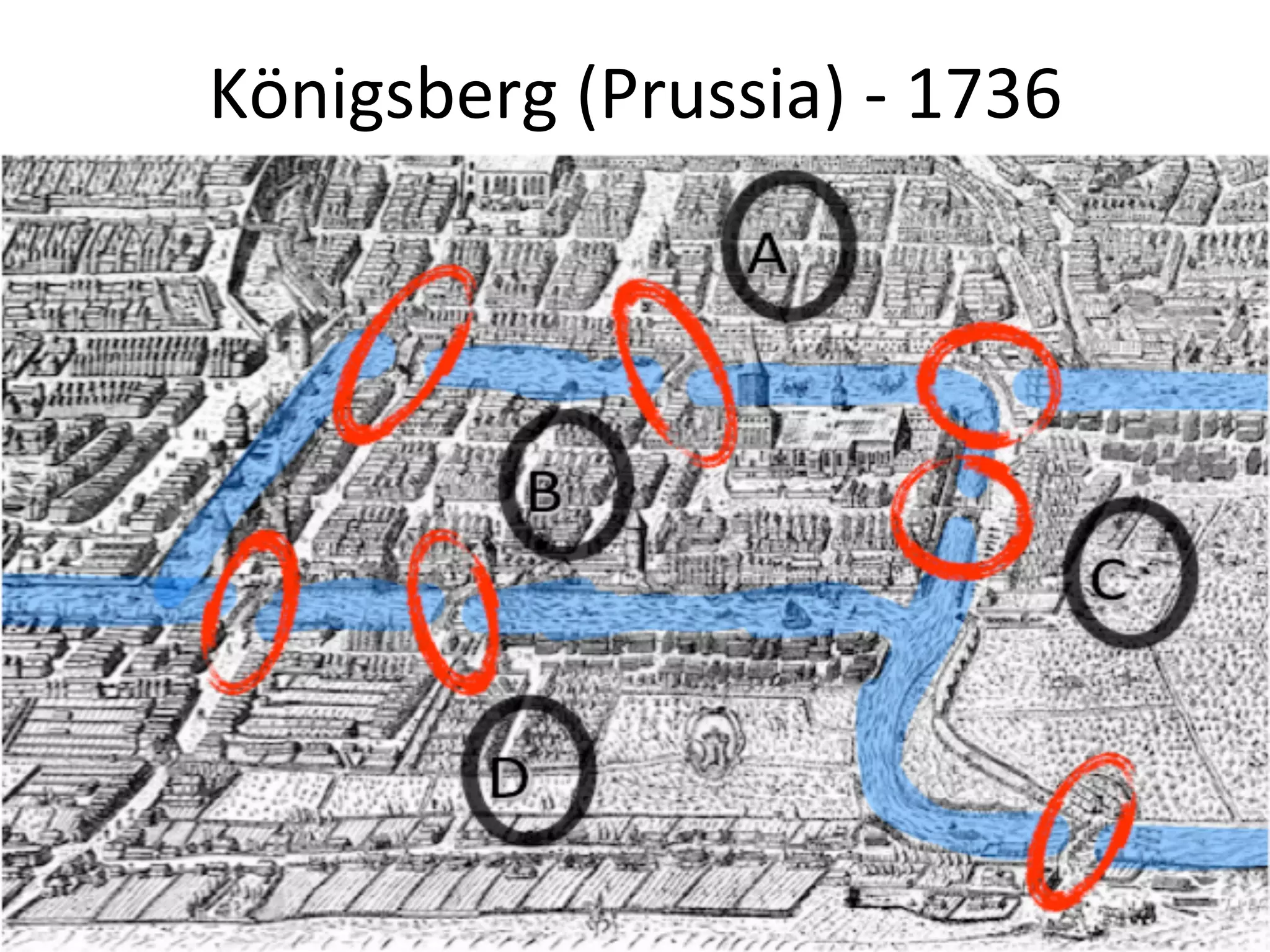
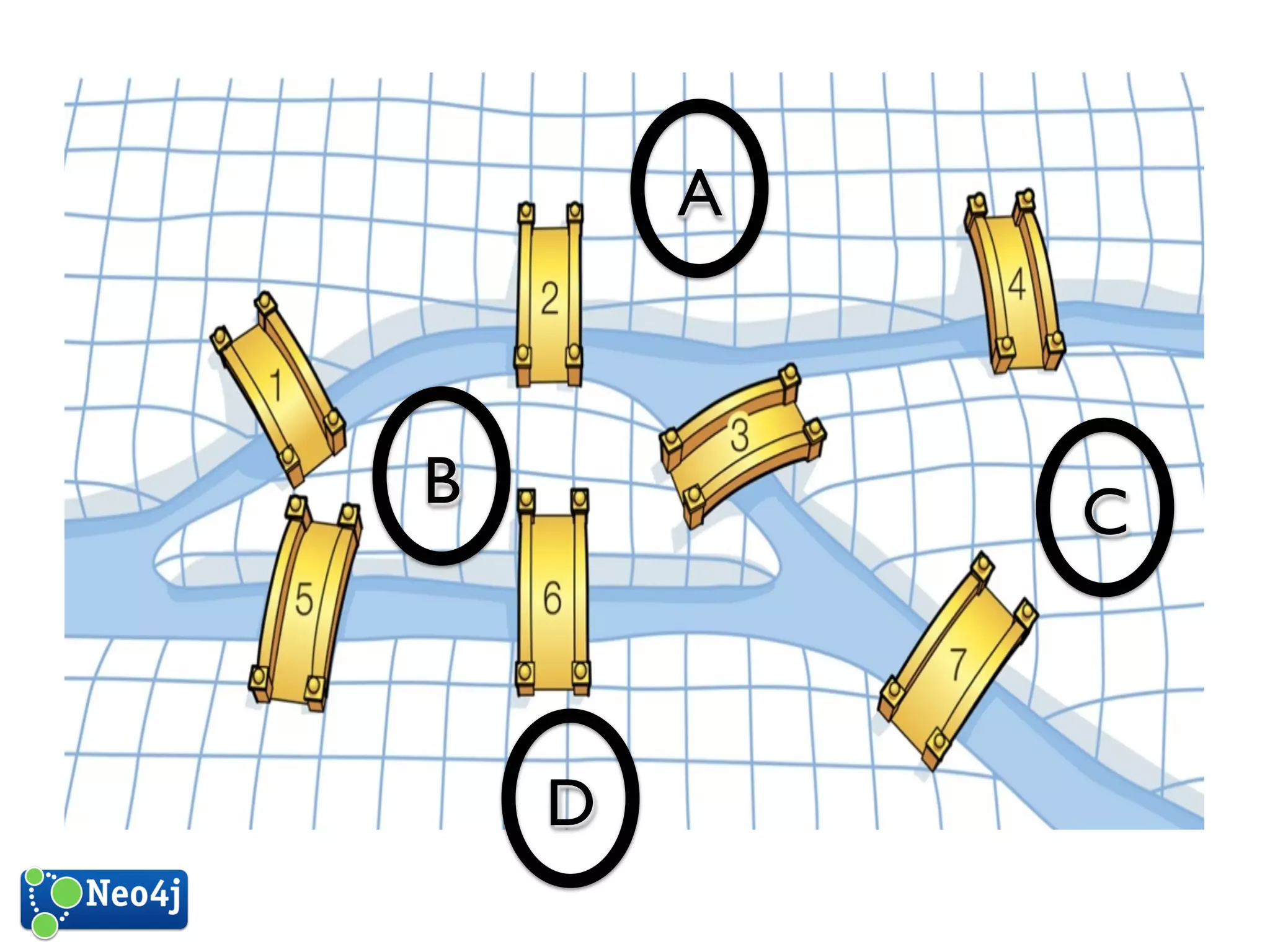
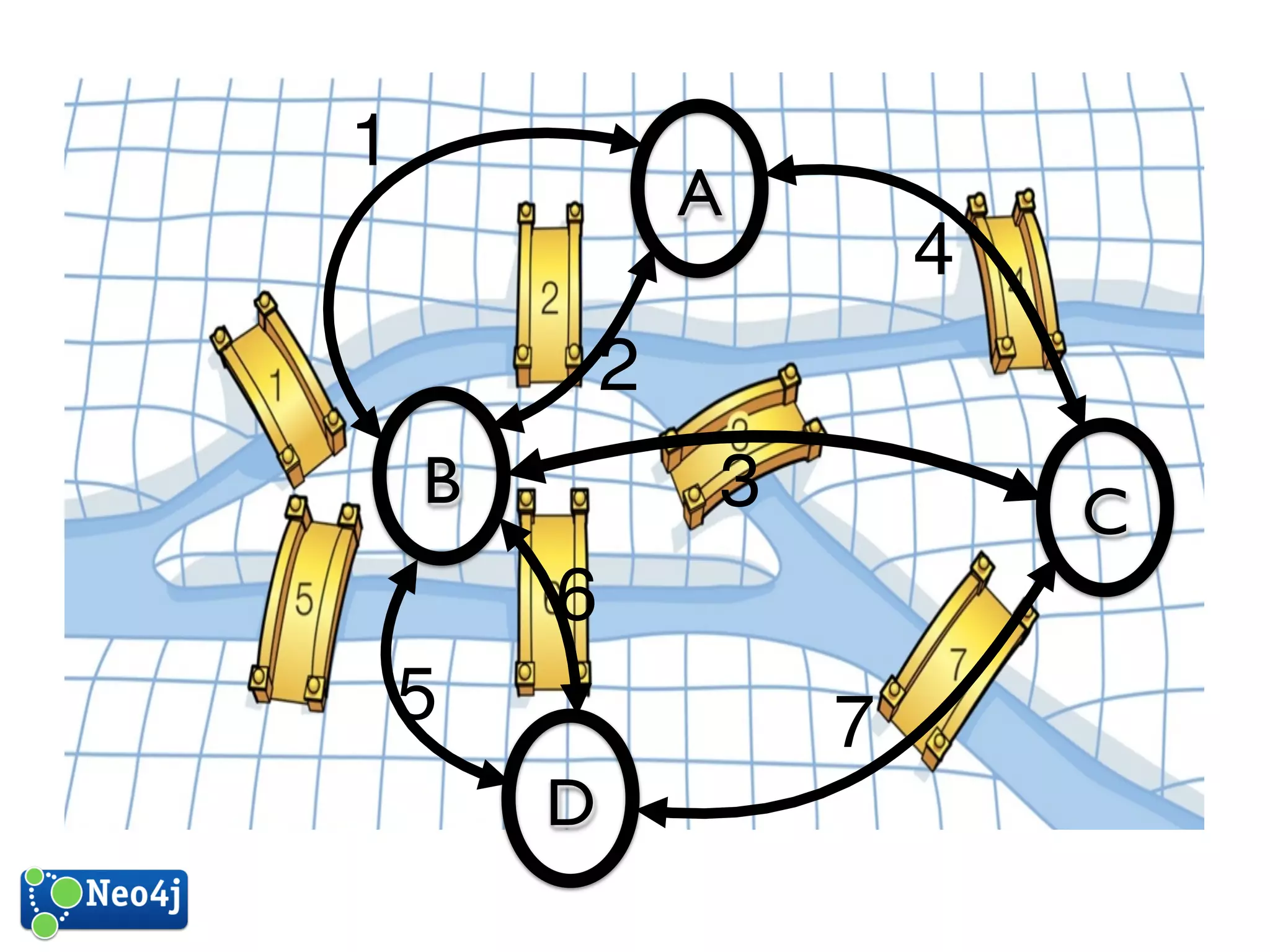
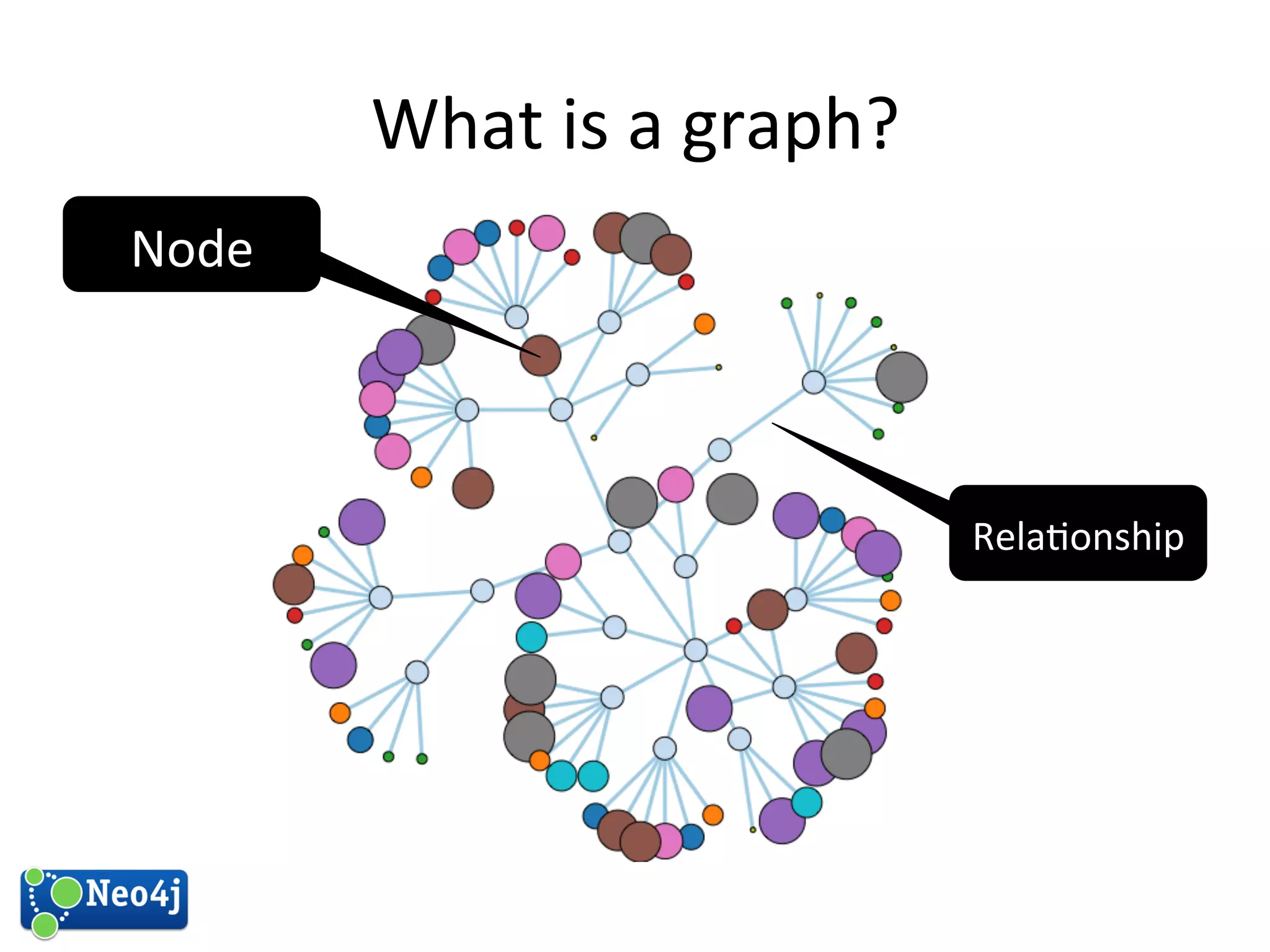
