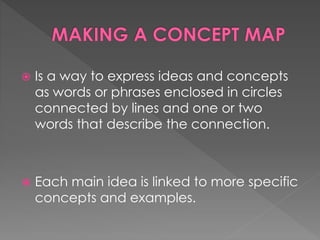
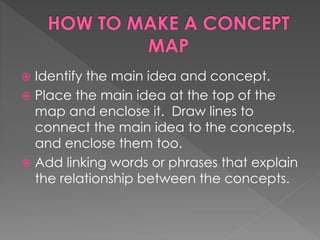
This document provides definitions and steps for scientific concepts including observation, interpretation, hypothesis, experiment, classification, concept mapping, analogy, and generalization. Observation is something detected by senses or instruments, while interpretation is a possible explanation. A hypothesis interprets observations, which can be tested through experimentation by varying one condition while keeping others constant. Classification organizes data into groups based on common features. Concept mapping uses a diagram of circles and lines to show relationships between ideas. Analogies compare new concepts to familiar things to aid understanding. Generalizations draw conclusions about broad categories based on multiple examples.