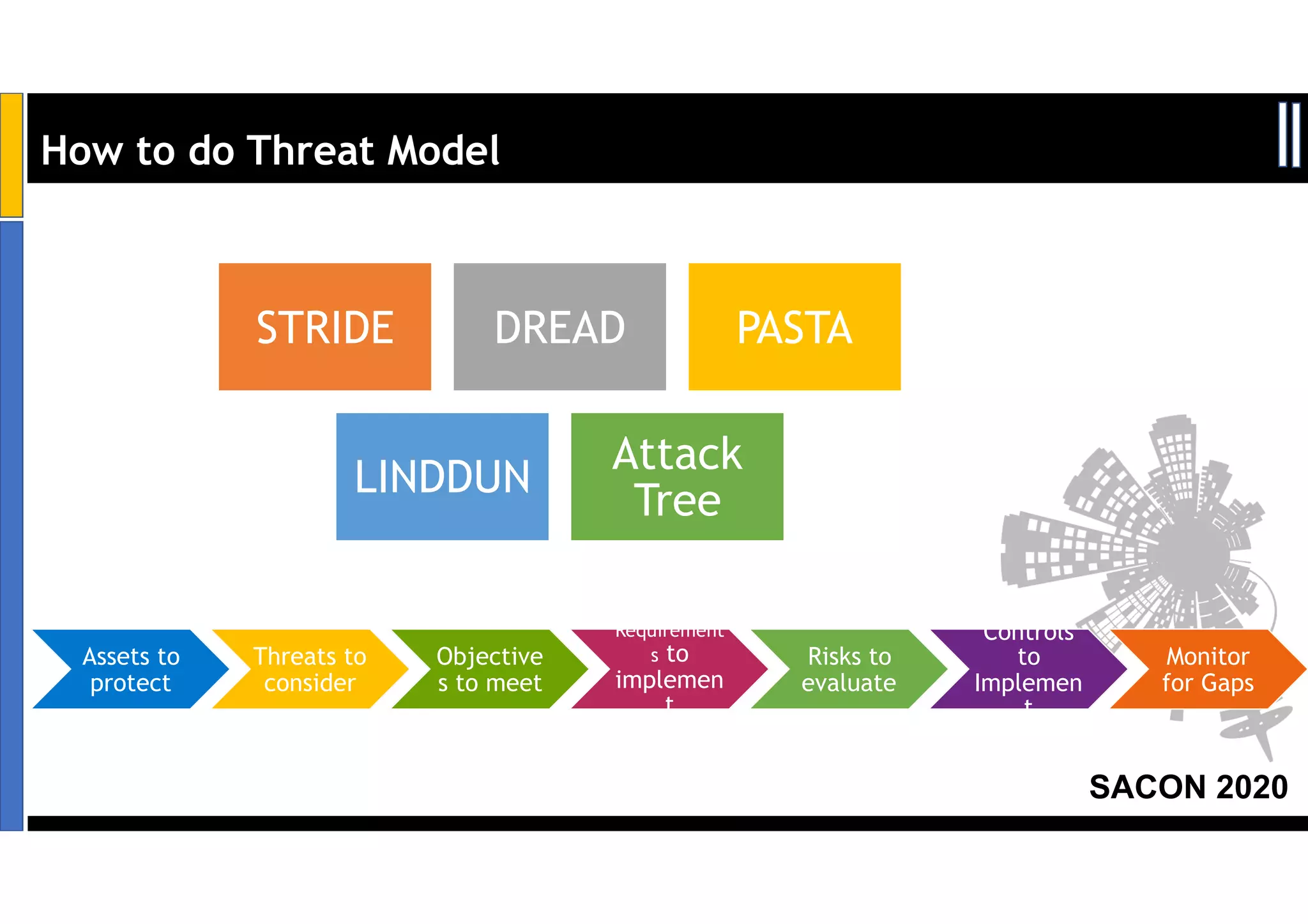
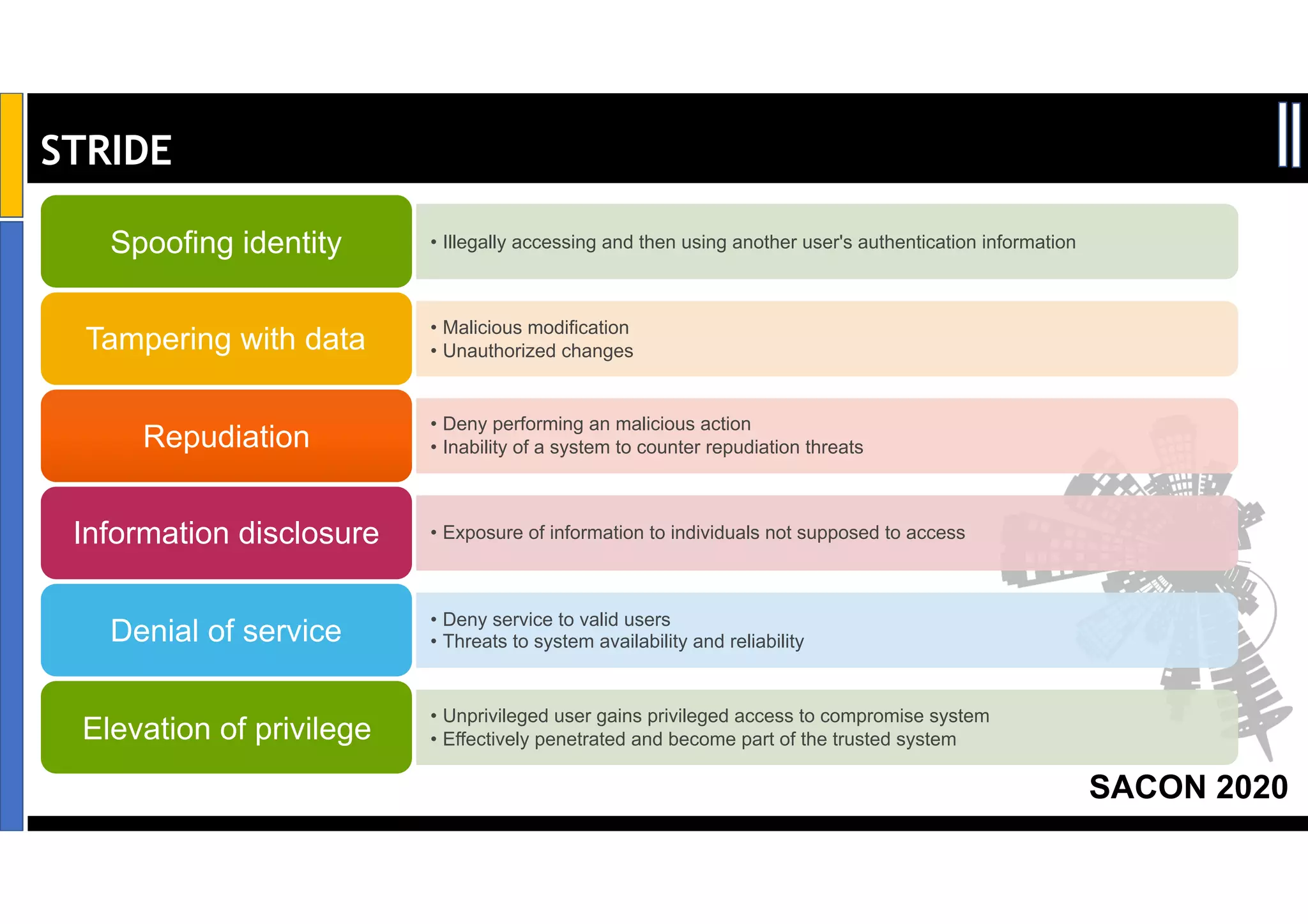
