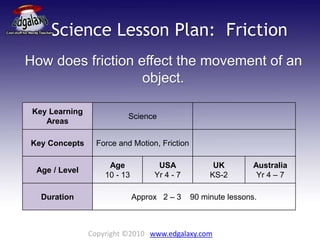
This document outlines a science lesson plan focused on the concept of friction and its effects on the movement of objects for students aged 10-13. It includes activities such as designing a wheeled cart to explore friction dynamics and creating a balloon rocket to understand friction’s role in motion. The plan emphasizes hands-on learning, group brainstorming, and formal reporting to enhance students' understanding of force and motion.