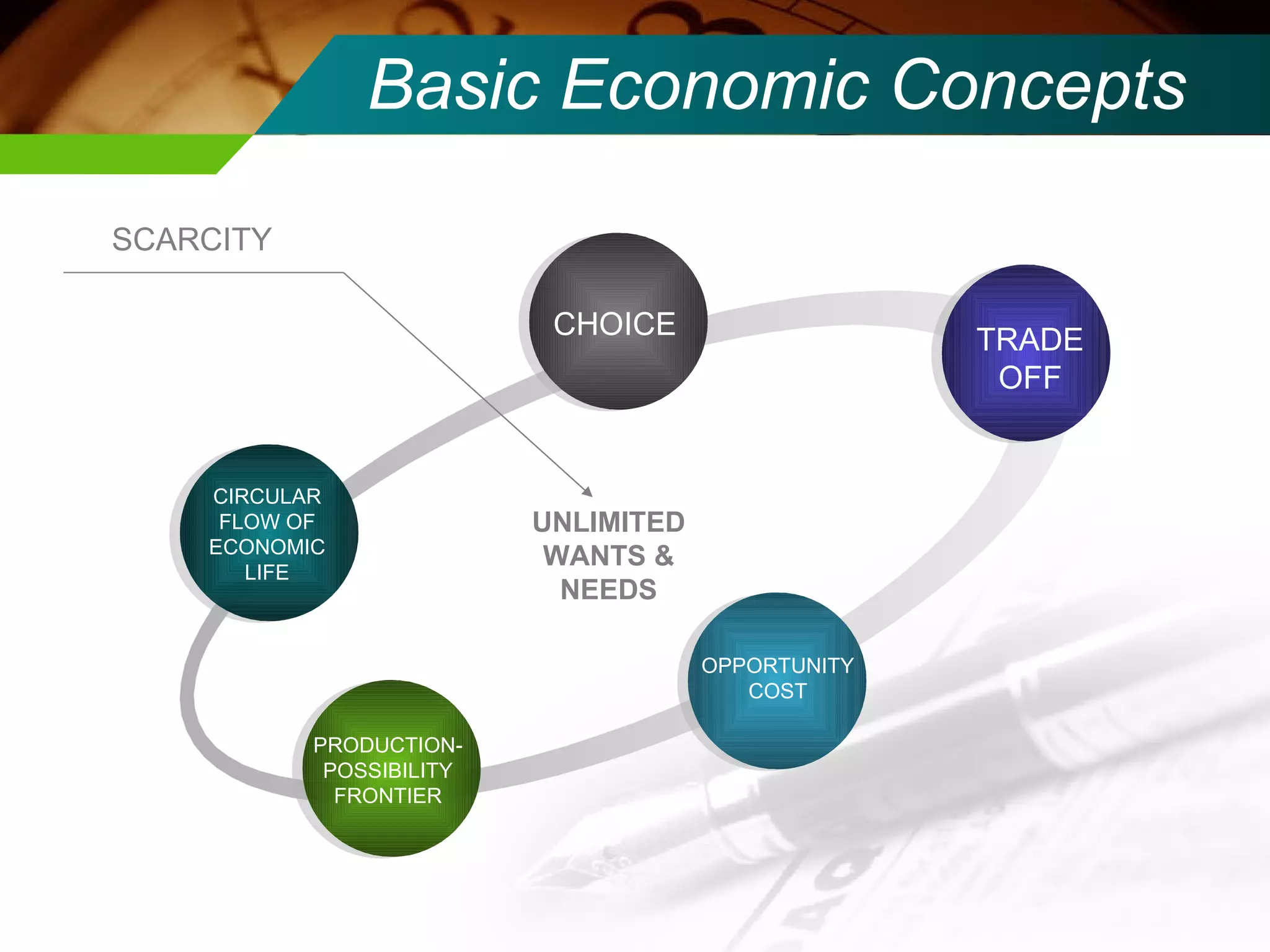
The document discusses several economic concepts related to scarcity including unlimited wants and needs, choice, opportunity cost, and production possibility frontier. It explains that while scarcity is permanent, shortages can be temporary when supply does not meet demand. Due to limited resources, societies cannot satisfy all goods and wants so choices must be made about allocating resources.