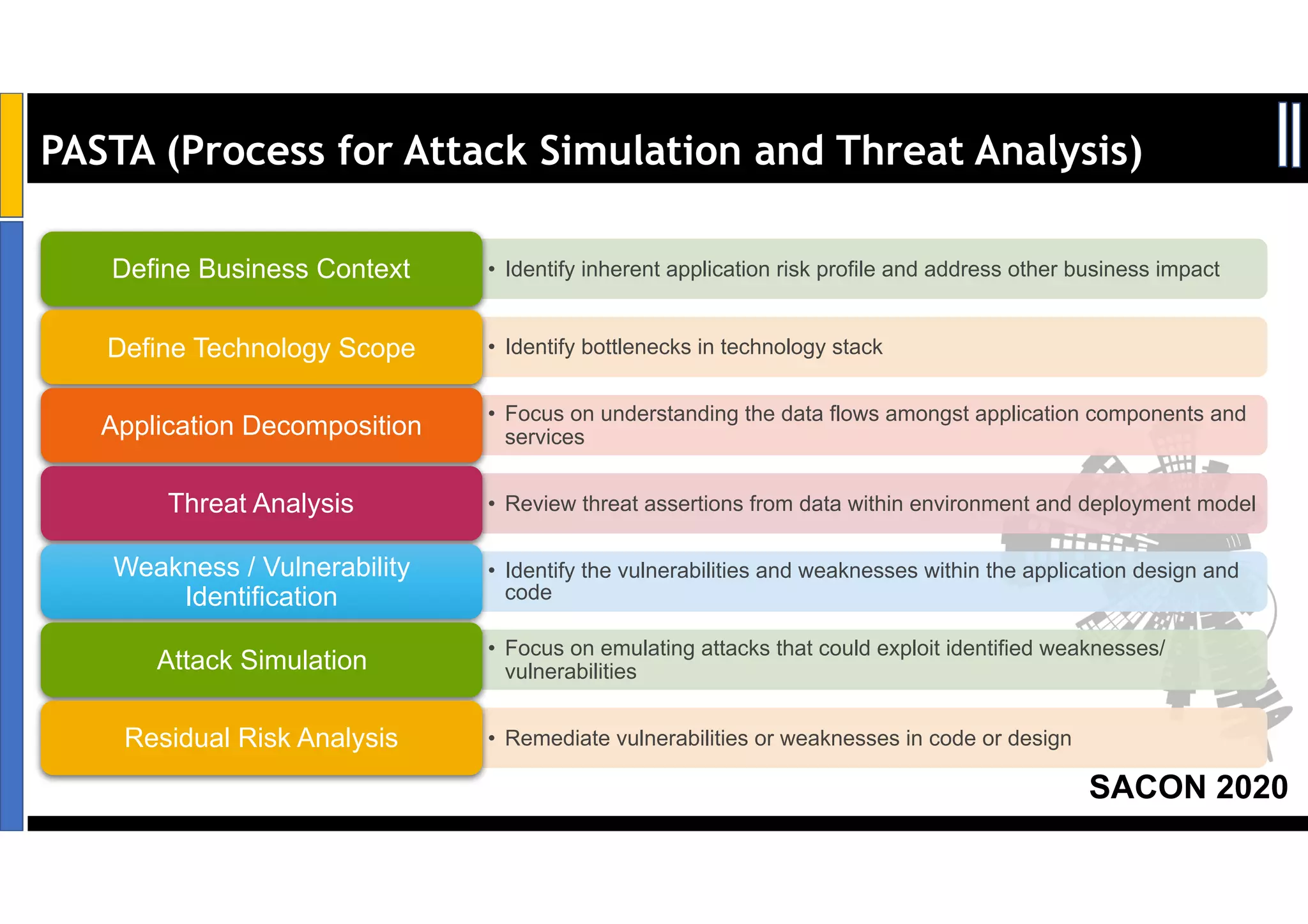
