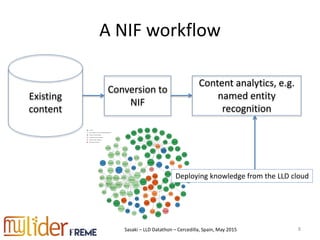
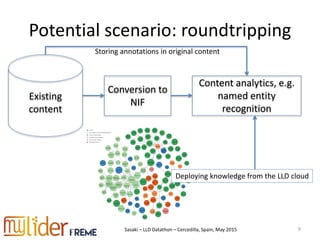
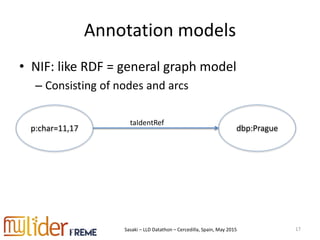
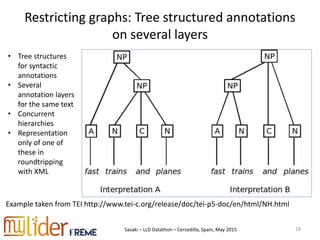
The document discusses the roundtripping of NIF-based linguistic linked data with non-linked data sources, focusing on its application in content enrichment and processing. It includes examples in JSON-LD format, outlines workflows for different content types, and addresses challenges associated with storing annotations in various formats. Additionally, it highlights lessons learned and tools for effective roundtripping in linguistic data processing.

![Sasaki – LLD Datathon – Cercedilla, Spain, May 2015
Example (Partial; JSON-LD Syntax)
{ "@graph" : [ {
"@id" : "p:char=0,18",
"@type" : [ "nif:Context", "nif:Sentence", "nif:RFC5147String" ],
"anchorOf" : "Welcome to Prague.",
"beginIndex" : "0",
"endIndex" : "18",
"isString" : "Welcome to Prague.",
"referenceContext" : "p:char=0,18”
}, {
"@id" : "p:char=11,17",
"@type" : [ "nif:RFC5147String", "nif:Word" ], …
"referenceContext" : "p:char=0,18",
"taIdentRef" : "http://dbpedia.org/resource/Prague" }, …] }
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sasaki-datathon-madrid-2015-150615210043-lva1-app6891/85/Sasaki-datathon-madrid-2015-3-320.jpg)
![Sasaki – LLD Datathon – Cercedilla, Spain, May 2015
Example (Partial; JSON-LD Syntax)
{ "@graph" : [ {
"@id" : "p:char=0,18",
"@type" : [ "nif:Context", "nif:Sentence", "nif:RFC5147String" ],
"anchorOf" : "Welcome to Prague.",
"beginIndex" : "0",
"endIndex" : "18",
"isString" : "Welcome to Prague.",
"referenceContext" : "p:char=0,18”
}, {
"@id" : "p:char=11,17",
"@type" : [ "nif:RFC5147String", "nif:Word" ], …
"referenceContext" : "p:char=0,18",
"taIdentRef" : "http://dbpedia.org/resource/Prague" }, …] }
4
• Identifying and typing
annotations
• Identifying annotation
offsets
• Adding additional
knowledge, e.g. named
entity identifier
• Interrelating
annotations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sasaki-datathon-madrid-2015-150615210043-lva1-app6891/85/Sasaki-datathon-madrid-2015-4-320.jpg)
![Sasaki – LLD Datathon – Cercedilla, Spain, May 2015
Example (Partial; JSON-LD Syntax)
{ "@graph" : [ {
"@id" : "p:char=0,18",
"@type" : [ "nif:Context", "nif:Sentence", "nif:RFC5147String" ],
"anchorOf" : "Welcome to Prague.",
"beginIndex" : "0",
"endIndex" : "18",
"isString" : "Welcome to Prague.",
"referenceContext" : "p:char=0,18”
}, {
"@id" : "p:char=11,17",
"@type" : [ "nif:RFC5147String", "nif:Word" ], …
"referenceContext" : "p:char=0,18",
"taIdentRef" : "http://dbpedia.org/resource/Prague" }, …] }
5
• Identifying and typing
annotations
• Identifying annotation
offsets
• Adding additional
knowledge, e.g. named
entity identifier
• Interrelating
annotations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sasaki-datathon-madrid-2015-150615210043-lva1-app6891/85/Sasaki-datathon-madrid-2015-5-320.jpg)
![Sasaki – LLD Datathon – Cercedilla, Spain, May 2015
Example (Partial; JSON-LD Syntax)
{ "@graph" : [ {
"@id" : "p:char=0,18",
"@type" : [ "nif:Context", "nif:Sentence", "nif:RFC5147String" ],
"anchorOf" : "Welcome to Prague.",
"beginIndex" : "0",
"endIndex" : "18",
"isString" : "Welcome to Prague.",
"referenceContext" : "p:char=0,18”
}, {
"@id" : "p:char=11,17",
"@type" : [ "nif:RFC5147String", "nif:Word" ], …
"referenceContext" : "p:char=0,18",
"taIdentRef" : "http://dbpedia.org/resource/Prague" }, …] }
6
• Identifying and typing
annotations
• Identifying annotation
offsets
• Adding additional
knowledge, e.g.
named entity identifier
• Interrelating
annotations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sasaki-datathon-madrid-2015-150615210043-lva1-app6891/85/Sasaki-datathon-madrid-2015-6-320.jpg)
![Sasaki – LLD Datathon – Cercedilla, Spain, May 2015
Example (Partial; JSON-LD Syntax)
{ "@graph" : [ {
"@id" : "p:char=0,18",
"@type" : [ "nif:Context", "nif:Sentence", "nif:RFC5147String" ],
"anchorOf" : "Welcome to Prague.",
"beginIndex" : "0",
"endIndex" : "18",
"isString" : "Welcome to Prague.",
"referenceContext" : "p:char=0,18”
}, {
"@id" : "p:char=11,17",
"@type" : [ "nif:RFC5147String", "nif:Word" ], …
"referenceContext" : "p:char=0,18",
"taIdentRef" : "http://dbpedia.org/resource/Prague" }, …] }
7
• Identifying and typing
annotations
• Identifying annotation
offsets
• Adding additional
knowledge, e.g.
named entity identifier
• Interrelating
annotations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sasaki-datathon-madrid-2015-150615210043-lva1-app6891/85/Sasaki-datathon-madrid-2015-7-320.jpg)