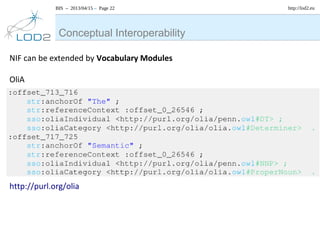
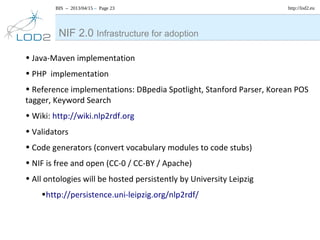
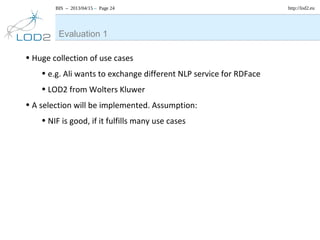
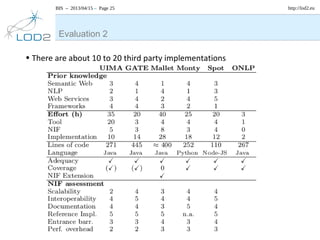
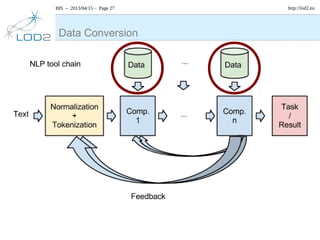
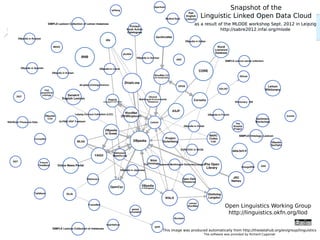
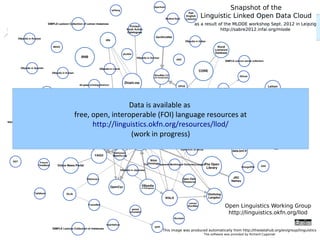
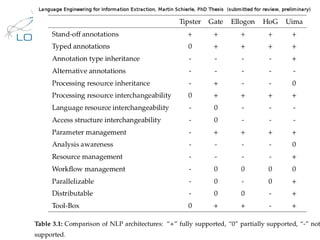
The document discusses the NLP Interchange Format (NIF) 2.0, which aims to achieve interoperability between NLP tools, resources, and annotations. It notes that NIF 2.0 will be published within 6-8 weeks and is highly likely to become the de facto standard for modeling RDF tool output in NLP. The document analyzes problems in the current NLP landscape such as heterogeneity of technologies, formats, languages, and lack of open collaboration and standards. It presents NIF as a solution to these problems by defining text normalization, an RDF-based core ontology, modular ontologies, and infrastructure for validation, hosting, and adoption. Evaluation approaches and a positive impact and reception of N



![BIS – 2013/04/15 – Page 15 http://lod2.eu
As a Web Service
curl
--data-urlencode prefix="http://prefix.given.by/theClient#"
--data-urlencode input="[...]"
(--data-urlencode source=”http://www.w3.org/DesignIssues/LinkedData.html”)
http://nlp2rdf.lod2.eu/demo/NIFStanfordCore
The new namespace is http://persistence.uni-leipzig.org/nlp2rdf/nif-core#](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nif2-0bispublic-130416033336-phpapp01/85/NIF-2-0-Phd-thesis-intermediate-report-15-320.jpg)