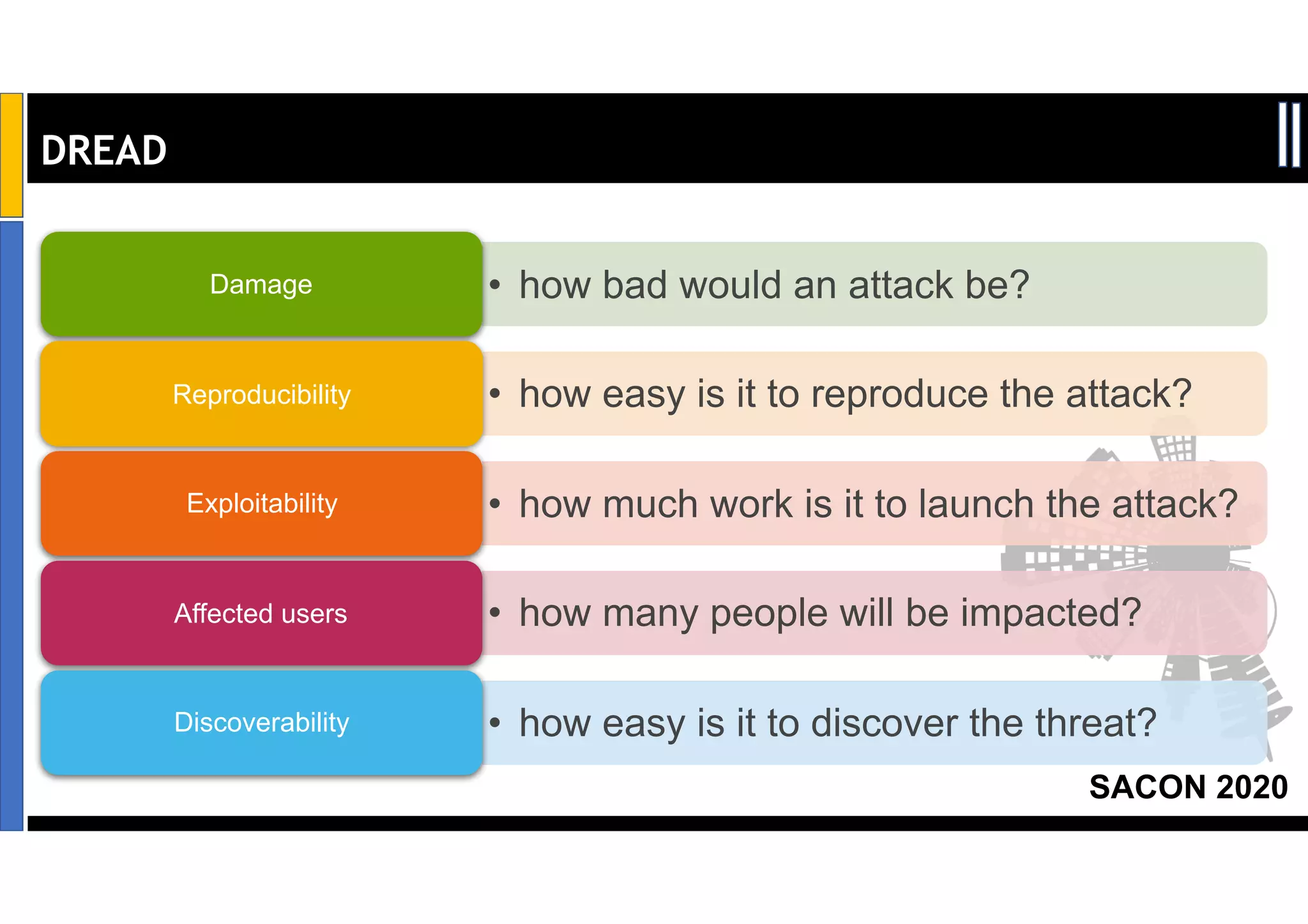
