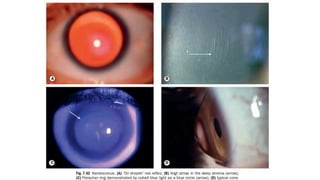
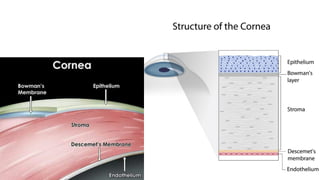
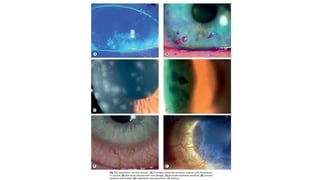
The cornea is the transparent outer layer of the eyeball and the most important refractive structure. It consists of 5 layers - epithelium, Bowman's layer, stroma, Descemet's membrane, and endothelium. The cornea remains transparent due to factors like its lack of blood vessels and pigmentation. Common corneal diseases include bacterial keratitis, fungal keratitis, herpes simplex keratitis, and keratoconus. Bacterial keratitis is treated with topical and oral antibiotics while fungal keratitis often requires systemic antifungals. Herpes simplex keratitis can cause recurrent epithelial defects treated with antivirals. Keratoconus is a degenerative condition causing irregular astigmat




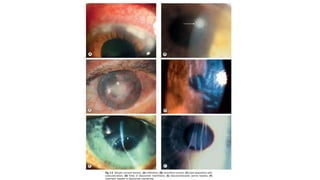












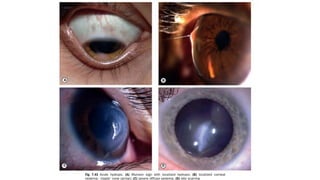
![Keratoconus
It is a progressive disorder in which the cornea assumes an irregular conical
shape. The onset is at around puberty with slow progression and become stationary
at any time.
Presentation:
1- Unilateral impairment of vision due to progressive myopia and regular
astigmatism, which subsequently becomes irregular.
2- Frequent changes in spectacle prescription or decrease tolerance to contact lens
(due changes in the shape of cornea).
3- The fellow eye usually has normal vision with negligible astigmatism at
presentation because of the asymmetrical nature of the condition. Most [not all] of
the cases are bilateral.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecornea-230321220327-18e8cbfb/85/The-cornea-pdf-26-320.jpg)