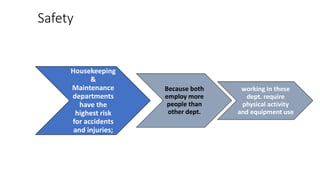
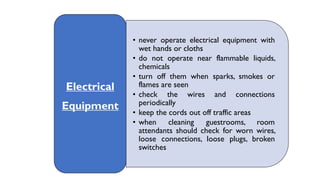
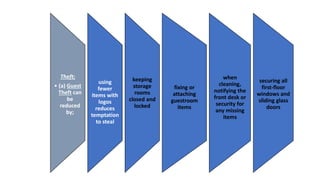
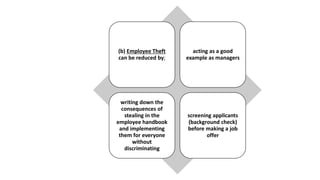
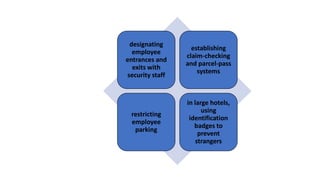
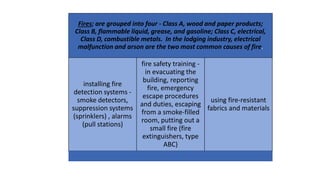
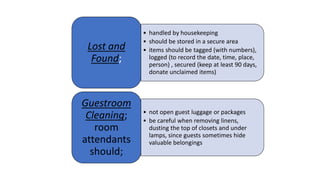
This document discusses safety and security procedures for hotel housekeeping operations. It addresses potential safety hazards in housekeeping and maintenance departments due to their labor intensity and physical activity. Some key points covered are developing safety training programs, ensuring proper lifting techniques and equipment use, identifying and addressing potentially hazardous conditions like wet floors or faulty electrical equipment. The document also discusses security measures like key control, addressing suspicious persons, theft prevention, bomb threats, fires, and procedures for lost and found items.