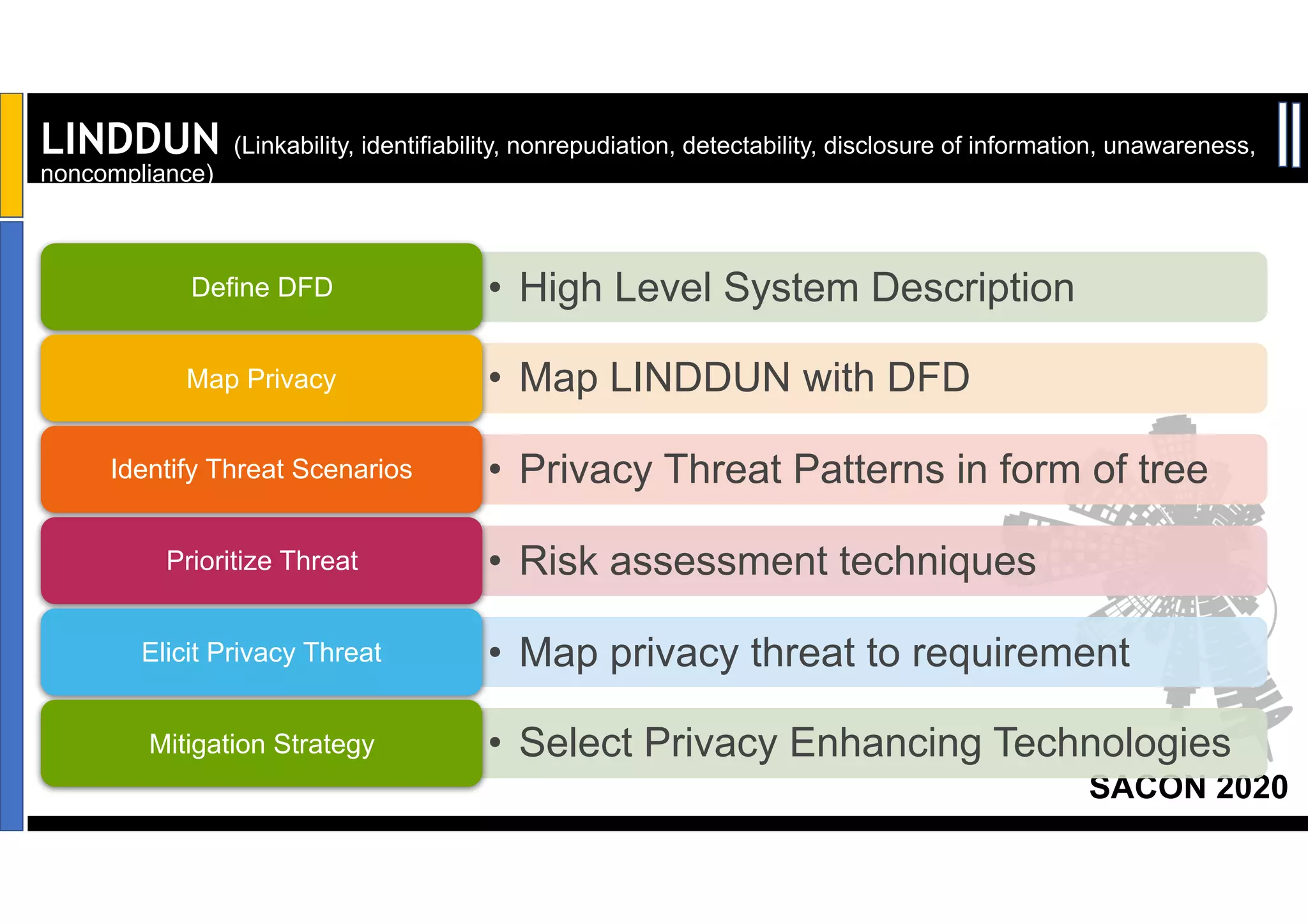
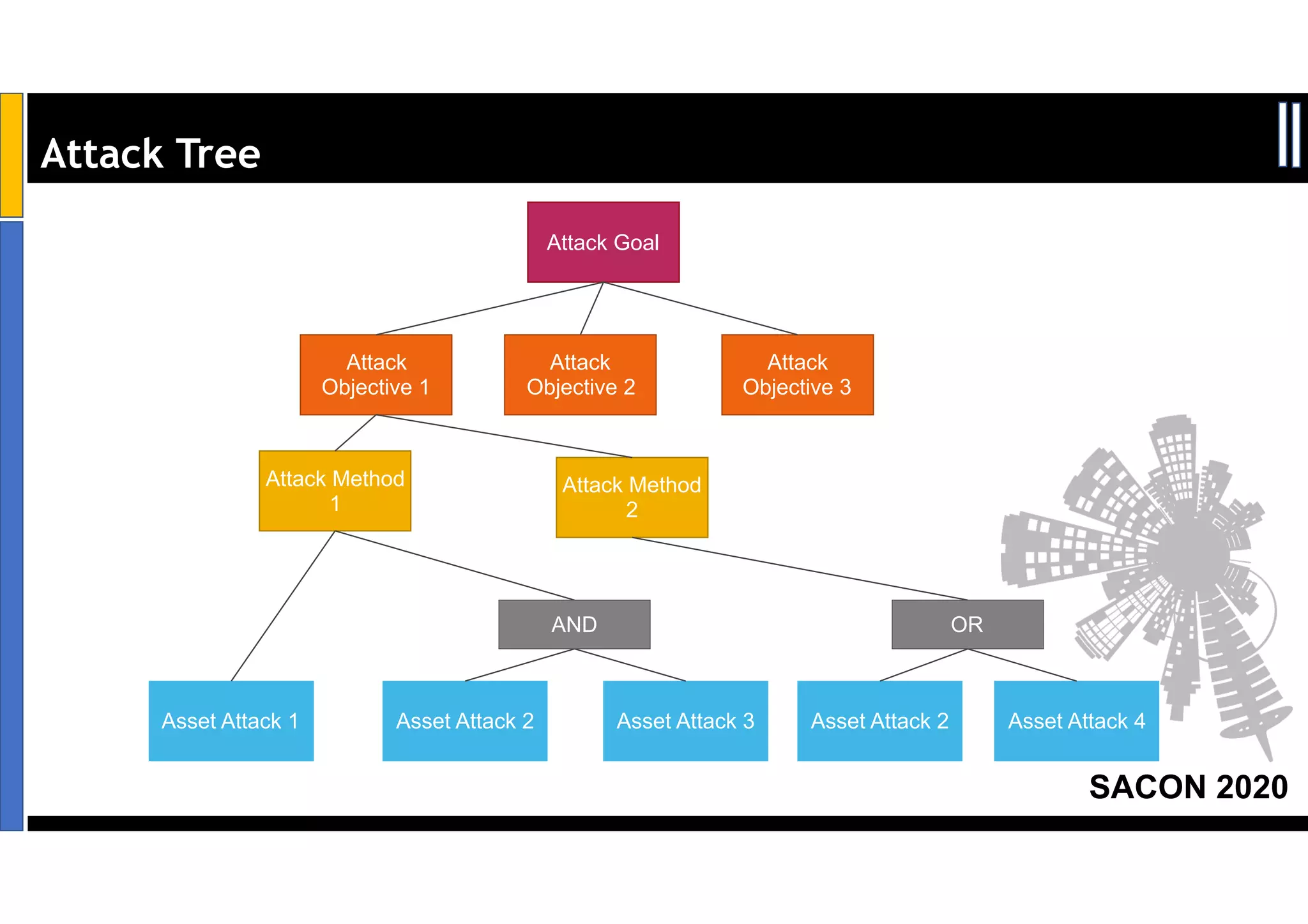
