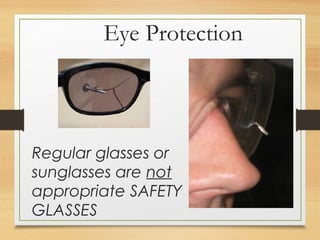
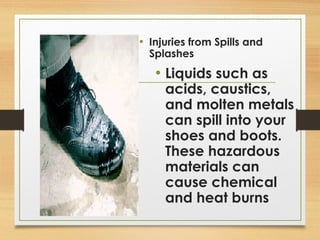
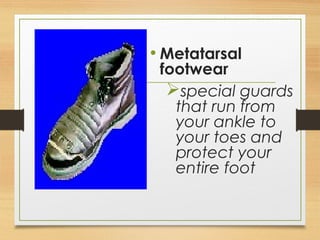
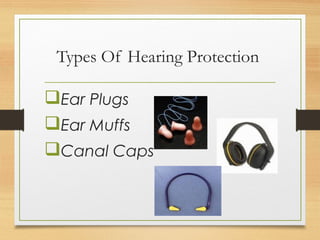
This document discusses various safety roles and personal protective equipment. It describes security personnel who help detect safety hazards and assist engineers. It outlines the types of checks security can perform and various hazards they may encounter. The document then discusses different types of personal protective equipment including head, eye, face, hand, foot, body, hearing and respiratory protection. For each type of protective equipment, it identifies common hazards, provides examples, and describes appropriate equipment to use.