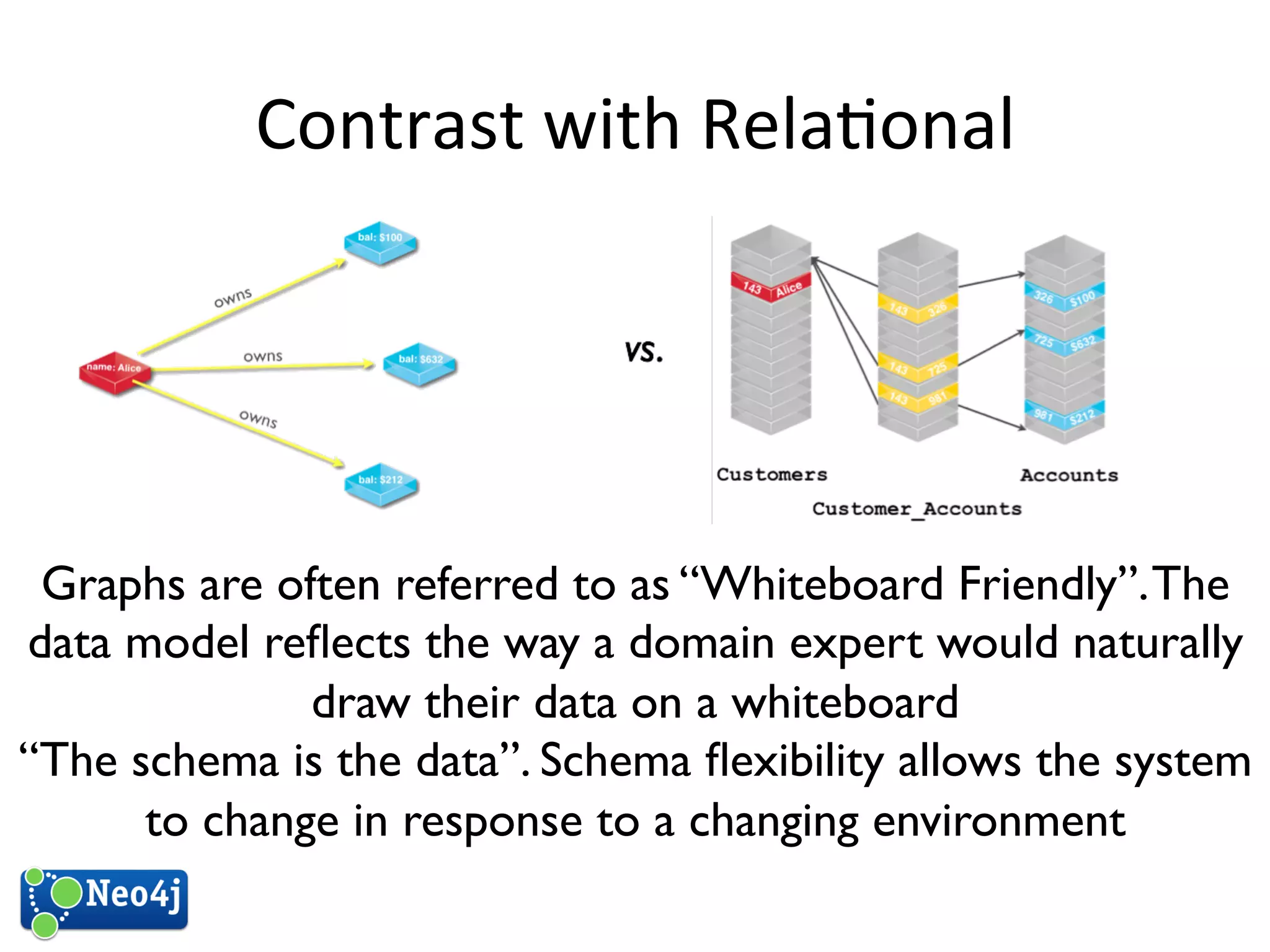
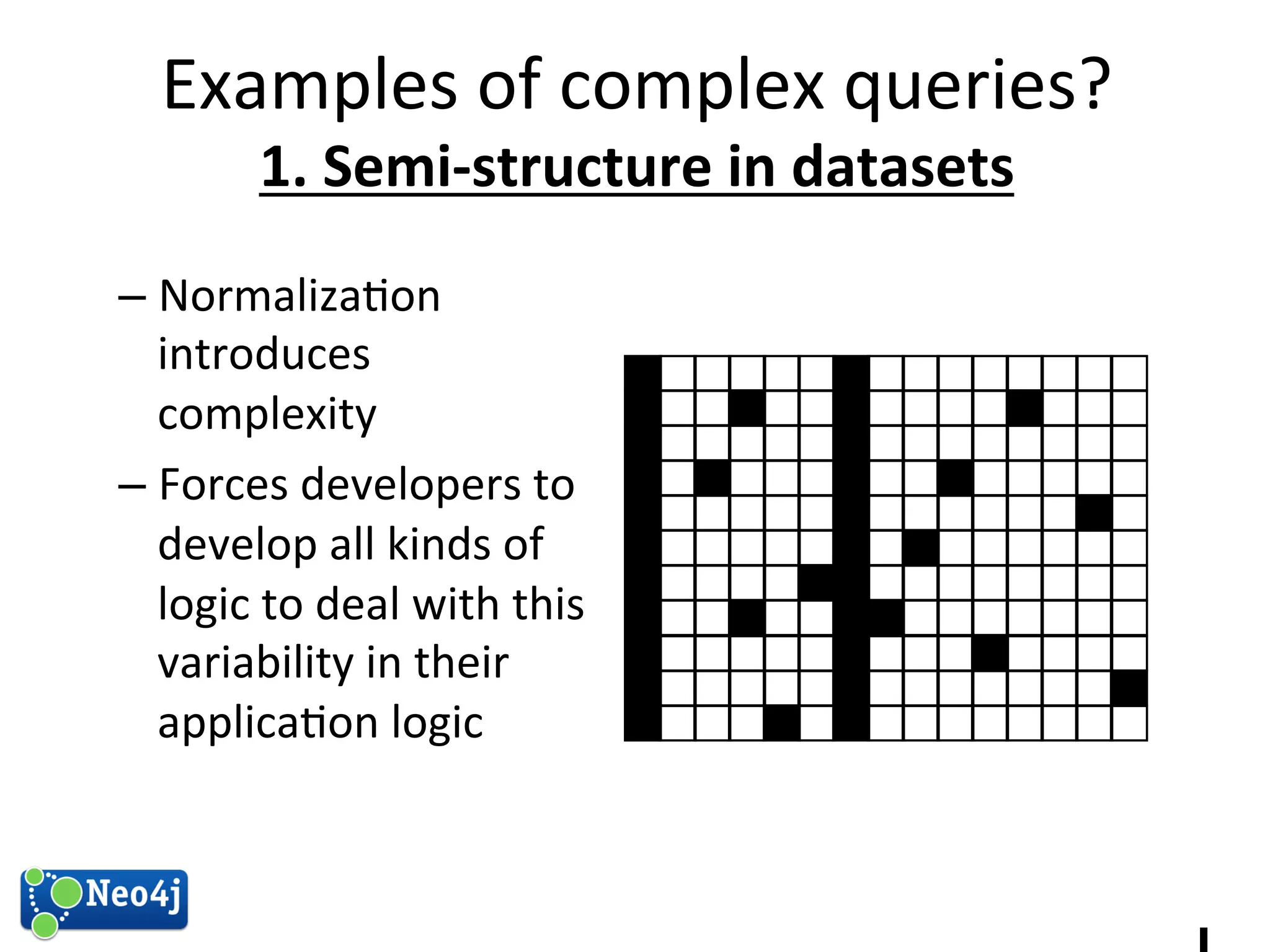
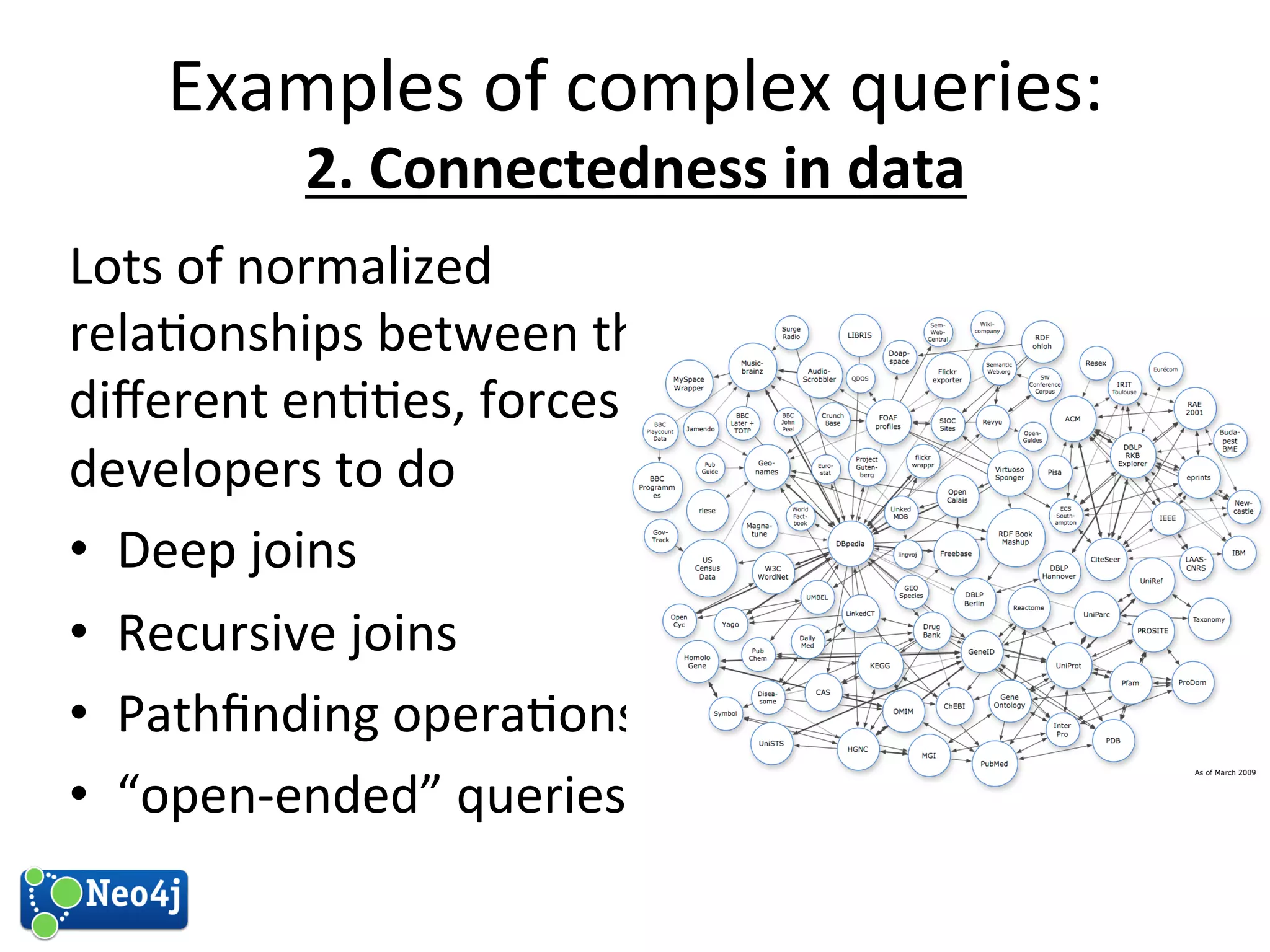
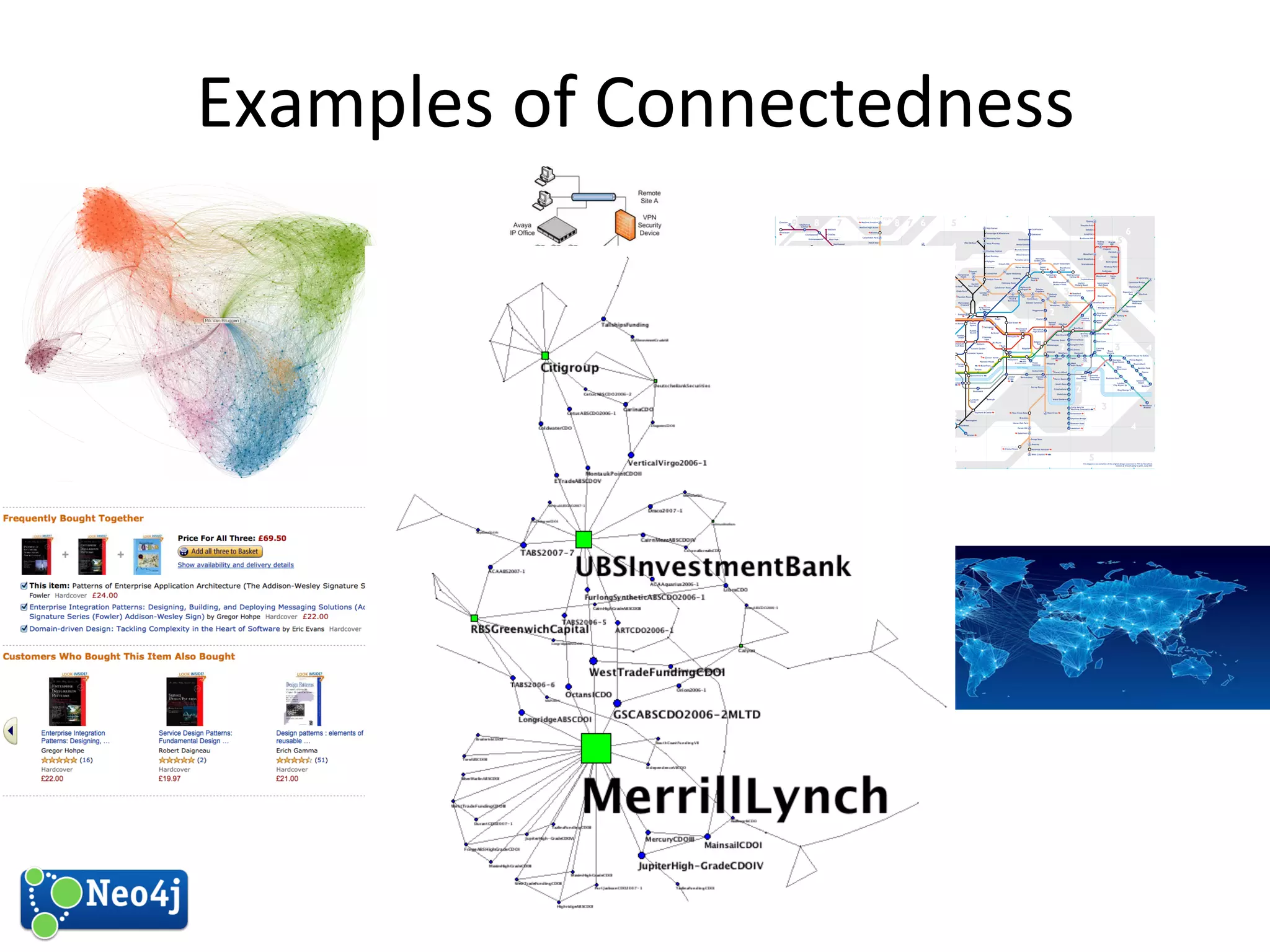
