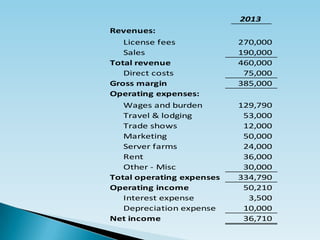
The document provides guidance on creating financial projections for a business called Area48. It recommends creating projections for 3-5 years, with the first 2 years projected monthly and subsequent years quarterly or annually. The document reviews terminology used in projections, accounting concepts, and the standard income statement format used to organize projections in a spreadsheet. It also lists common line items to include in projections such as revenues, costs, operating expenses like wages, rent, and marketing.