Science notes grade 6
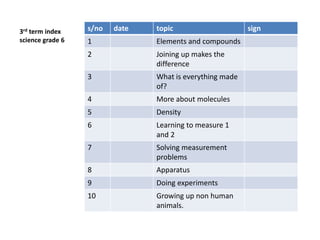
- 1. 3rd term index science grade 6 s/no date topic sign 1 Elements and compounds 2 Joining up makes the difference 3 What is everything made of? 4 More about molecules 5 Density 6 Learning to measure 1 and 2 7 Solving measurement problems 8 Apparatus 9 Doing experiments 10 Growing up non human animals.
- 3. ELEMENTS: • Answer the following: 1. What is an element? An element is a chemical substance which cannot be broken into anything more simpler. 2. What is a symbol? A symbol is the shortened form of the name of the element. 3. What is a periodic table? It is a list of all the elements with their symbols on a chart.
- 4. 4. How many kinds of atoms are there in a lump of copper? Explain? Copper has only copper atom as it is an element and can’t be broken down into anything simpler. 5. Most elements are solids, liquids and gases. Give 2 examples each. solids liquids gases Magnesium Mercury Oxygen Iron Bromine Nitrogen
- 5. s/no Elements Symbol nature 1 Hydrogen H Gas 2 Helium He Gas 3 Lithium Li Solid 4 Beryllium Be Solid 5 Boron B Solid 6 Carbon C Solid 7 Nitrogen N Gas 8 Oxygen O Gas 9 Florine F Gas 10 Neon Ne Gas 11 Sodium Na Solid 12 Magnesium Mg Solid 13 Aluminium Al Solid 14 Silicon Si Solid 15 Phosphorus P Solid 16 Sulphur S Solid 17 Chlorine Cl Gas
- 6. Compounds: 1. What is a compound? A compound is formed when two or more substances [elements] are mixed together by joining up [combined chemically] e.g Na + Cl = NaCl 2. What is a mixture? A mixture is formed when two or more substances are mixed together without joining up [combined physically] e.g sand and water; water and oil.
- 7. 3. What elements are joined up in: a) Sand [Silicon dioxide(SiO2)= Silicon and Oxygen b) Common salt [Sodium Chloride (NaCl)] = sodium and chlorine c) Water [Hydrogen oxide (H2O) = Hydrogen and Oxygen d) Copper iodide or copper iodine (CuI) = copper and Iodine e) Iron Sulphide (FeS) = Iron and Sulphur
- 8. Class activity: Make a table to show the difference between element, compound and mixture Element Compound Mixture Simple chemical substance Two or more elements combined chemically Two or more elements or substances mixed together without joining Can’t be broken into simple substances Can be broken Can’t be separated easily Can separated easily Examples; carbon, Hydrogen Example; sand, water Example; mixture of Iron and Sulphur.
- 9. JOINING UP MAKES THE DIFFERENCE ANSWER THE FOLLOWING: 1. How is water different from the elements which makes it up? The elements hydrogen and Oxygen are both in the form of gas, they lose their identity when they combine to form a compound.( water in liquid form). 2. Do you think milk contains Calcium as an element or compound? It is present as a compound since milk contains 87% of water. 3. What happens when; a) Calcium is put in water: it bubbles and fizzes in water.
- 10. b) Phosphorus is exposed to dry air: it catches fire. 4a. Name the elements which makes up Calcium Phosphate, where is it found? Calcium, Phosphorus and Oxygen are the elements that makes up Calcium Phosphate, it is found in bones and teeth. b. What would happen to our teeth if they are made only from the element Calcium? Our teeth would bubble and fizz in water as calcium reacts in water.
- 11. Home work Find out the uses of the following elements (mineral) present on our body. 1. Iron: we need it to transport oxygen in our body 2. Sodium: it helps in blood pressure and normal fluid balance in the body. 3. Potassium: it helps in building proteins and metabolize carbohydrates.
- 12. 4. Calcium: it helps in building bones and teeth and keeping then healthy. It is found in diary. 5. Iodine: it controls the body’s metabolism and many other important functions. It is found in sea vegetables and food
- 13. WHAT IS EVERYTHING MADE OF? Answer the following: 1. What is a molecule? A molecule is the smallest particle of a substance that can exist independently. A molecule is a group of atoms joined together. E.g water, has two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom (H2O), carbon dioxide, has one carbon atom joined to two oxygen atoms (CO2),
- 14. 2. What is an atom? an atom is the smallest particle of an element that takes place in a chemical reaction. It can’t exist independently.
- 15. 3. What are solids, liquids and gases made up of? They are made up of tiny particles called atoms and molecules. 4. Why does a balloon go down quickly if a pin is pricked in it? The air escapes from it easily and the balloon goes down.
