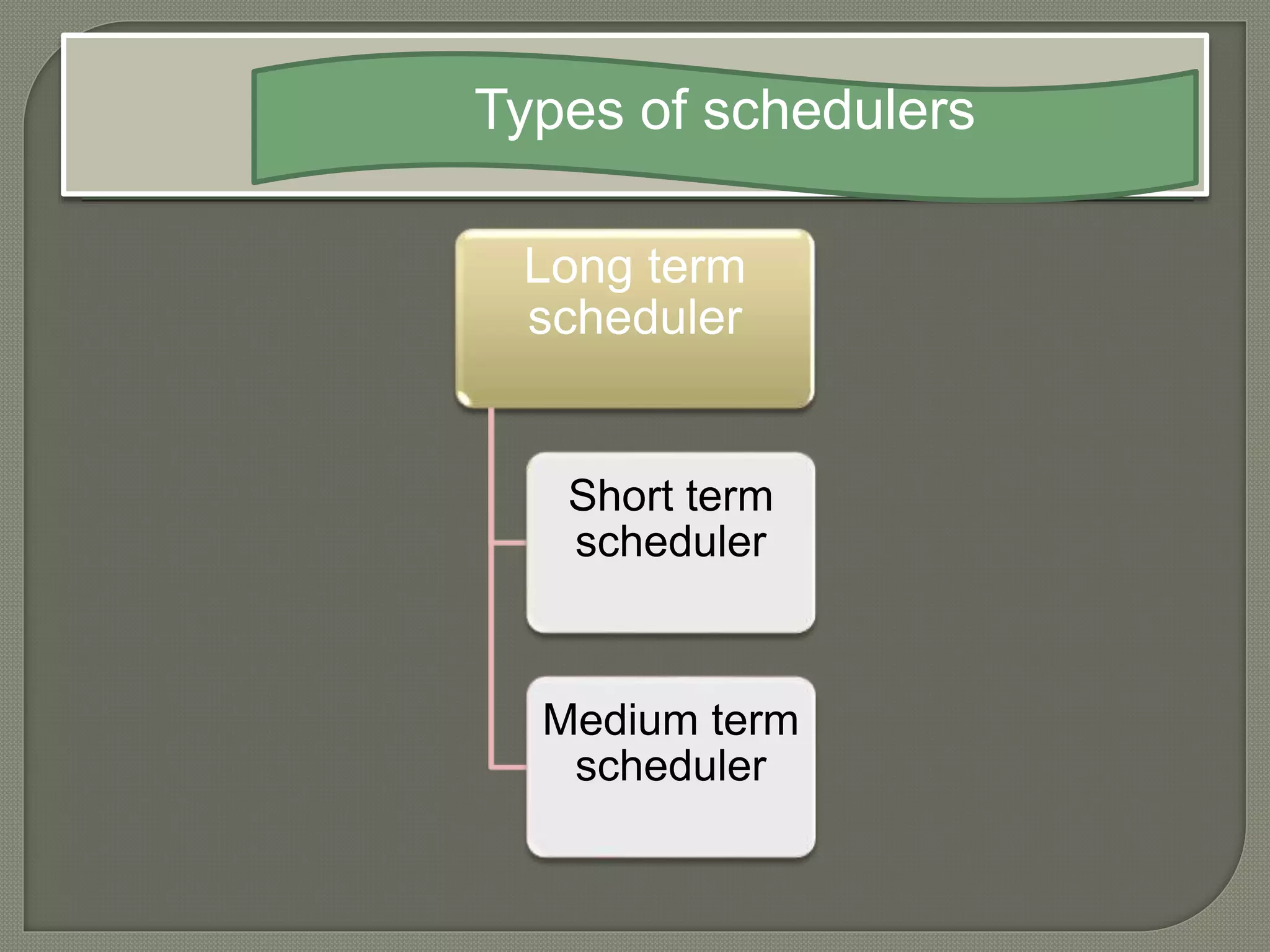
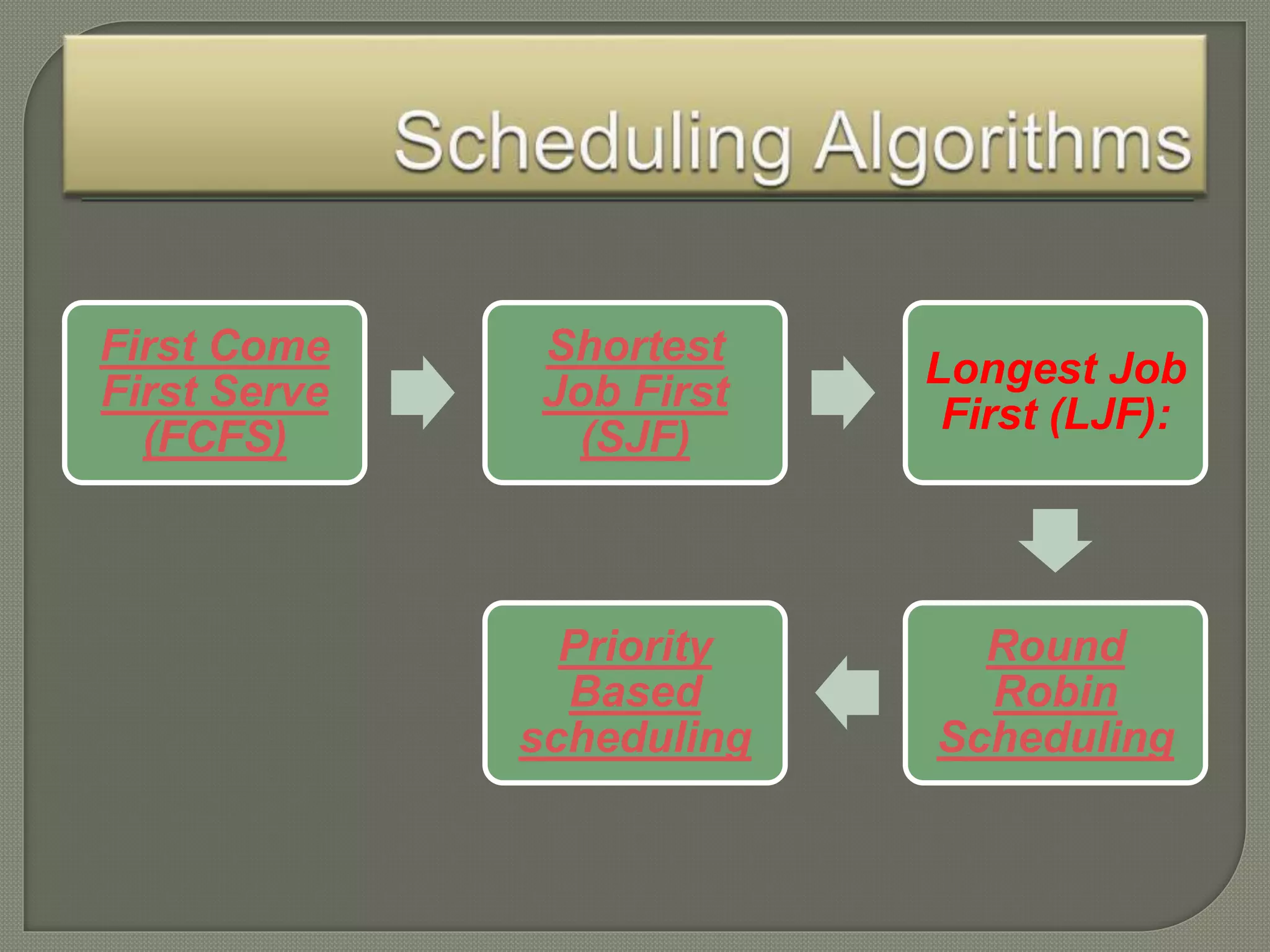
The document discusses process schedulers. It defines scheduling as allowing one process to use the CPU while another process is on hold waiting for resources. The objectives of scheduling are to make the system efficient, fast, and fair. There are three types of schedulers: long term schedulers which select processes to load into memory, short term (CPU) schedulers which select the next process to run on the CPU, and medium term schedulers which swap processes in and out of memory during I/O waits. Common scheduling algorithms discussed include first come first serve, shortest job first, longest job first, round robin, and priority-based scheduling.