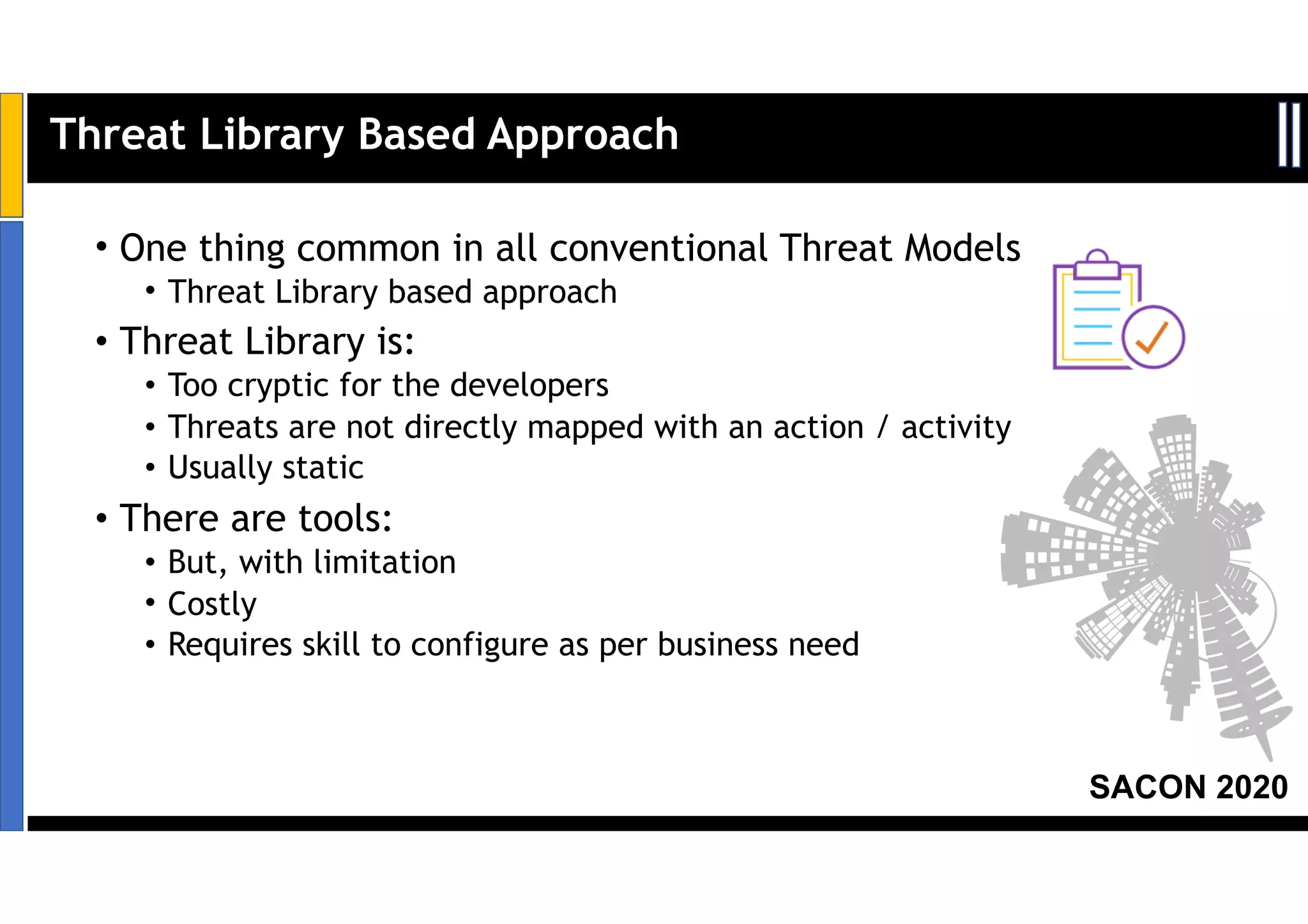
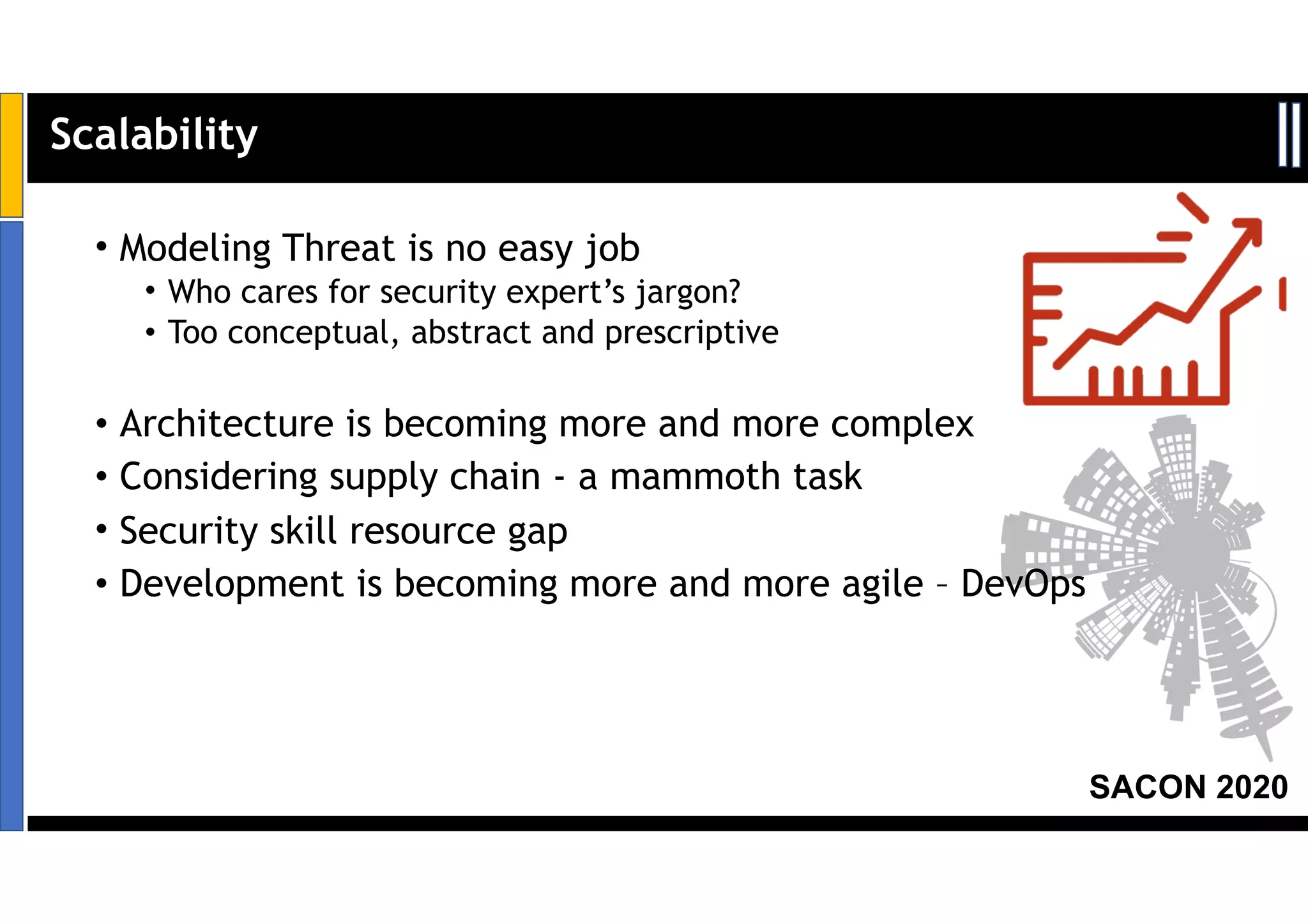