- 16. 5. Air slowly escapes from a balloon even when it’s tightly tied. Why? a) Balloon rubber behaves as if it has very small holes in it. b) Air is made up of millions of tiny particles moving about c) These tiny air particles are small enough to escape through the holes in the balloon. d) Draw diagram from notebook.
- 17. MORE ABOUT MOLECULES. Answer the following: 1. What is meant by diffusion? The movement of molecules from areas of HIGH concentration to areas of LOW concentration.
- 18. 2. Why does gases spread easily through each other? Gases spread easily through each other because the space between the molecules in gas is more and the molecules are moving. 3. Do molecules move fast in gas or liquid? explain. Molecules move fast in gases than in liquids because the molecules in gas are far apart and free to move about than in liquids.
- 19. 4. Adding 50cm3 water to 50cm3 of alcohol, gives a volume of 95cm3. Explain why? When alcohol and water are mixed, water molecules fit into some of the spaces between alcohol molecules, this makes the volume less than expected. 5. How far could gas molecules travel in one second? 100-2000m/s
- 20. the students were asked to predict what would happen if 50mL of water was mixed with another 50mL of water. We then mixed two graduated cylinders, each containing 50mL of water into a 100mL graduated cylinder. The result was 100mL of water total. The students were then asked what would happen if 50mL of water and 50mL of ethanol were mixed. We again mixed 50mL of water with 50mL of ethanol. The result was a total volume of approximately 96mL. We asked the students to explain this 500mL of rice and mixed it with another 500mL of rice. We explained to the students that the rice represented the water molecules. The result was 1000mL of rice. We then took 500mL of rice and 500mL of rigatoni noodles and mixed them. The rigatoni noodles represented the ethanol. The result was approximately 650mL to 700mL.
- 21. DENSITY Answer the following? 1. What is density? The density of a substance is a measure of mass per volume of the substance.
- 22. 2. What is the unit of density? The unit is grams per cubic centimetre written as g/cm3 or gcm-3 3. How does some objects float and some sink in water? If the density of object is more than water, it sinks. If the density of object is less than water, it floats on water. Density of object makes it float or sink. 4. Why do hot air balloon rise?
- 23. Hot air has low density than cold air, so they rise. 5. It is easier to float in sea water than a lake, why? This is because, sea water is denser than the water in the lake. 6. On what does the density of a substance depend? Density depends on; the mass of its atoms and molecules volume
- 24. 7. Why does gold have high density? It is made up of heavy atoms and they are closely packed. 8. Why does gases have very low densities? Gas molecules spread out to occupy large volume with lots of empty space. 1cm3 of any gas is very light.
- 25. Look at density ladder [draw from notebook] a) Why does oak wood float on water but not on paraffin? because oak wood is less dense than water and more dense than paraffin. b) Suggest densities for X and Y explaining each choice. X is less dense than water. Y is denser than water. c) The density of nylon is 1.1g/cm3. where on the ladder would a piece of nylon float? Explain your answer.
- 26. In Perspex, Y, copper and mercury. Because it is less dense than these substances.
- 27. Solved Problems on Density 1. Find the density of the following: a. Brass nut, mass 34g, volume 4cm3 D = m/v =34/4=8.5g/cm3
- 28. b. A cork mass 2g, volume 8cm3 D = 2/8 = ¼ = 0.25g/cm3 2. Iron has density 7.8g/cm3, mass = 7.8g. Find volume. V = m/d = 7.8/7.8 = 1 cm3 3. You have a rock of volume of 15cm3 and a mass of 45g. What is the density? D = M/V = 45/15 = 3g/cm3 4. Calculate the density of 500g rectangular block with dimension L=8cm, w=6cm, h=5cm. volume=LxBxH =8x6x5=240cm3 D=m/d=500/240=2.08g/cm3
- 29. 5. Oak wood 1800g of mass, 2000cm3 of volume. Find the density of the oak- wood? [class work] d=m/v = 1800/2000 = 0.9g/cm3 6. If a 96.5g piece of aluminium has density of 2.7g/cm3. what is the volume? v = m/d = 96.5/2.7 =965/27 = 35.7g 7. Calculate the mass of a liquid with a density of 3.2g/ml and volume of 25ml m = d X v = 3.2 x 25 = 80g
- 30. LEARNING TO MEASURE 1 AND 2 Answer the following: 1. Name your 5 senses: the 5 senses are seeing, hearing, tasting, touching and smelling. 2. Why do scientist use measuring instruments whenever they can? Scientist use measuring instruments whenever they can because we can’t depend on our senses for exact measurement.
