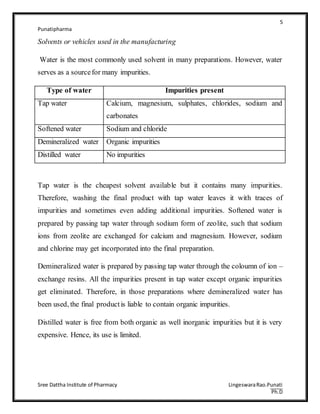
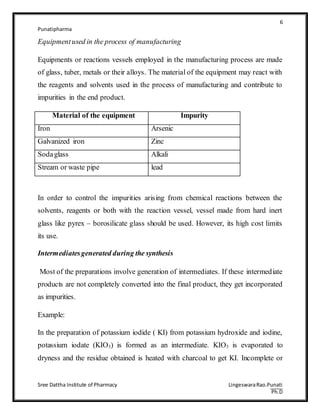
The document discusses various types of impurities that can be present in pharmaceutical preparations and their sources. It describes six main types of impurities: 1) those that cause toxic or adverse reactions, 2) those that deteriorate the activity of the substance, 3) those that cause incompatibility, 4) those that cause technical problems, 5) those arising from humidity/temperature, and 6) those arising from coloring/flavoring substances. Potential sources of impurities discussed include raw materials, starting materials/reagents, solvents, equipment, intermediates generated during synthesis, and manufacturing defects. Proper control of sources like raw materials, processes, storage conditions, and packaging can help minimize impurities in pharmaceutical preparations.