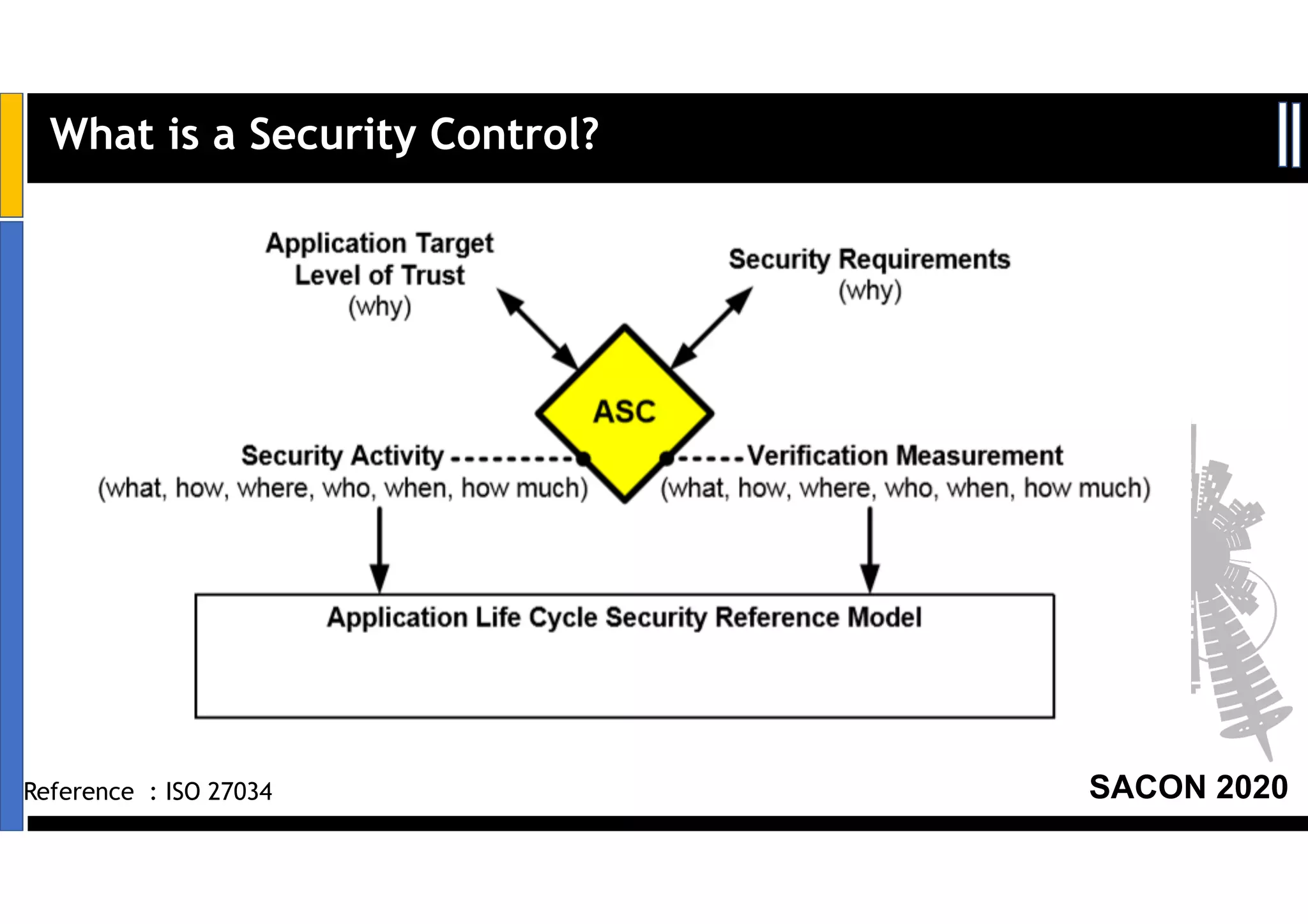
