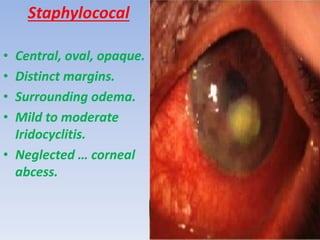
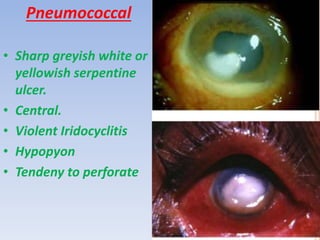
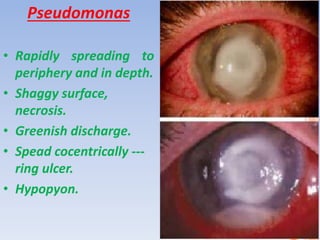
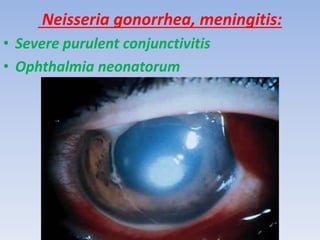
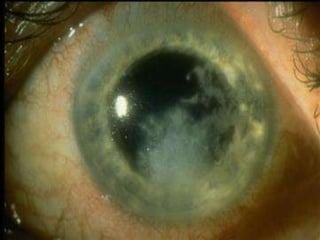
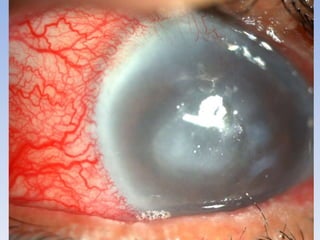
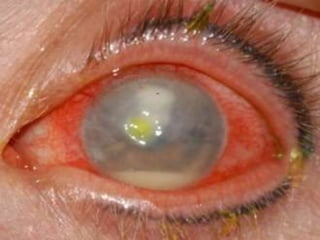
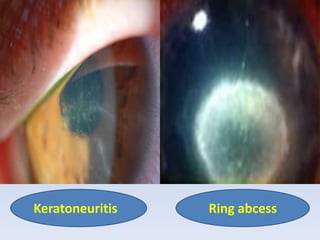
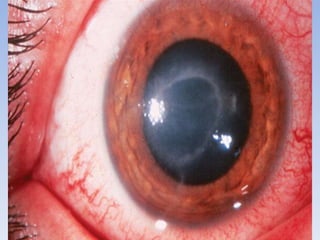
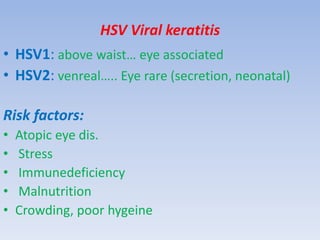
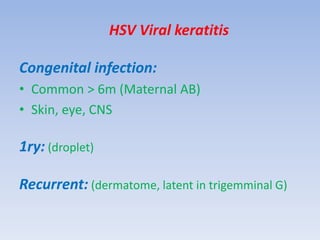
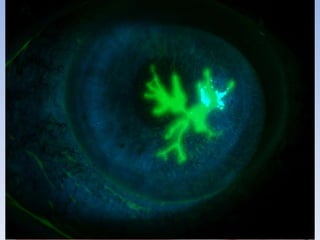
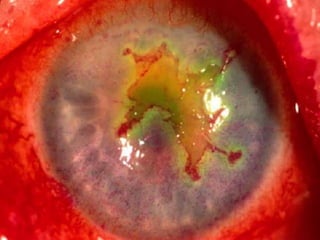
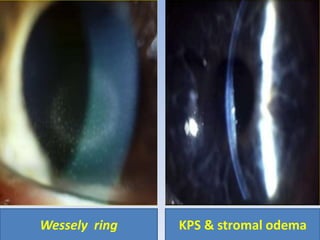
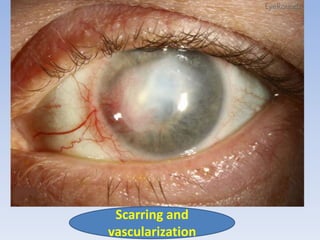
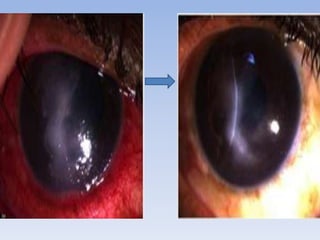
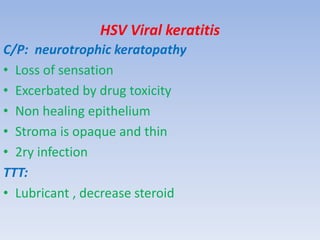
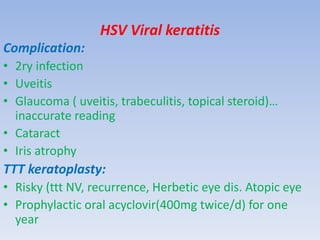
