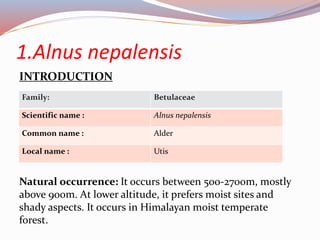
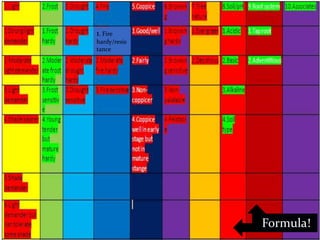
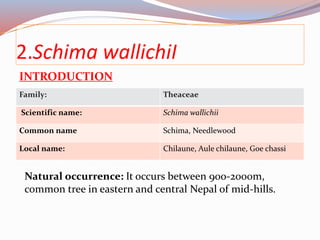
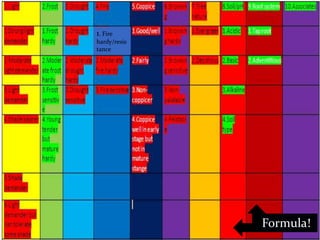
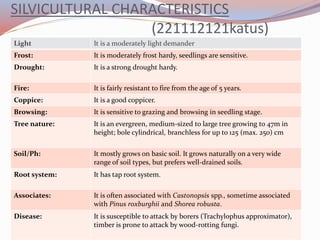
This document provides information about two tree species: Alnus nepalensis (Alder) and Schima wallichi (Needlewood). It discusses their silvicultural characteristics such as light and frost hardiness, drought tolerance, fire resistance, coppicing ability, soil preferences, growth rates, and diseases. It also outlines their uses including for timber, fuelwood, fodder, medicine, and other purposes. The document is presented by Anoj Subedi for a class on forestry at the Institute of Forestry in Pokhara, Nepal.