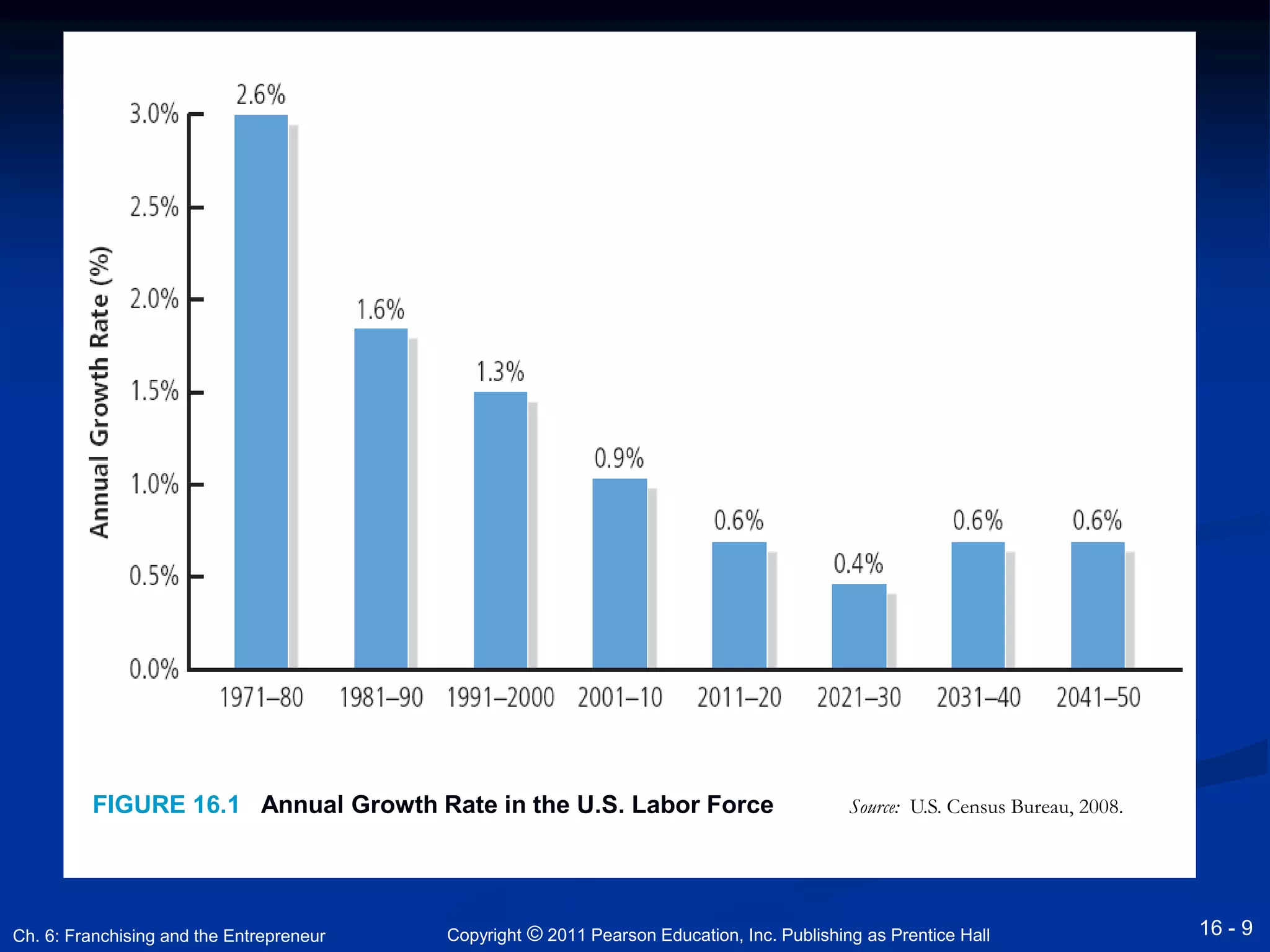
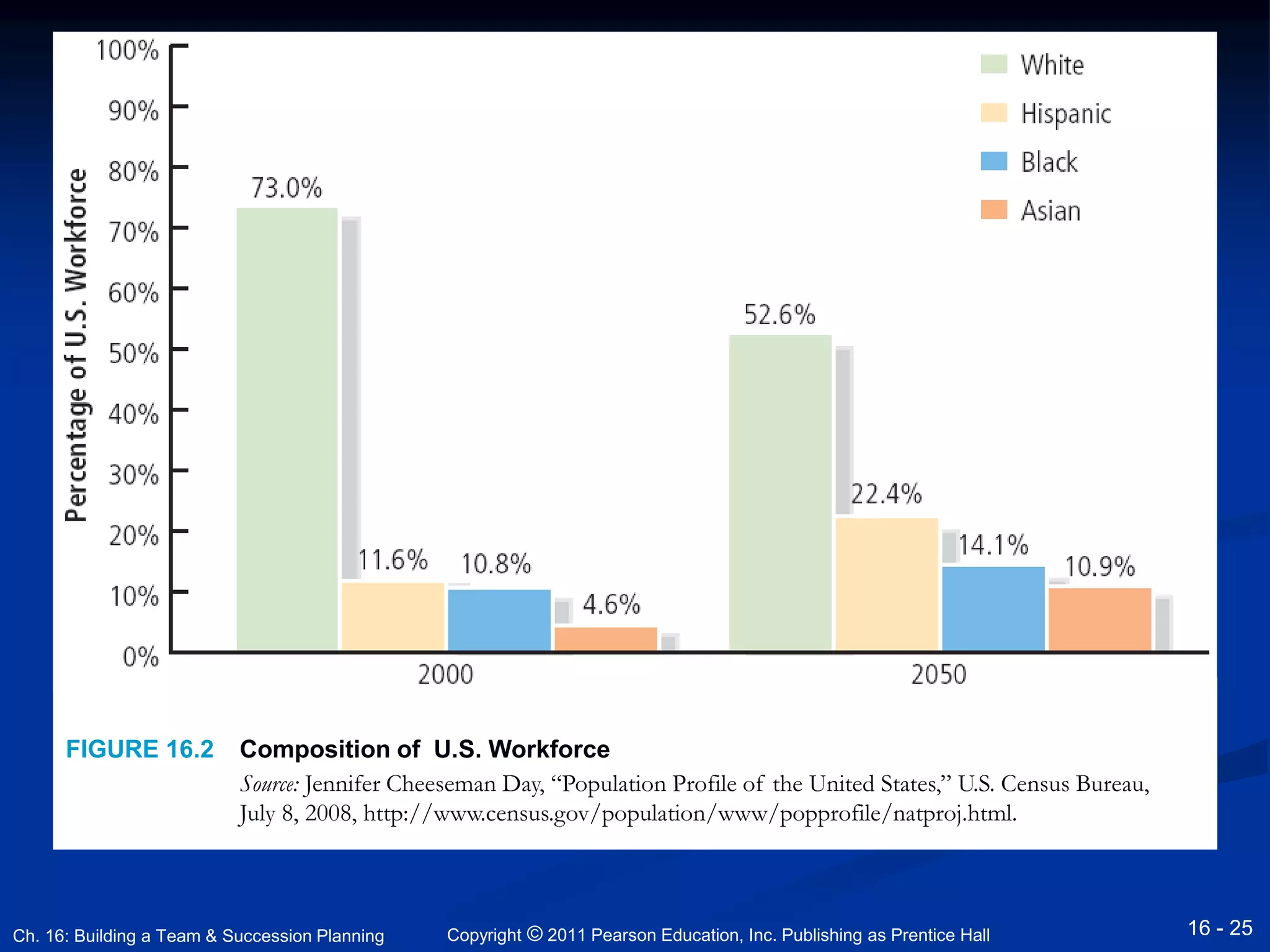
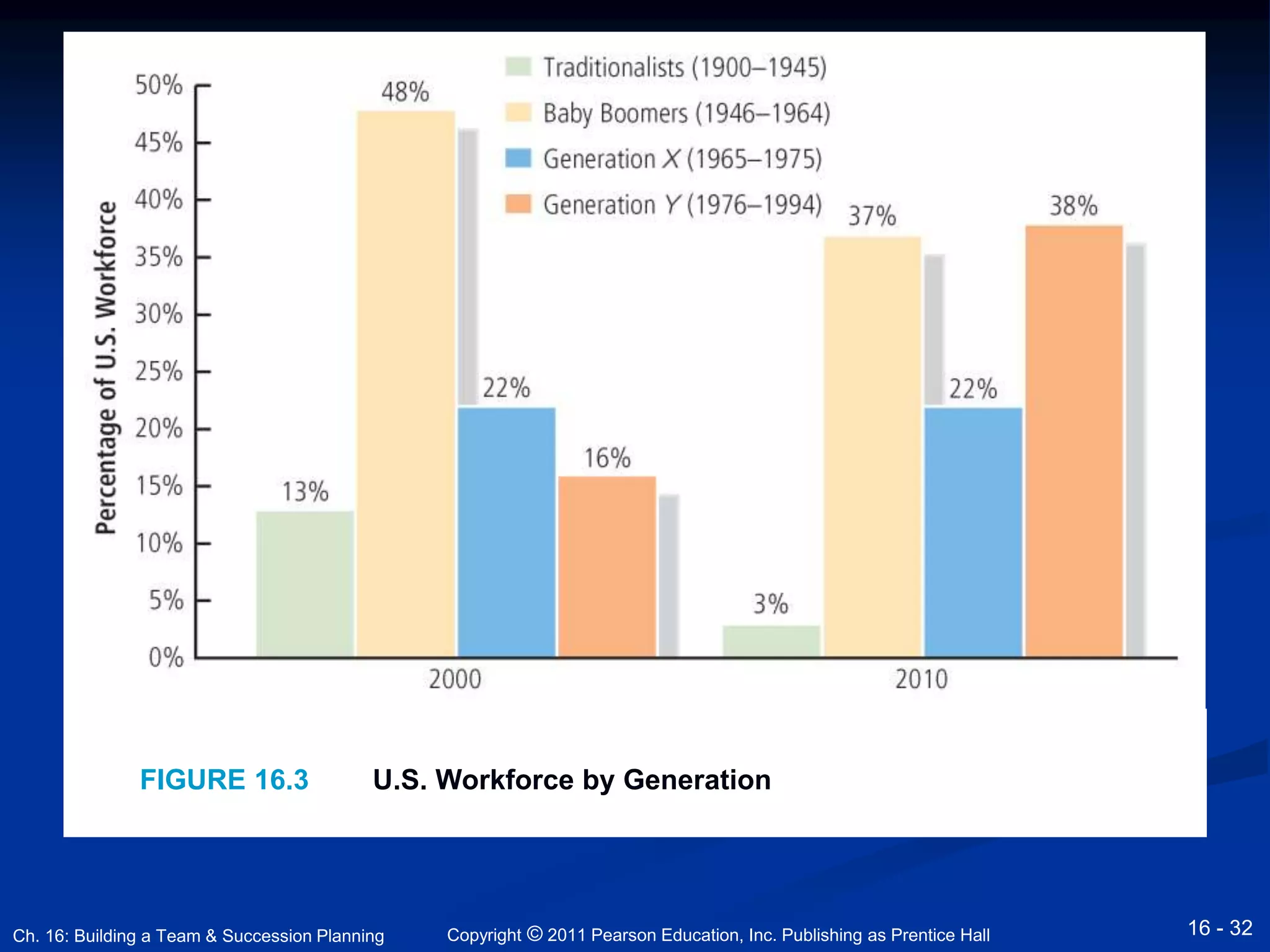
This document discusses building an entrepreneurial team and succession planning. It covers topics such as leadership, hiring effective employees, developing company culture, job design, compensation, and succession planning for family businesses. The key points are that entrepreneurs must take a leadership role, hire the right employees through strategic recruiting and interviews, create a positive company culture, and develop a succession plan to pass the business to future generations of leadership. Effective leadership, team building, and succession planning are vital for business success and longevity.