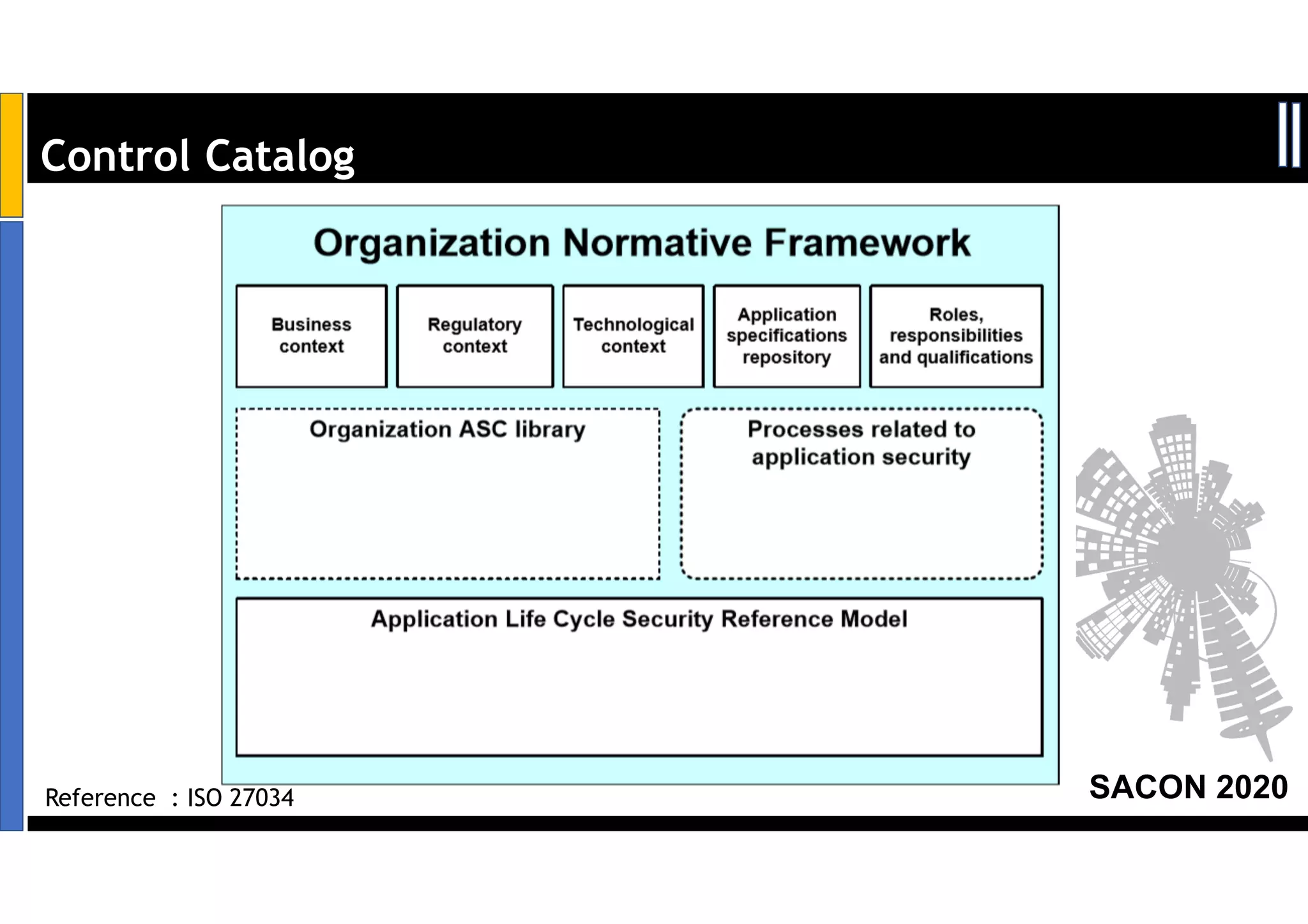