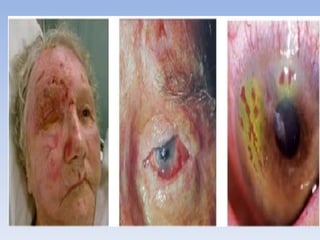
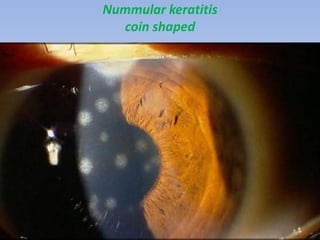
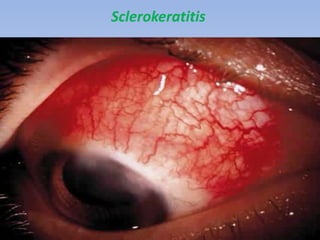
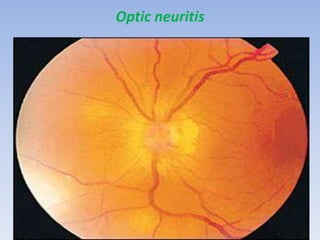
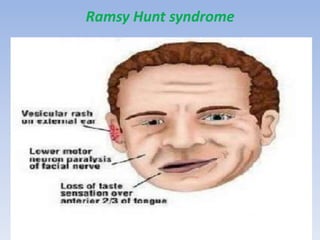
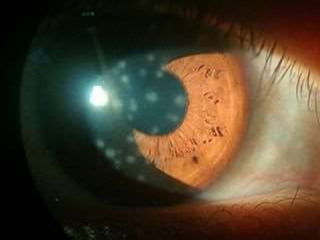
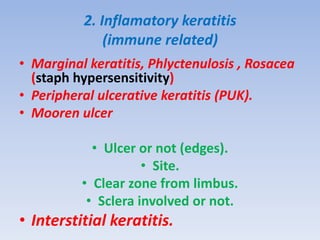
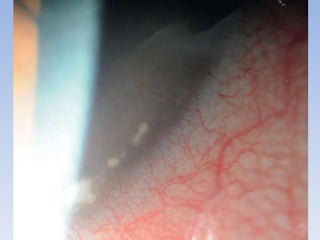
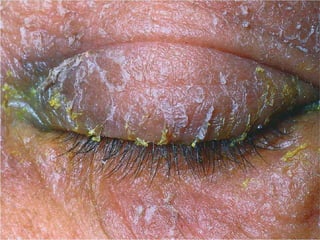
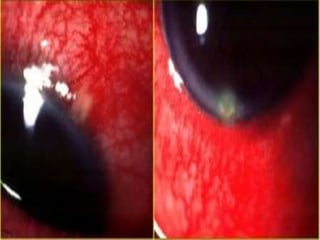
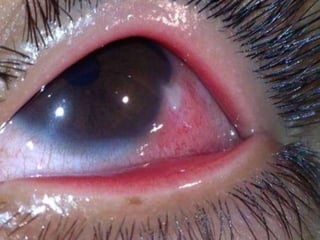
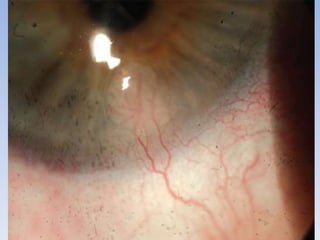
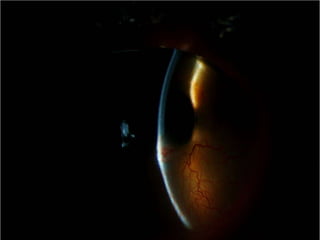
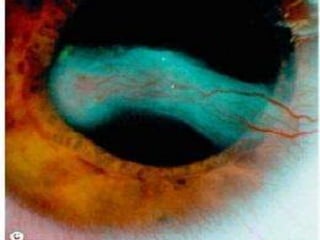
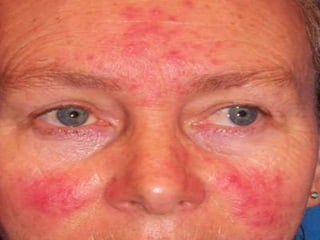
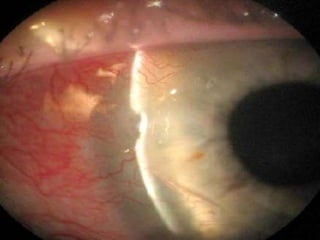
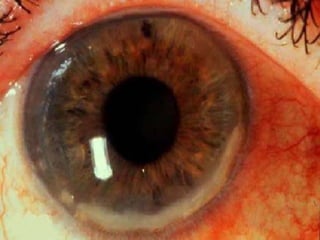
