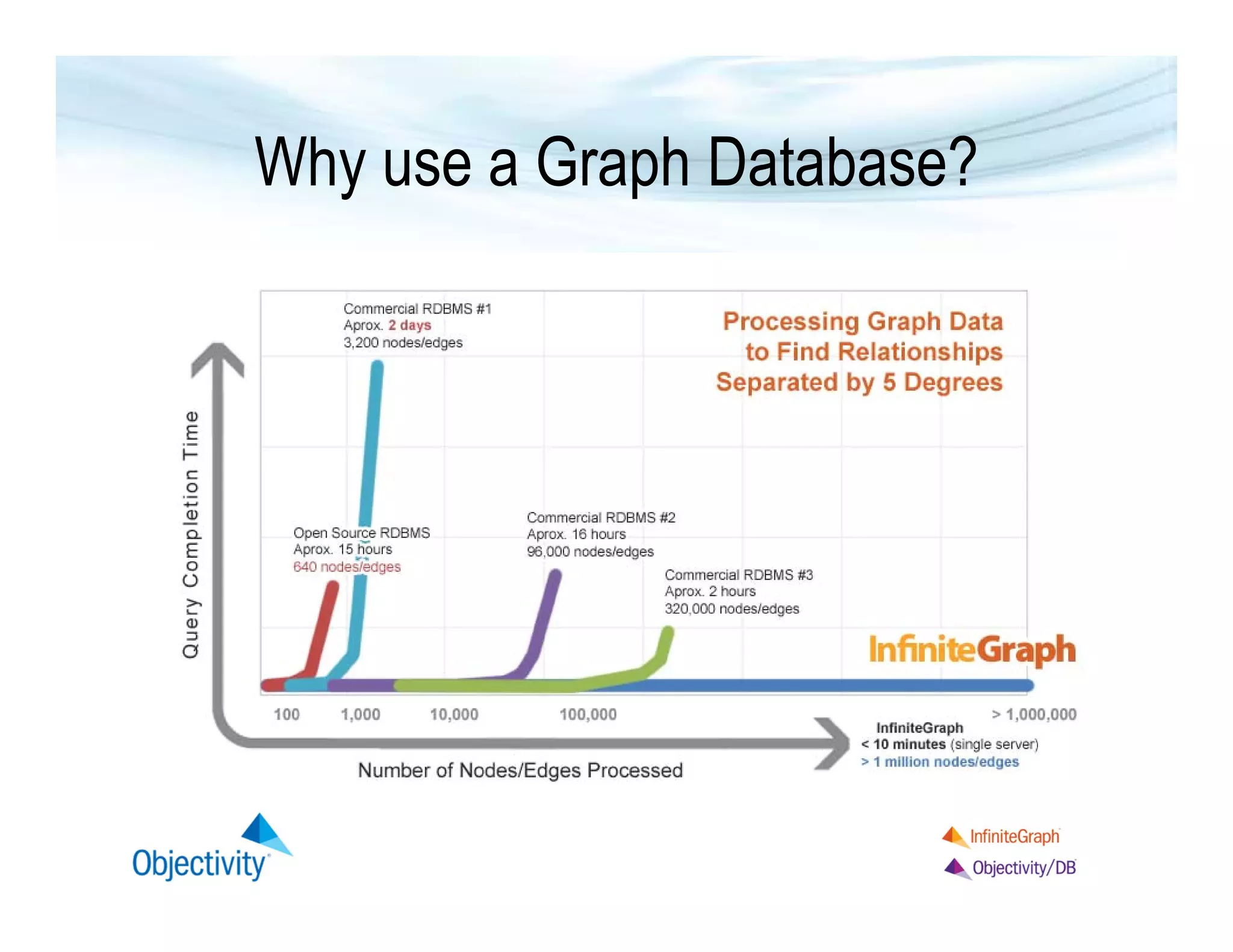
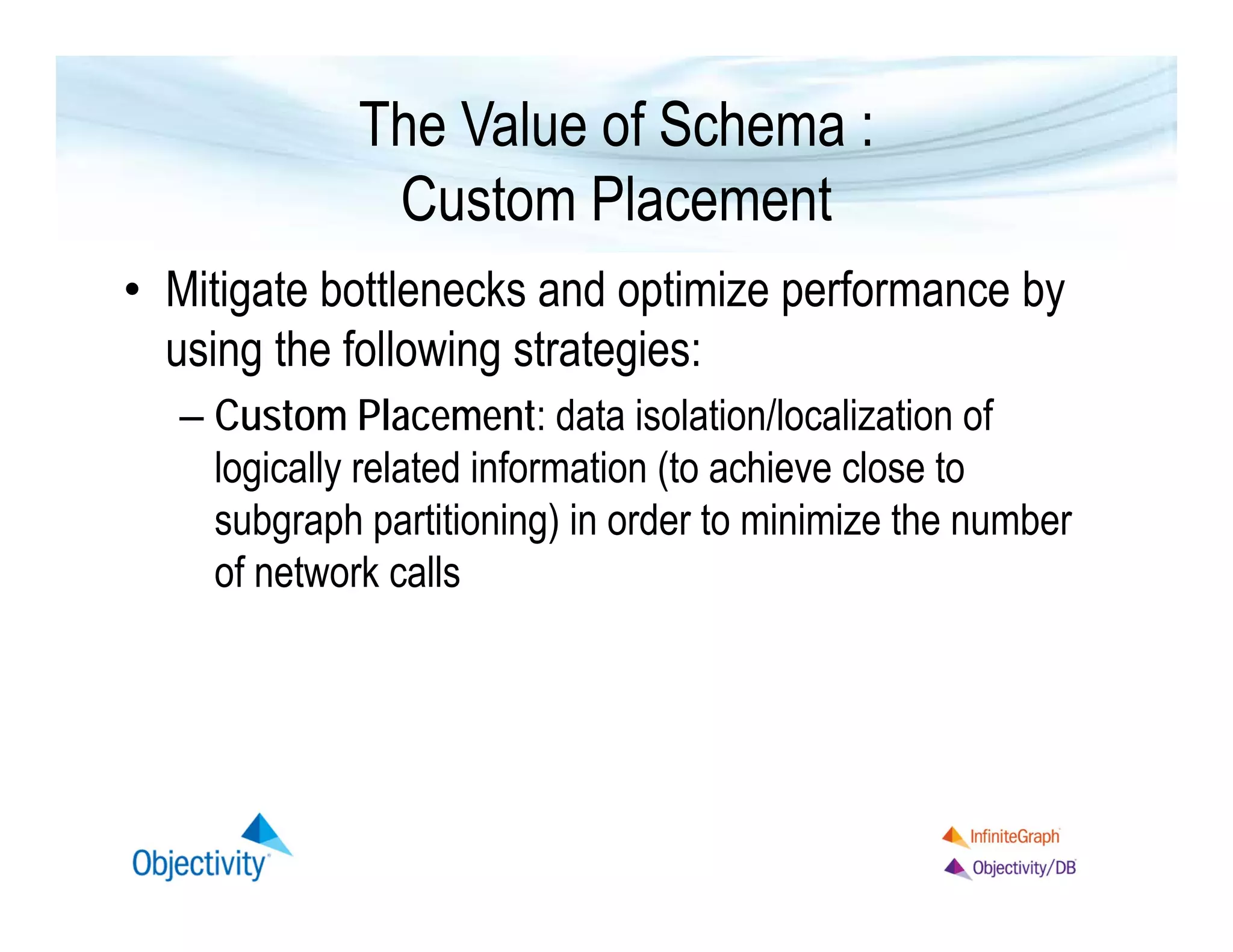
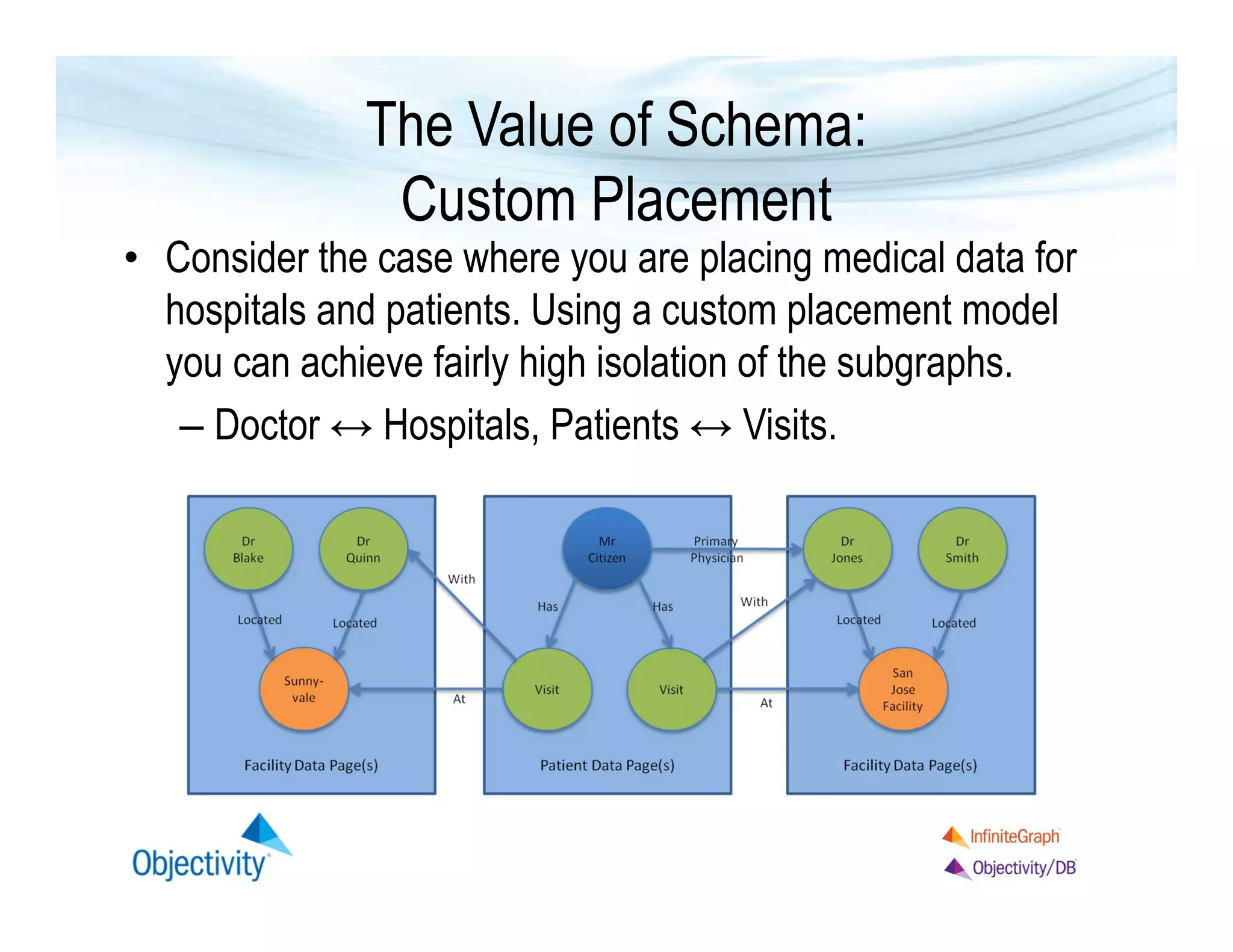
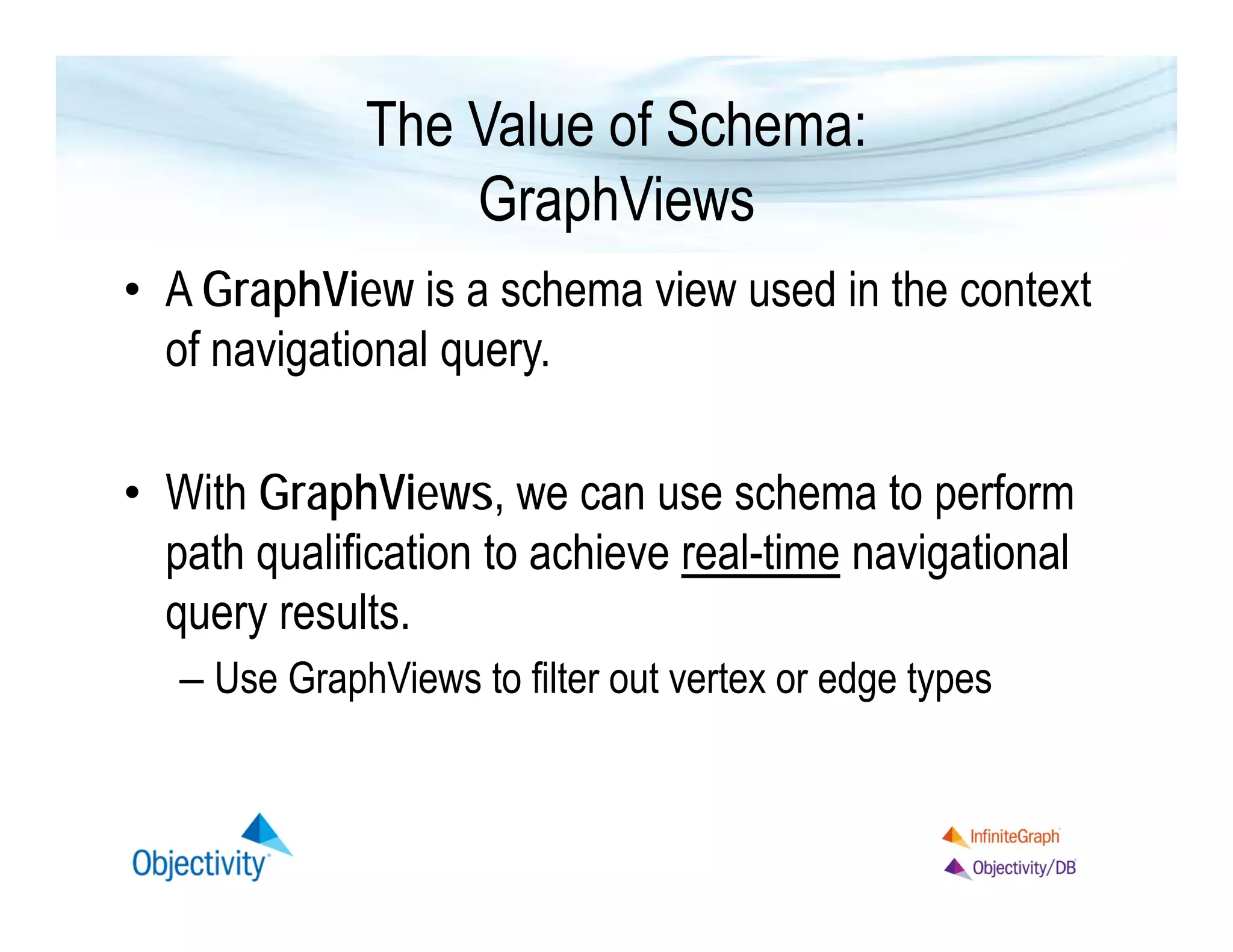
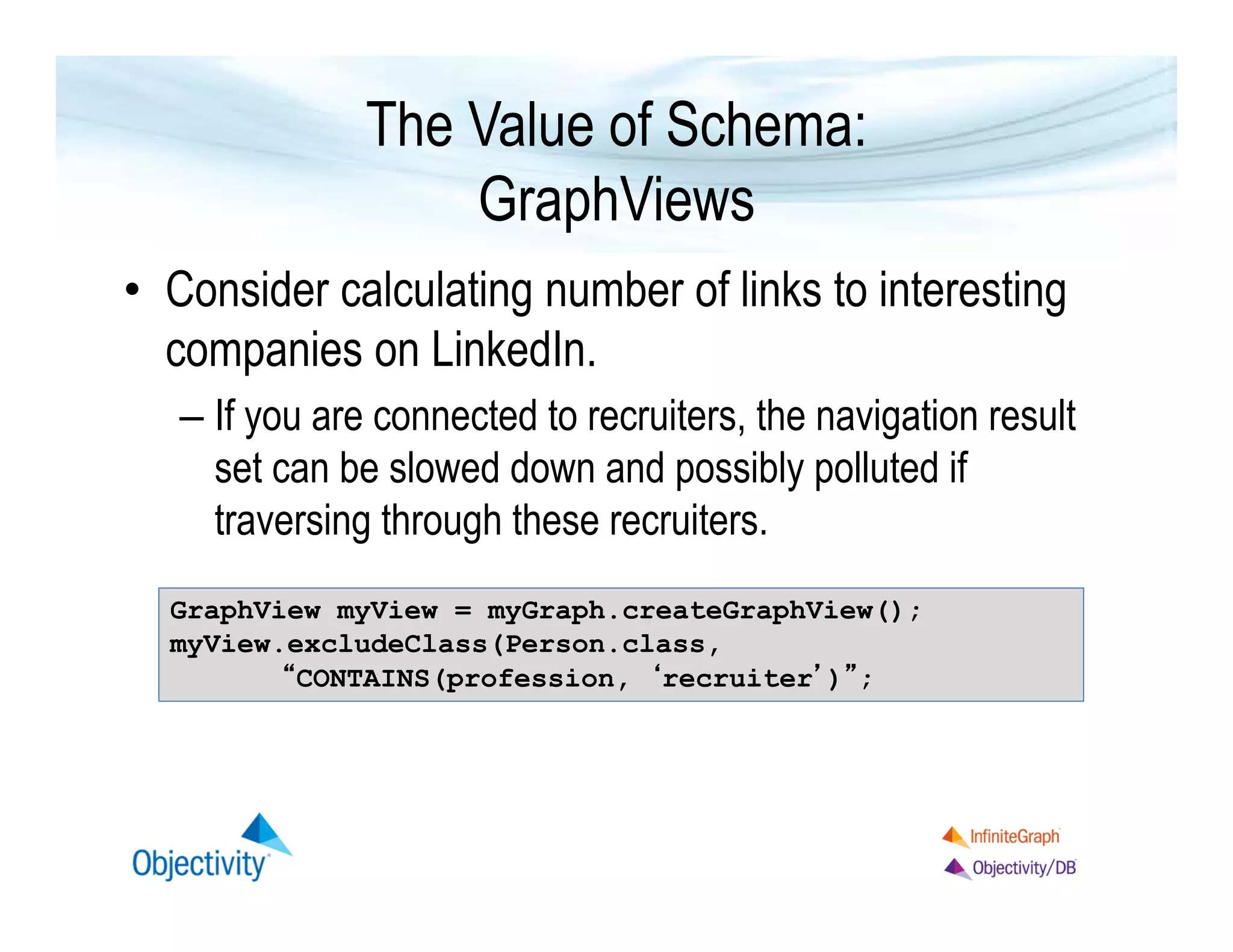
