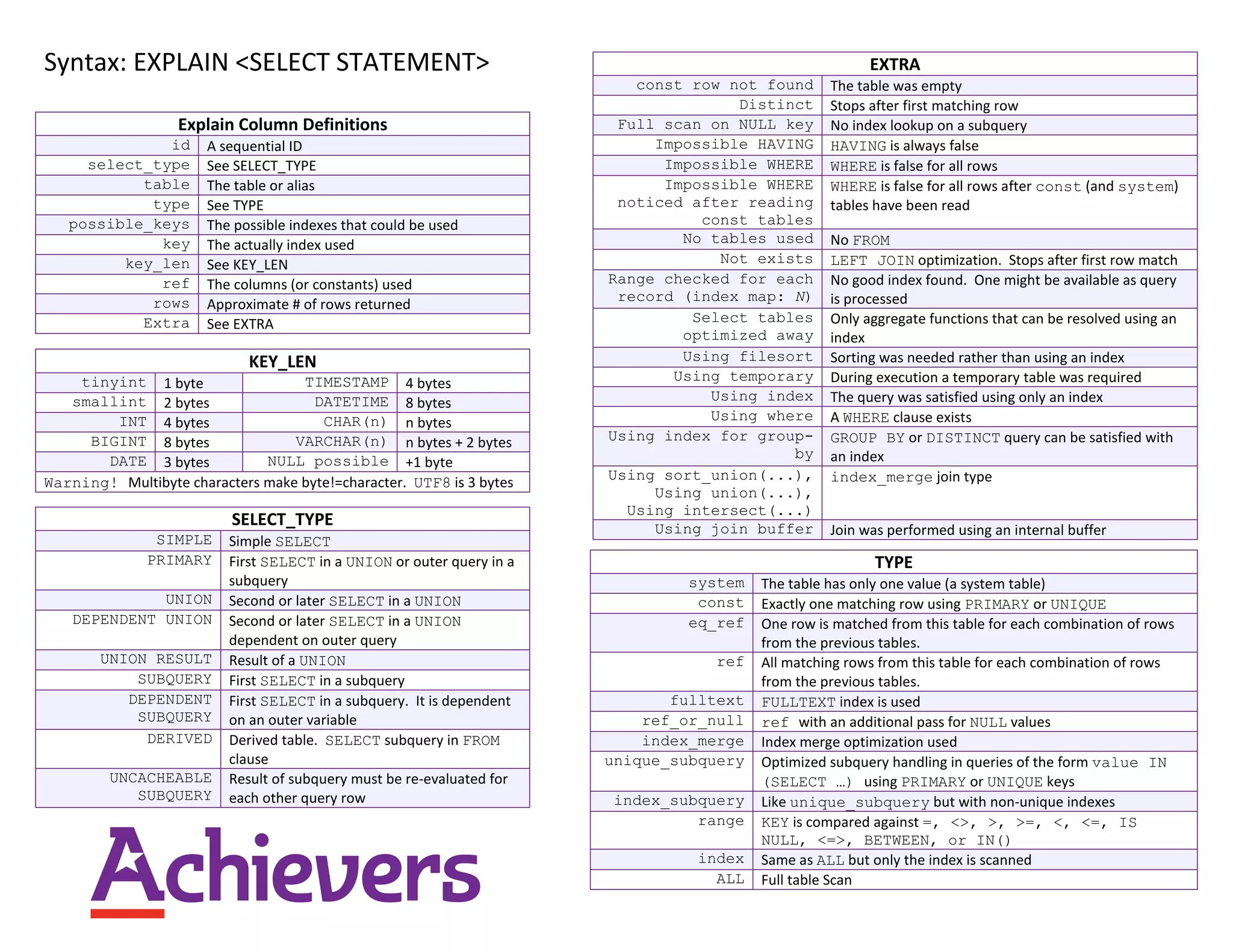
The document defines terms used in the output of the EXPLAIN statement in MySQL. It provides definitions for the column names, possible values in those columns, and descriptions of what those values mean in terms of the query execution plan and optimization techniques used. Key terms defined include SELECT_TYPE values like SIMPLE, UNION, and SUBQUERY; TYPE values indicating the type of join or index used like system, index, and ALL; and EXTRA values providing additional context like Using filesort and Using temporary.