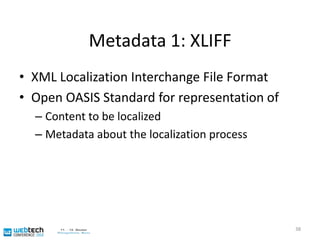
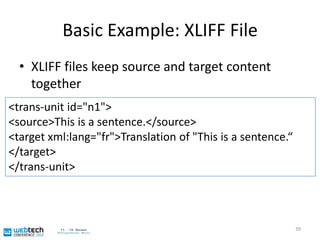
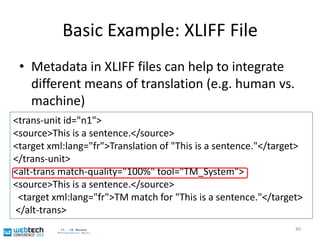
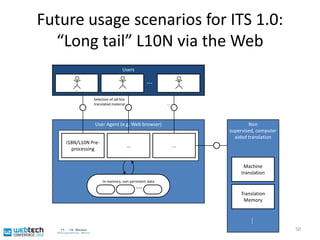
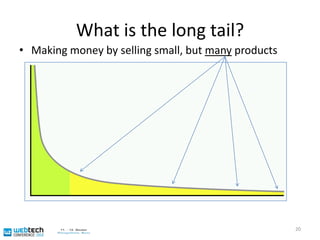
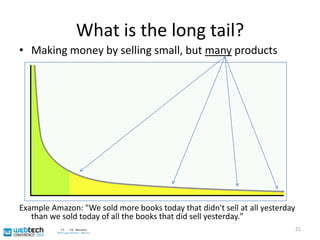
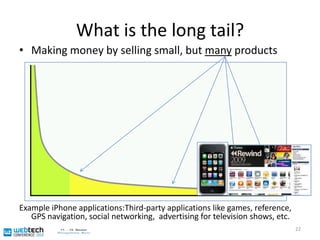
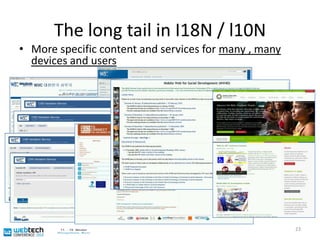
The document discusses the multilingual web and internationalization (I18N) and localization (L10N) topics. It covers traditional topics like language tags and internationalized domain names. It also discusses newer topics like the "long tail" effect and its consequences for a multilingual web with more specific content and services. Metadata standards like XLIFF and ITS 1.0 help bridge technology gaps and make localization of long tail content easier and more affordable. The document advocates for content authors and developers to use standards like ITS to better enable computer-aided translation tools.











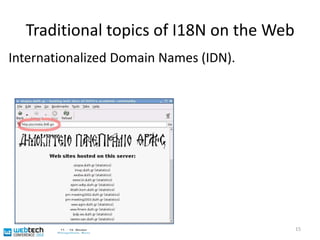

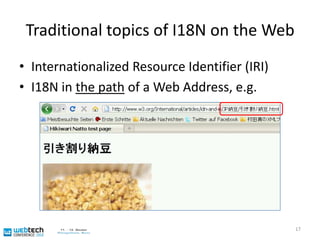
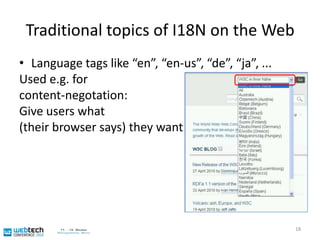








![Language tags leads to layout ...Already possible for a while: selection of culture-specific glyph images based on language tags32<span xml:lang="zh-CN">[雪 zh-CN]</span> <span xml:lang="ja">[ 雪 ja]</span><span xml:lang="ko">[ 雪 ko]</span>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sasaki-webtechcon2010-101206123254-phpapp02/85/Sasaki-webtechcon2010-33-320.jpg)