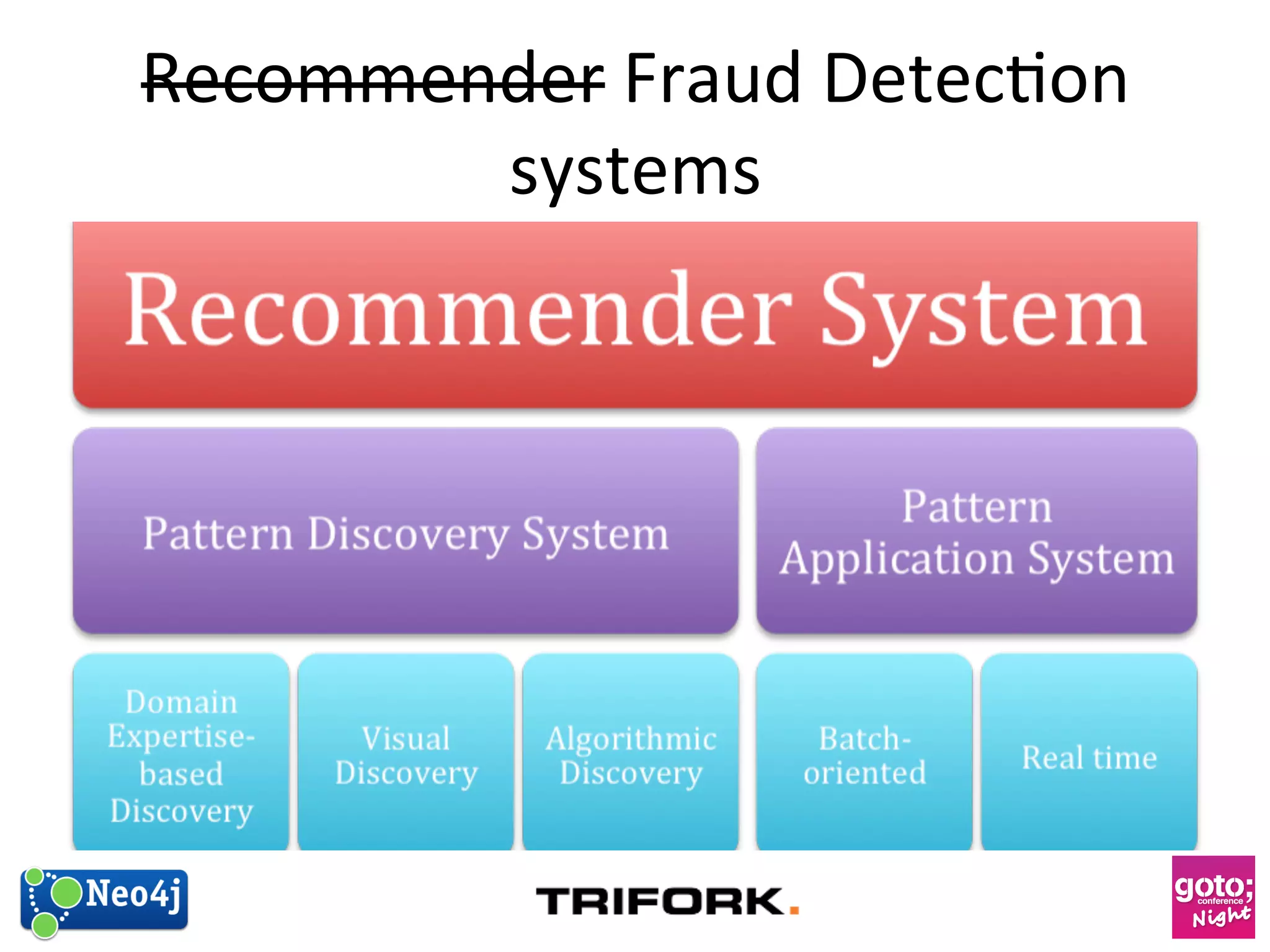
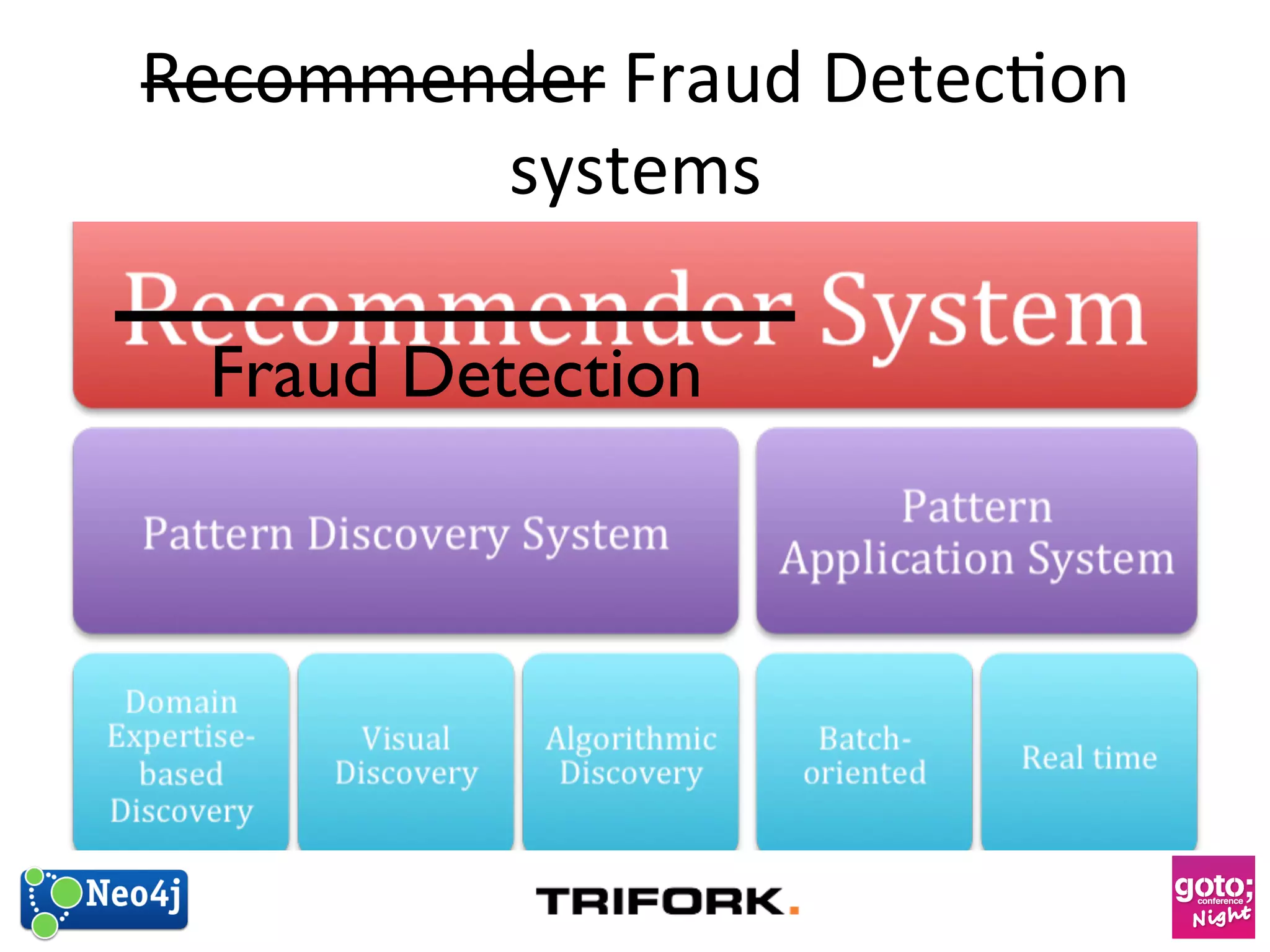
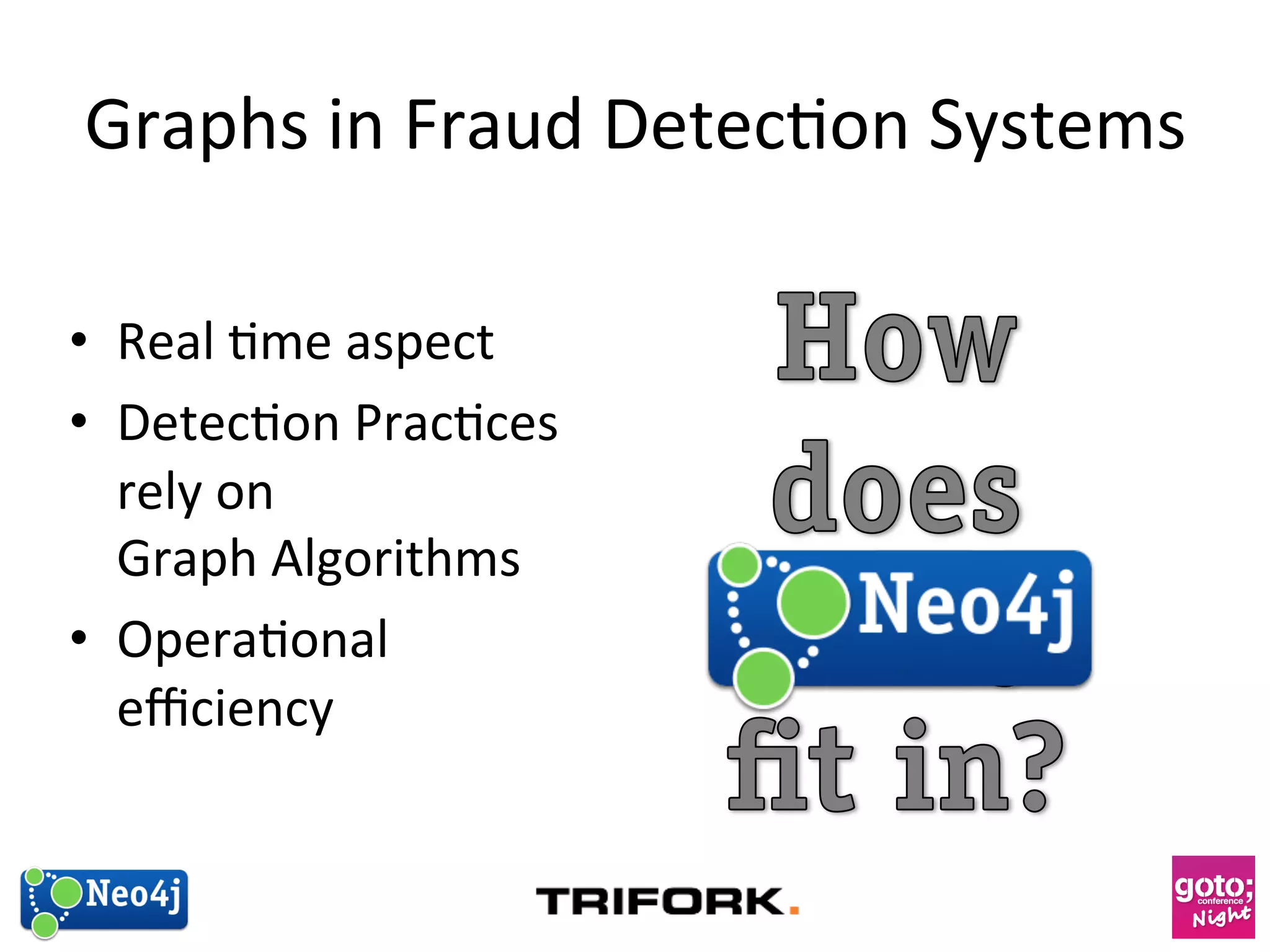
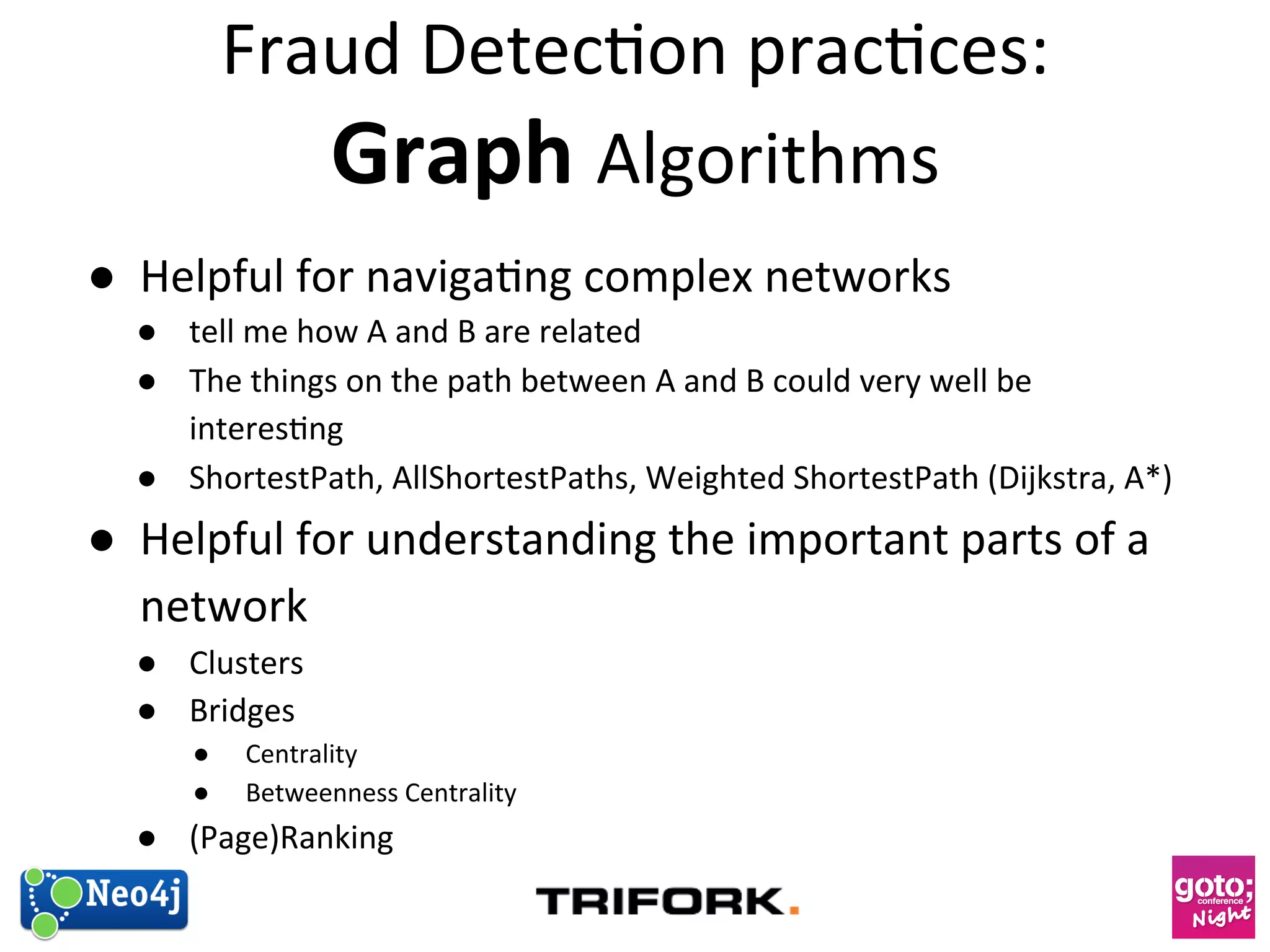