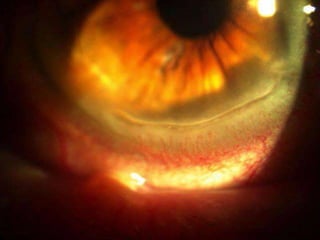
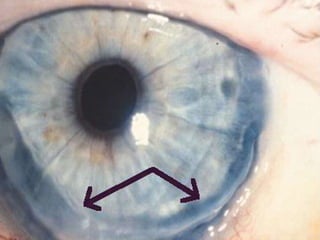
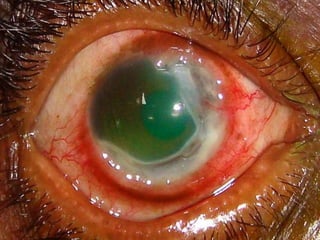
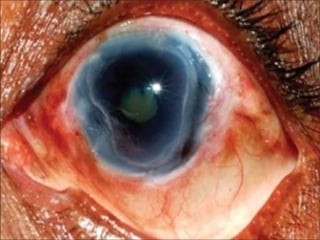
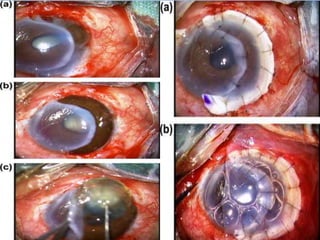
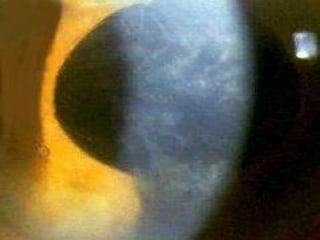
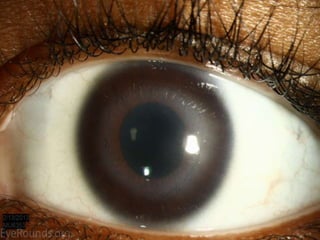
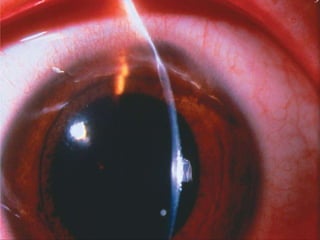
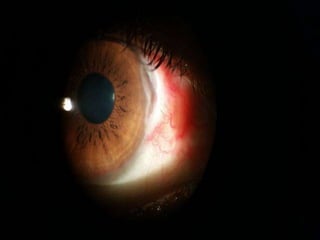
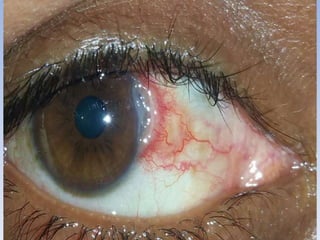
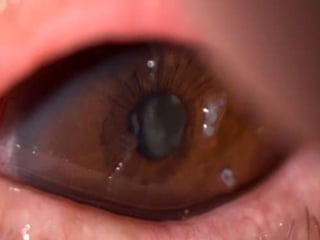
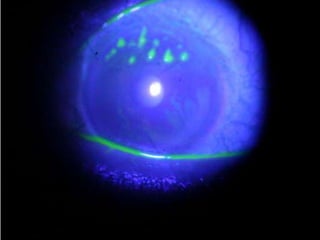
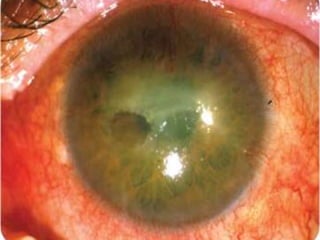
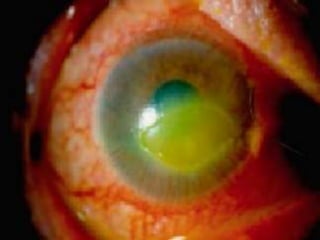
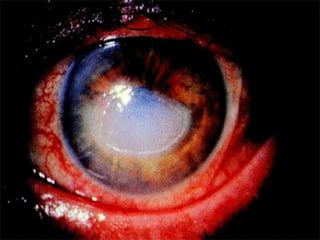
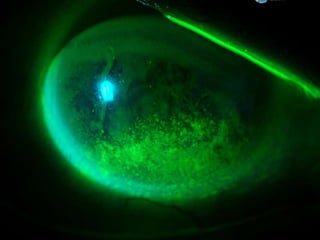
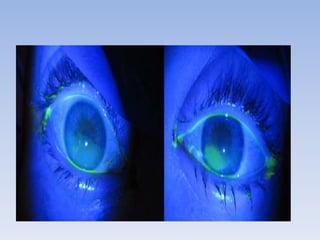
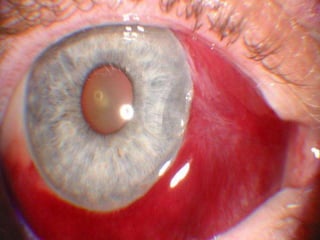
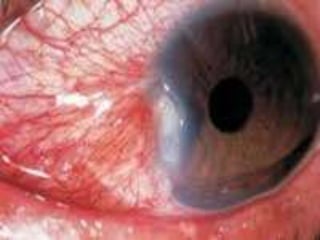
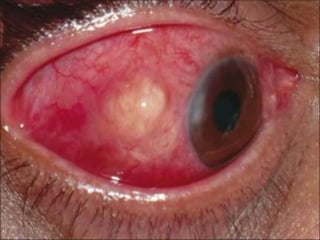
The document discusses various types of corneal diseases including congenital, traumatic, inflammatory, degenerative/dystrophic, and neoplastic conditions. It provides details on infectious keratitis caused by bacteria like Staphylococcus, Pseudomonas, and Neisseria as well as fungi and protozoa. Viral keratitis from herpes simplex virus, herpes zoster virus, and adenovirus are also examined. Signs, risk factors, investigations, and treatment approaches are described for each condition. Inflammatory keratitis can be infective or immune-related disorders like marginal keratitis and Mooren's ulcer are also reviewed.