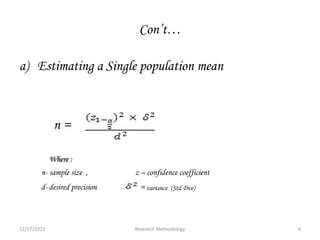
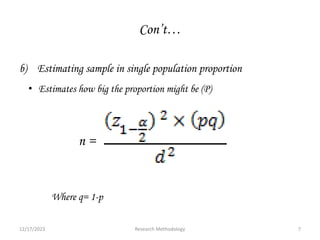
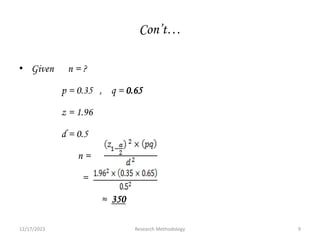
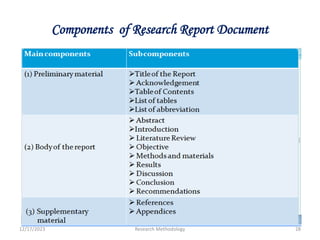
The document provides guidance on components that should be included in a research report. It discusses preliminary parts such as the title, acknowledgements, and abstract. It describes the body of the report which includes an introduction describing the topic and importance of the study, statement of the problem, literature review, significance and objectives of the study. The method section outlines the study design, period, population, data collection and analysis. The results, discussion, limitations and conclusions/recommendations are also highlighted as important components to include to effectively communicate the study findings.