This document discusses key aspects of project scheduling, including:
- Scheduling determines the timing and sequence of project tasks.
- Schedules are created to better manage projects, control changes, and monitor progress.
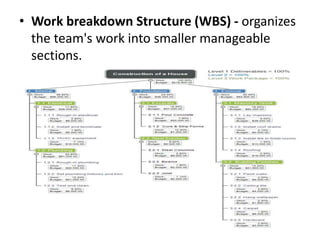
- Key elements that are scheduled include milestones, activities, resources, and durations.
- The scheduler must determine what tasks are needed, how they will be performed, who will perform them, and their sequence.
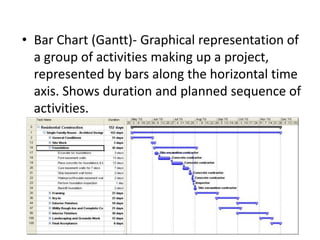
- Common scheduling tools include Gantt charts, critical paths, floats, and scheduling software.
- The scheduling process involves defining activities, sequencing them, estimating durations, developing the schedule, and controlling it.