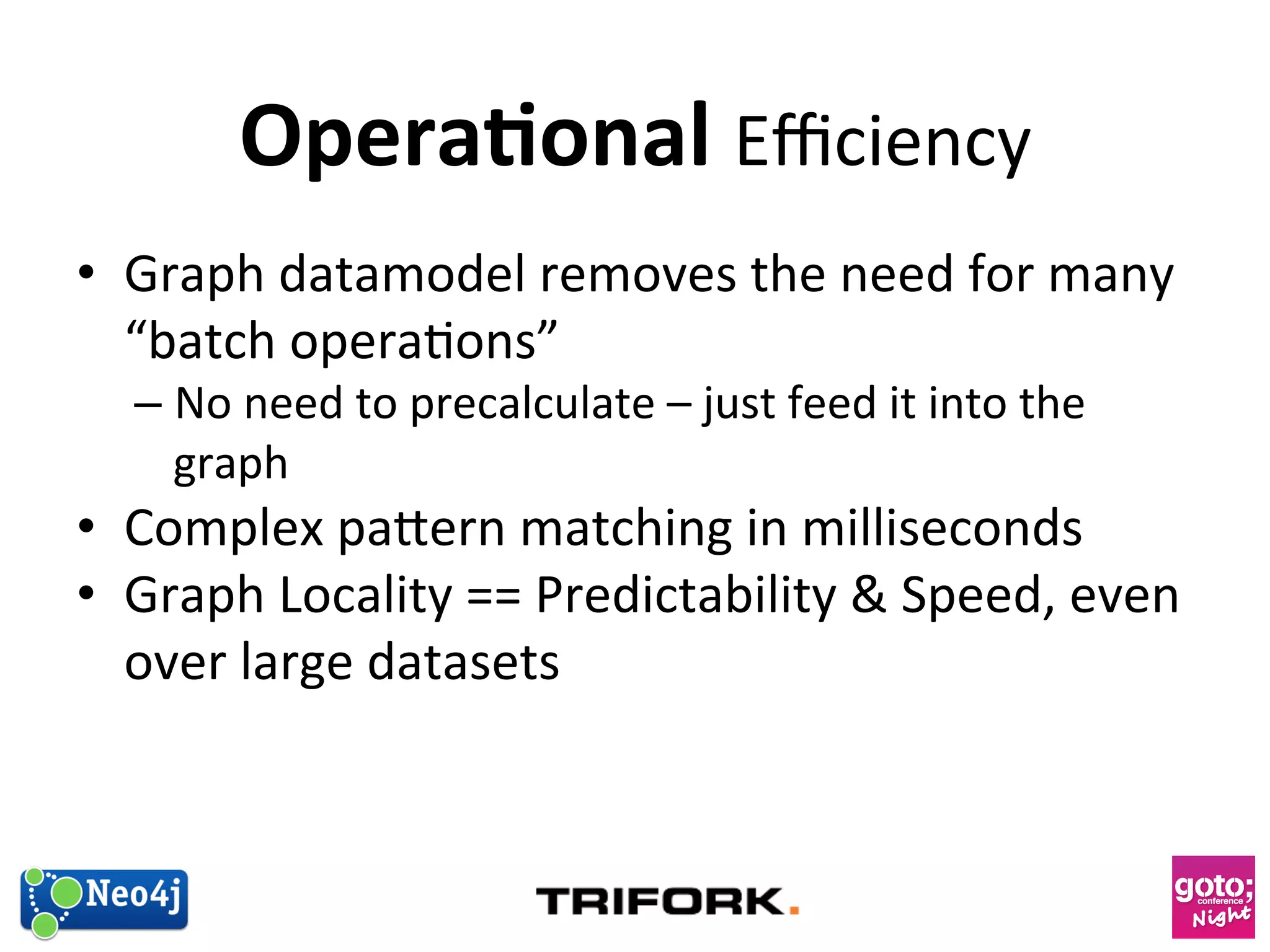
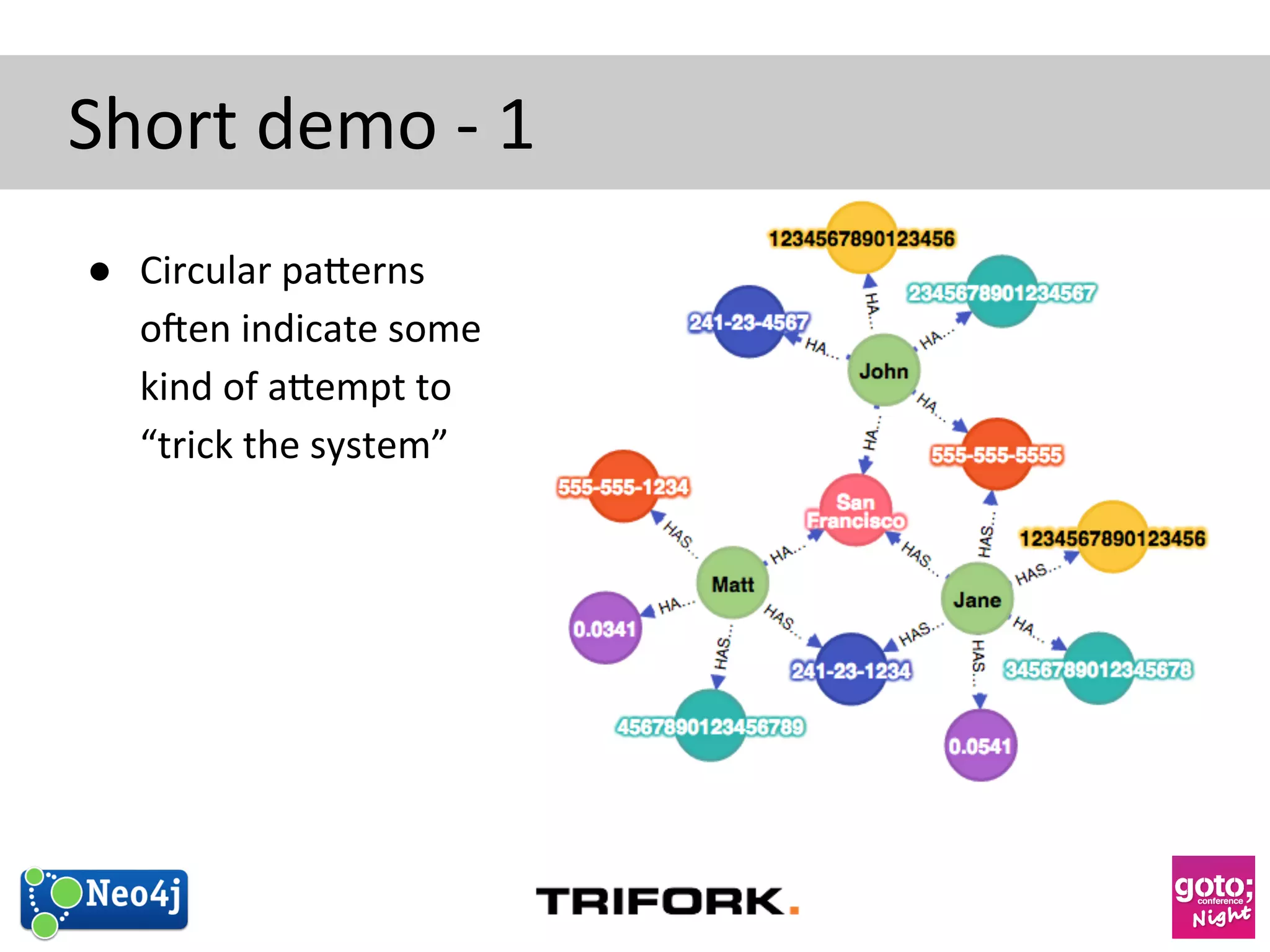
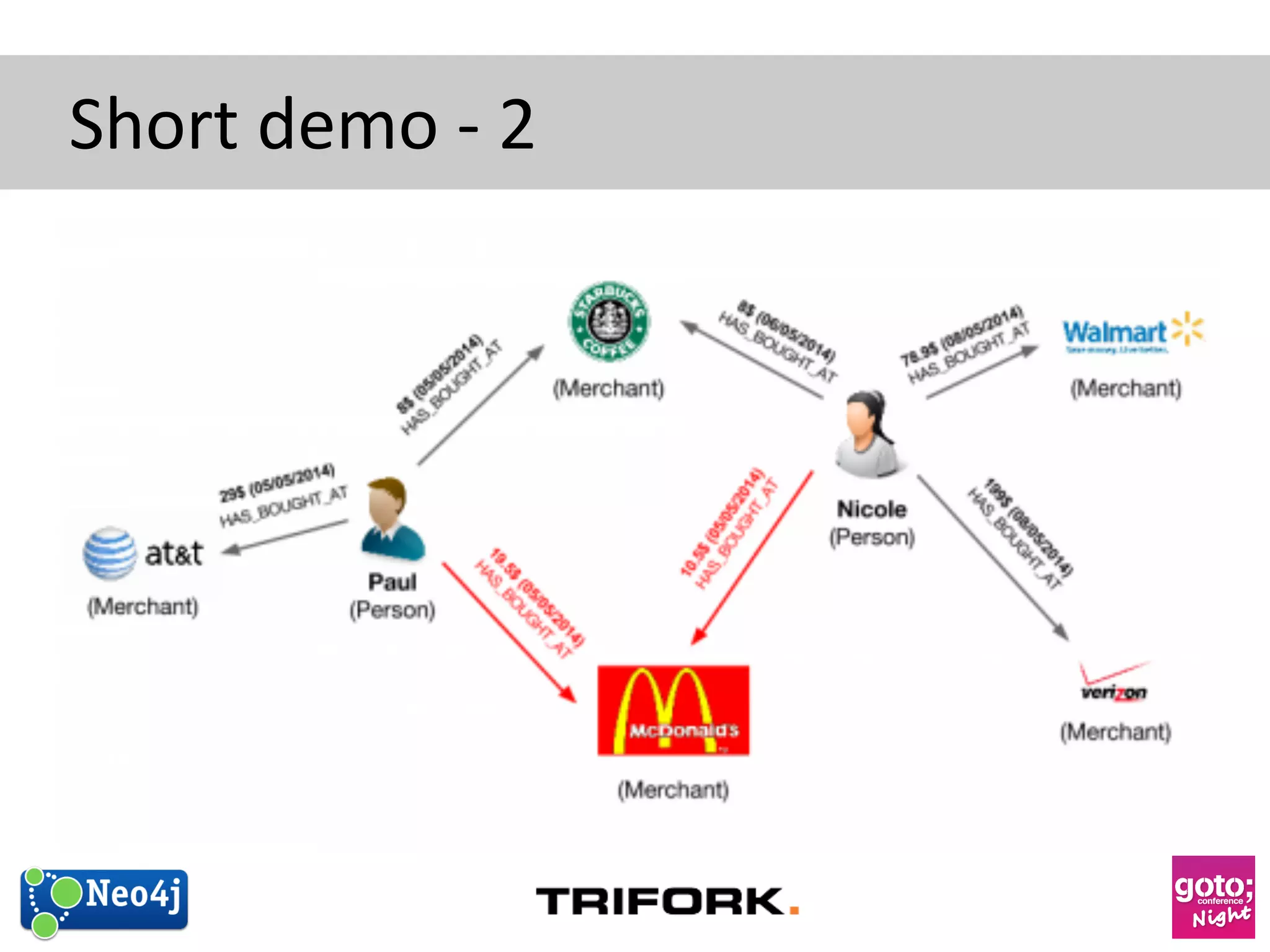
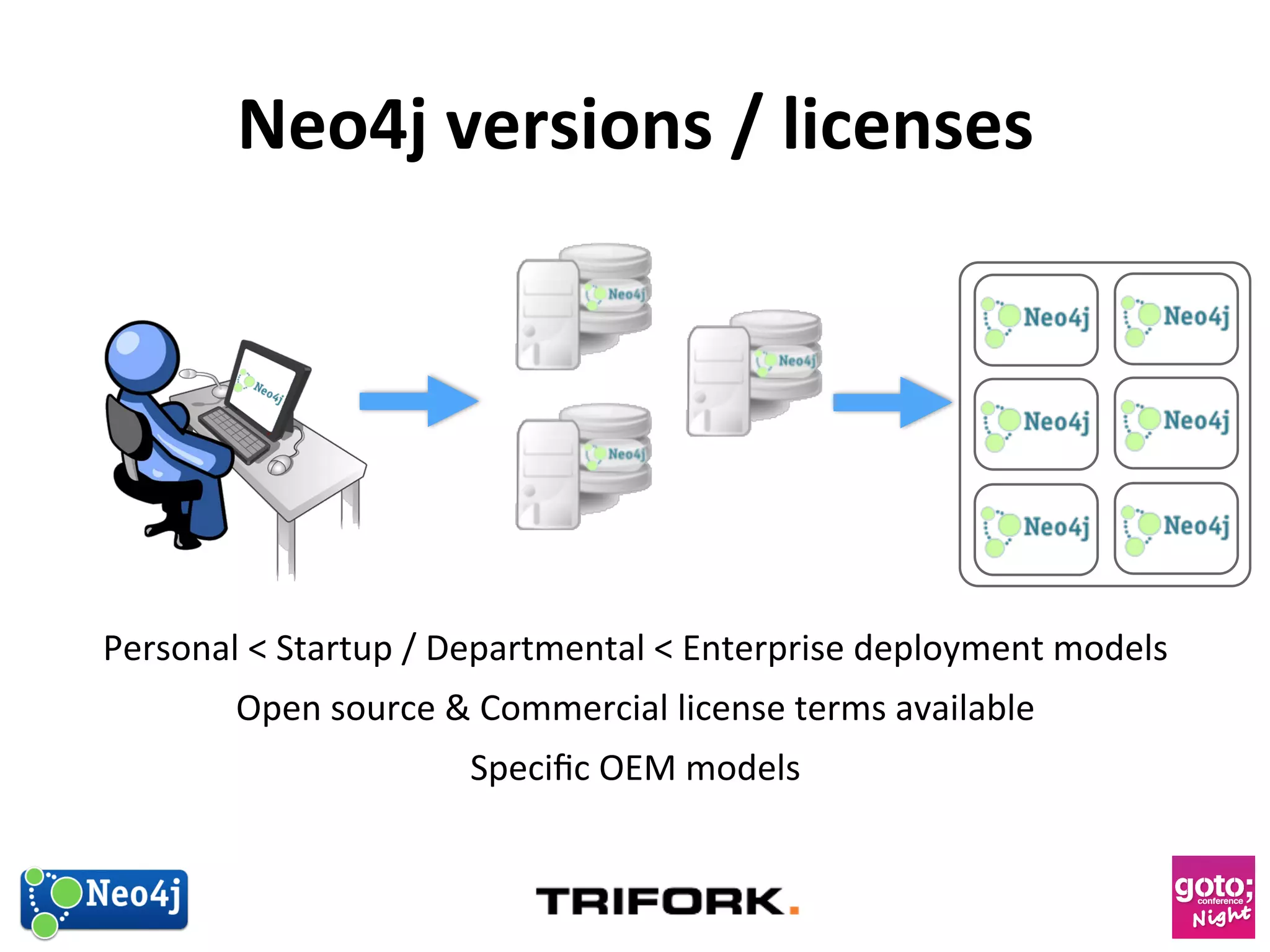
This document discusses how graph databases can be useful for fraud detection. It begins with an introduction to graphs and graph theory, then discusses how graph databases work and their advantages over relational databases for complex querying and modeling connected data. The document notes that fraud detection relies on real-time analysis, complex patterns, and graph algorithms to navigate relationships. It provides a short demonstration and discusses case studies where graph databases have been successfully used for fraud detection due to their ability to efficiently handle large, interconnected datasets.