- 31. 3. What could you measure using: a) stop watch, clock, watch: Time [hour, minutes, second] b) Thermometer: Temperature [degree Celsius oC, Fahrenheit F and kelvin K] c) Measuring cylinder, beaker: volume of liquid [lxbxh, cm3, m3] d) Balance : Mass [kg, g, mg] e) Ruler, meter sticks and tape: Length [km, m, cm, mm, feet, miles, yards]
- 32. 4. Which units are used to measure: a. volume: the units to measure volume are millilitre(ml), litres(l), cubic centimetre(cm3), cubic metre(m3). b. Mass: units of mass are gram(g) and kilogram(kg) c. Length: units used to measure length are metre(m), millimetre(mm) and kilometre(km) d. Time: the units of time are seconds(s), minutes(m) and hour(h).
- 33. e. Temperature: units to measure temperature are degree Celsius(oC), Fahrenheit(F) and kelvin(K) 5. Why can’t you depend on your senses to find out the temperature of the air? It is because the same air may feel warm to one person and cold to another. 6. What is meant by: a. Volume: volume of an object is the space taken up by it.
- 34. b. Temperature: temperature of an object means the degree of hotness of the object c. Mass: mass of an object is the amount of matter contained in it. 7. What are the reading on the instruments shown: [class activity]
- 37. Individual project 1. Make a list of 5 measuring instruments used in your home 2. Stick pictures of the following: a. Ruler b. Thermometer c. Stopwatch d. Measuring cylinder e. Balance
- 38. SOLVING MEASURMENT PROBLEMS Answer the following: 1. How could you find the volume of a pebble? By using a measuring cylinder a. Put some water in the measuring cylinder and measure the volume b. Drop the pebble and measure the volume again c. The difference in the volume is equal to the volume of the pebble. final volume – initial volume = volume of pebble.
- 40. 2. What is special about pendulum swing? In the case of pendulum swing, the time for one swing is always the same 3. How would you find time for one swing of the pendulum if the time taken is 12sec for 10 swings? time taken for 10 swings = 12 sec time taken for 1 swing = time for 10 swings/ no of swings 12/10 = 1.2 sec.
- 41. 4. Find the average mass of 1 nail, if 50 nails have a mass of 175g. m= m of 50 nails/ no of nails = 175/50 = 3.5g 5. How can you make a simple pendulum? We can make a simple pendulum from a string and an iron bob
- 43. Apparatus Measuring cylinder. Measuring volume Beaker. Measuring liquid Test tube Test tube holder Conical flask Round flask Flat bottom flask funnel
- 44. Wire gauge Tripod stand pipette burette Retort stand Laboratory dish
- 45. Doing experiments Answer the following: Experiment 1: a) What happens when sand and gravel are shaken in the sieve? A sieve is used to separate small particles from large ones. Sand passes through the sieve. Gravel settles at the bottom of the sieve.
- 46. b) Why does this happens? Because the size is different; i. A sieve is a shallow tray with holes in it ii. The mixture is placed in the sieve which is shaken from side to side iii. The sand particles are much smaller than gravel and fall through the holes in the sieve.
- 48. Experiment 2 a. What happens when the magnet is moved through the mixture of iron powder and sand? Iron powder will stick to the magnet. b. Why does this happen? Iron is metal, it has magnetic property.
- 50. Experiment 3 a. What happens when chalky water is put into the filter funnel? Chalk is insoluble in water. The filter paper separate the chalk that hasn’t dissolve in water
- 52. Growing up non human animals. Egg when laid 10 days later young adult
- 53. Look at the diagram and answer the following: 1a. How does the embryo get oxygen it needs? The oxygen it needs travels through the egg shell. b. Why does the egg yolk become smaller in the diagram? The embryo gets it’s food from the yolk so as the chicken grows, the size of the yolk becomes smaller.
- 54. c. How does the embryo get food? The embryo gets food from the yolk.
- 55. Look at the diagram and answer the following: [class activity 2] 1a. Write the name of frog’s egg. Frog spawn. b. Name the larvae stage of frog. Tadpole c. What is the gestation period of frog? 6-21 days
- 56. Answer the following: 1. Define gestation period? The time between fertilisation of the egg to the birth of a young adult is called gestation period. 2. What is common between embryo of different animals? They all grow from fertilised egg which divides to produce more cells They all need food and oxygen to grow They are all surrounded by water as they grow.
- 57. 3. How does human embryo get food and oxygen? From the mother’s blood. 4. How do different embryo grow in different ways? Some embryo develop inside the egg Some embryo develop inside the mother’s worm Some embryo gets food from egg’s yolk and oxygen passes through the shell Some get food and oxygen from the mother’s blood Most embryo grow into adult Some embryo grow into larvae and larvae changes into adult. E.g frog, insects etc