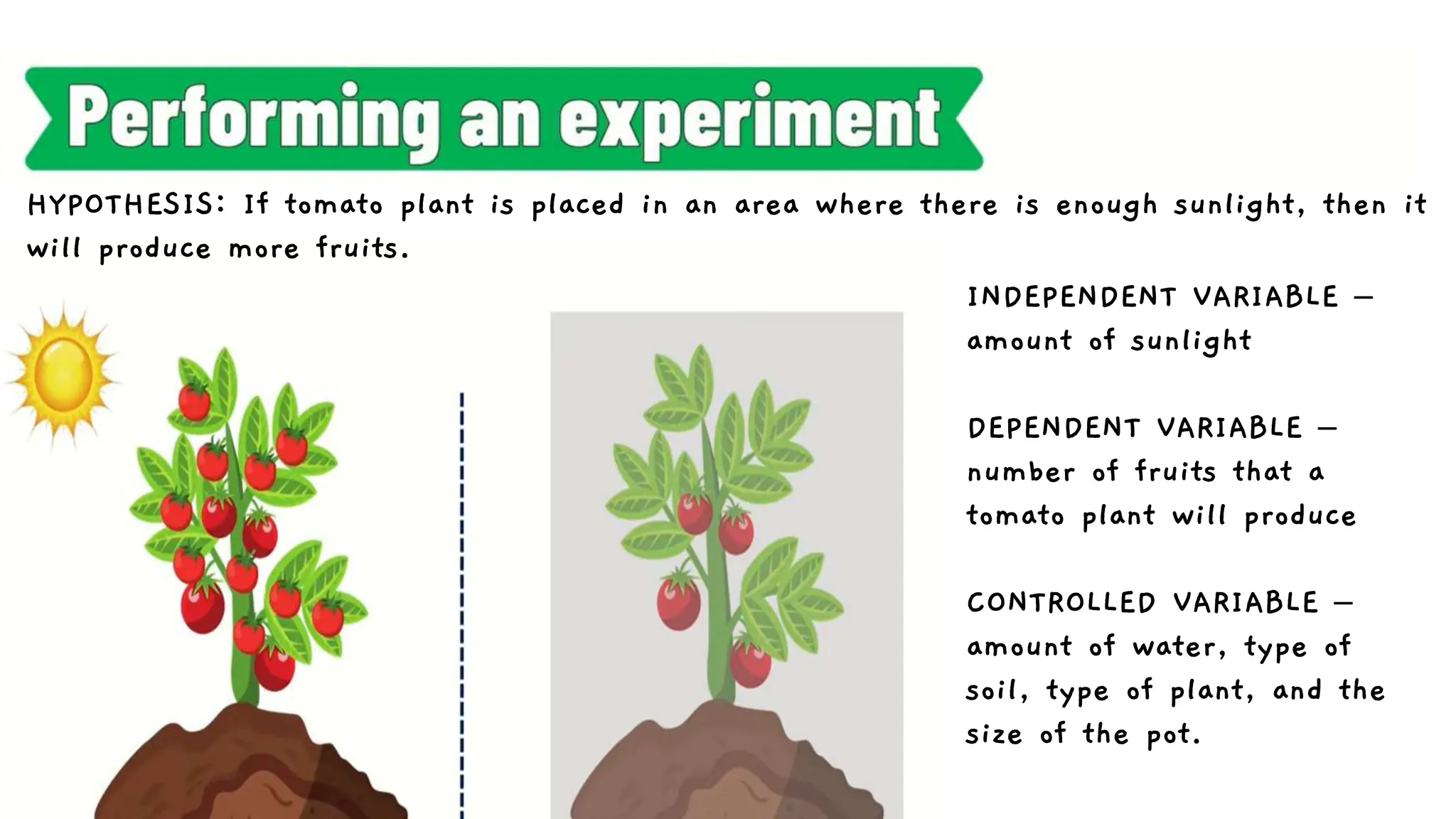
The document outlines the steps of the scientific method, beginning with making observations, asking questions, forming hypotheses, performing experiments, and finally analyzing results and drawing conclusions. It emphasizes the importance of both qualitative and quantitative observations and illustrates these steps with an example of tomato plants and their sunlight exposure. The document concludes with the significance of communicating results to the scientific community.