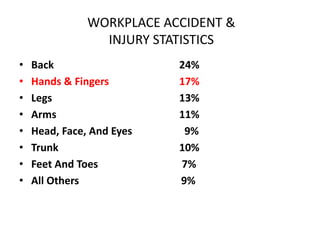
This document provides an overview of personal protective equipment (PPE) including the objectives of PPE training, selection of appropriate PPE based on hazard evaluation, and descriptions of common types of PPE like head protection, eye protection, hand protection, hearing protection, respiratory protection, foot protection, leg protection, and full body protection. It also discusses care and maintenance of PPE and stresses the importance of wearing PPE both at work and at home.