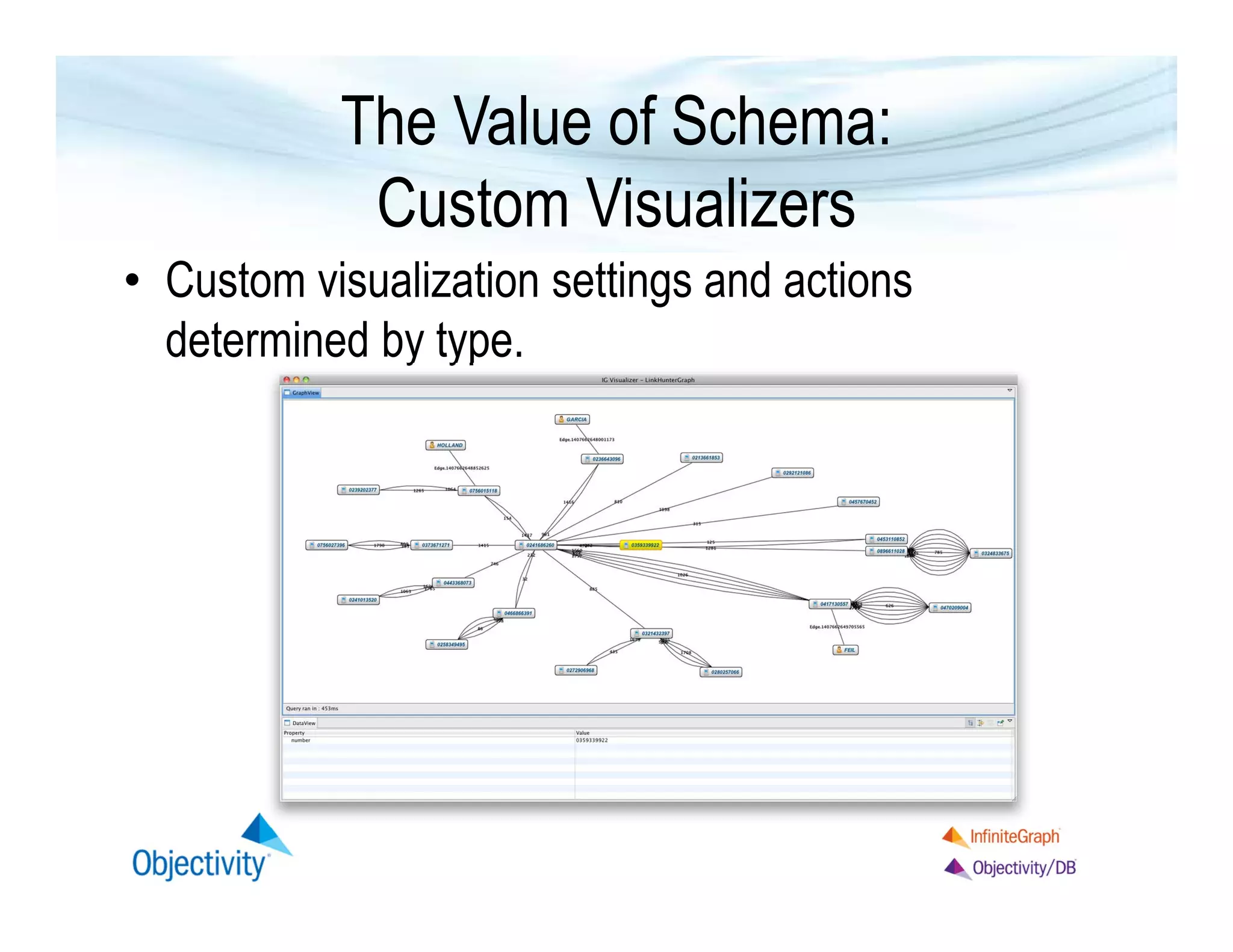
The document discusses the benefits of using a graph database, particularly focusing on the value of explicit schemas for optimizing performance through strategies like custom placement and graphviews. It emphasizes the importance of data isolation in use cases such as healthcare and provides examples of how to perform real-time navigational queries using graphviews. Additionally, it highlights the simplicity of query language and Objectivity's experience in building distributed databases.
![The Value of Schema:
Other Topics
• Life is like a box of chocolates– Class metadata
is preserved in the database (Relationships and
Hierarchies)
• Query Language Simplicity– Using types and
filters on types is more intuitive than using labels
– MATCH [Person(name==“Steve Jobs”)] –[Friend(where ==
“Facebook”)]->[Person];
– MATCH [p:Person] –[f:Friend]->[:Person] WHERE p.name==
“Steve Jobs” && f.where == “Facebook”;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schemavsschemalessmeetup2-20-14-140221182402-phpapp02/75/The-Value-of-Explicit-Schema-for-Graph-Use-Cases-8-2048.jpg)