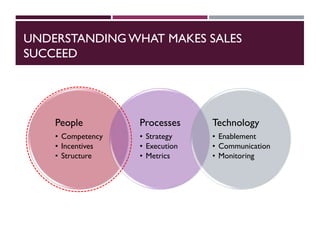
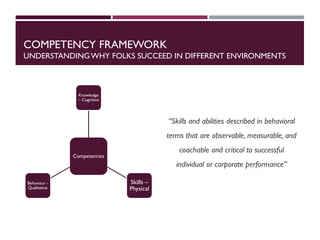
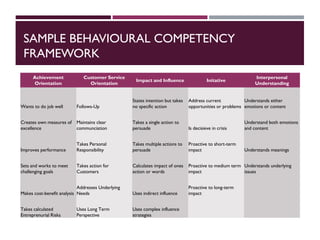
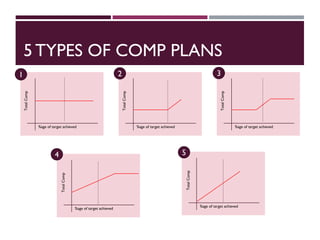
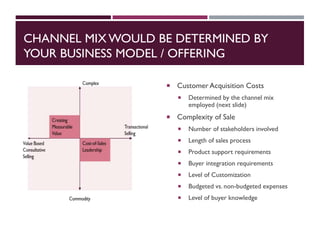
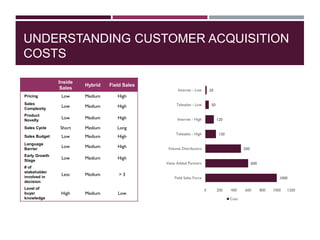
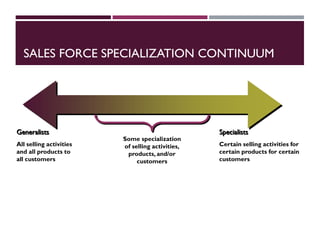
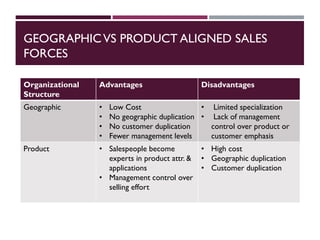
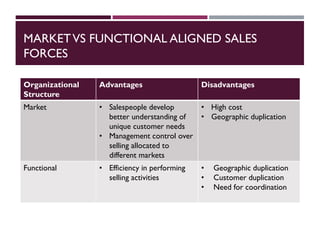
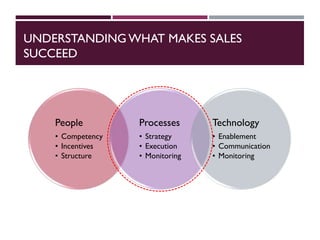
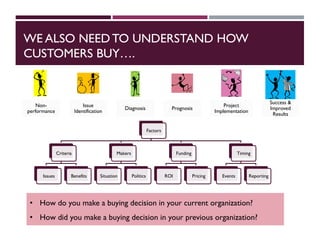
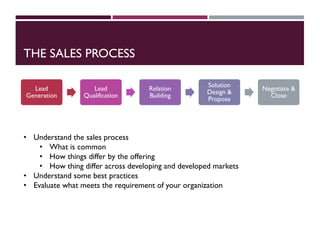
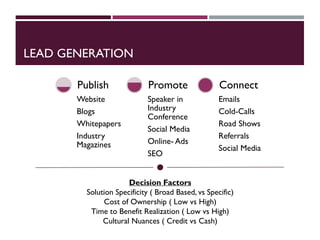
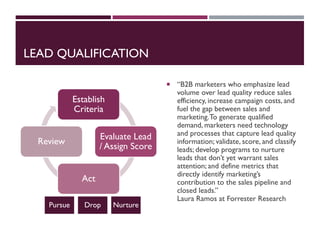
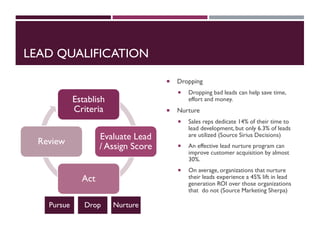
This document discusses best practices for setting up and managing an effective sales function. It covers three key areas: people, processes, and technology. For people, it emphasizes competency frameworks, incentive structures, and organizational structures. For processes, it outlines strategies for sales funnel management, lead generation and qualification, relationship building, and solution proposals. For technology, it discusses tools that can enable sales, improve communication, and facilitate monitoring. The document provides models and examples for each of these areas based on the author's experience to help organizations design stronger sales capabilities.