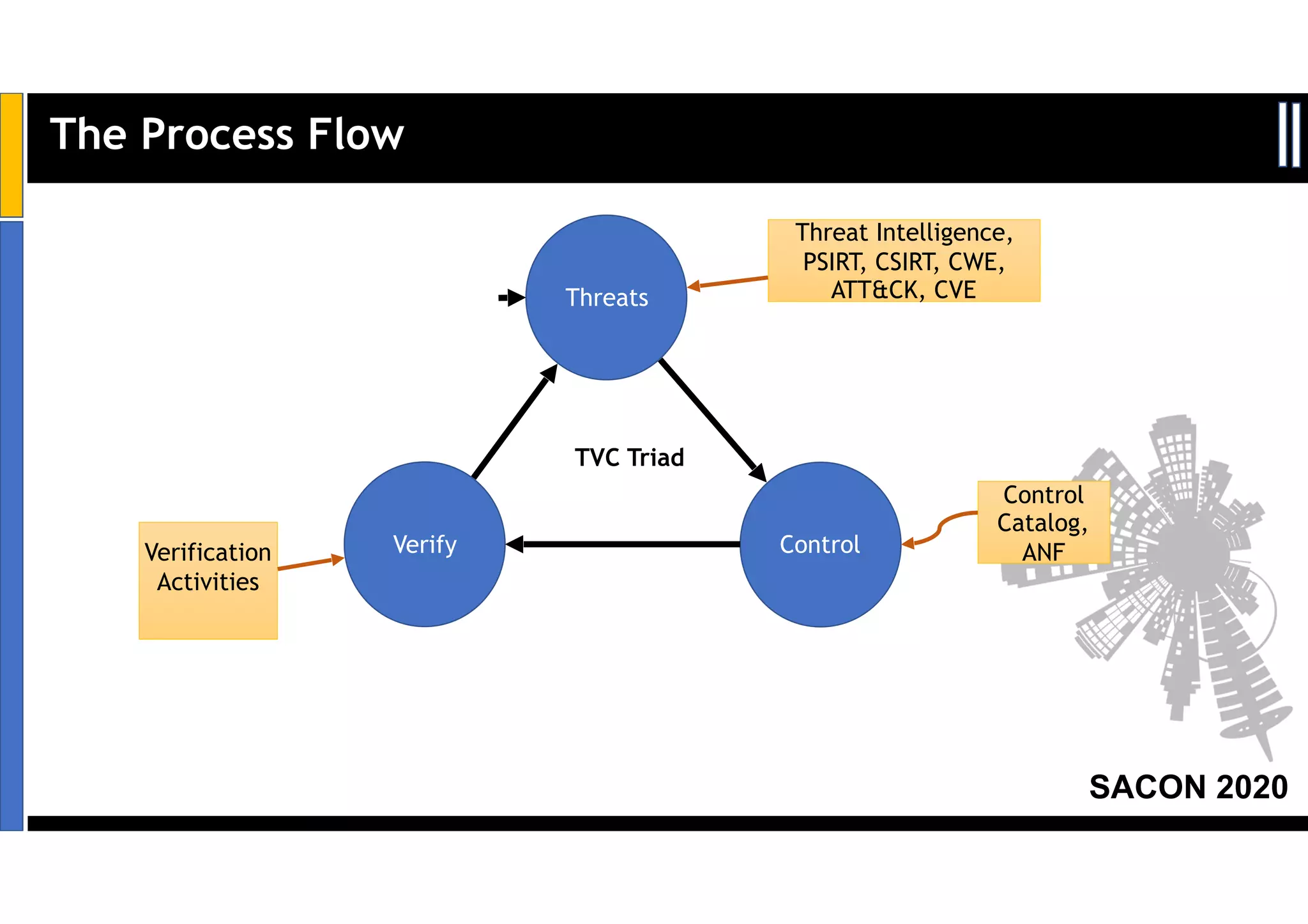
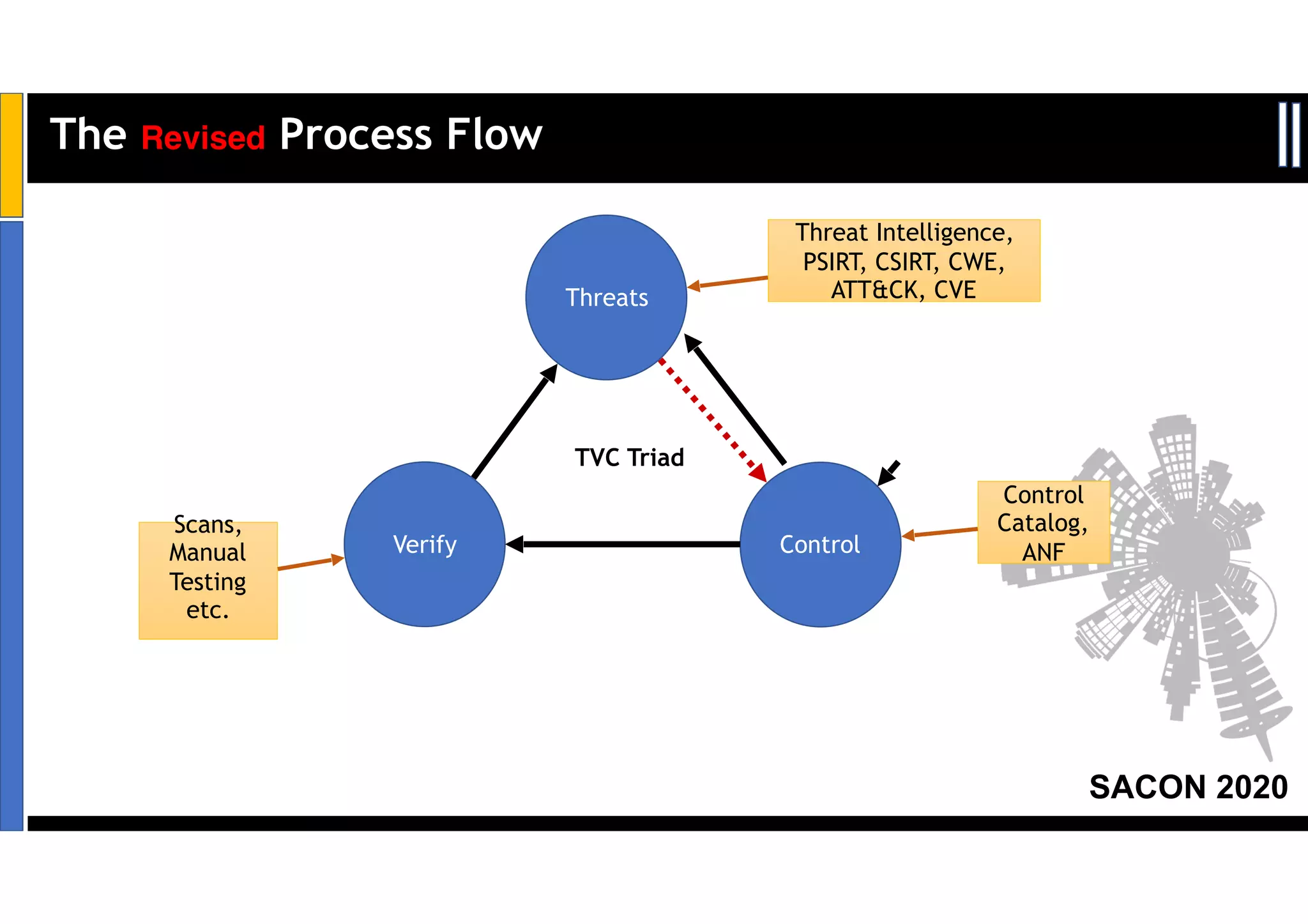
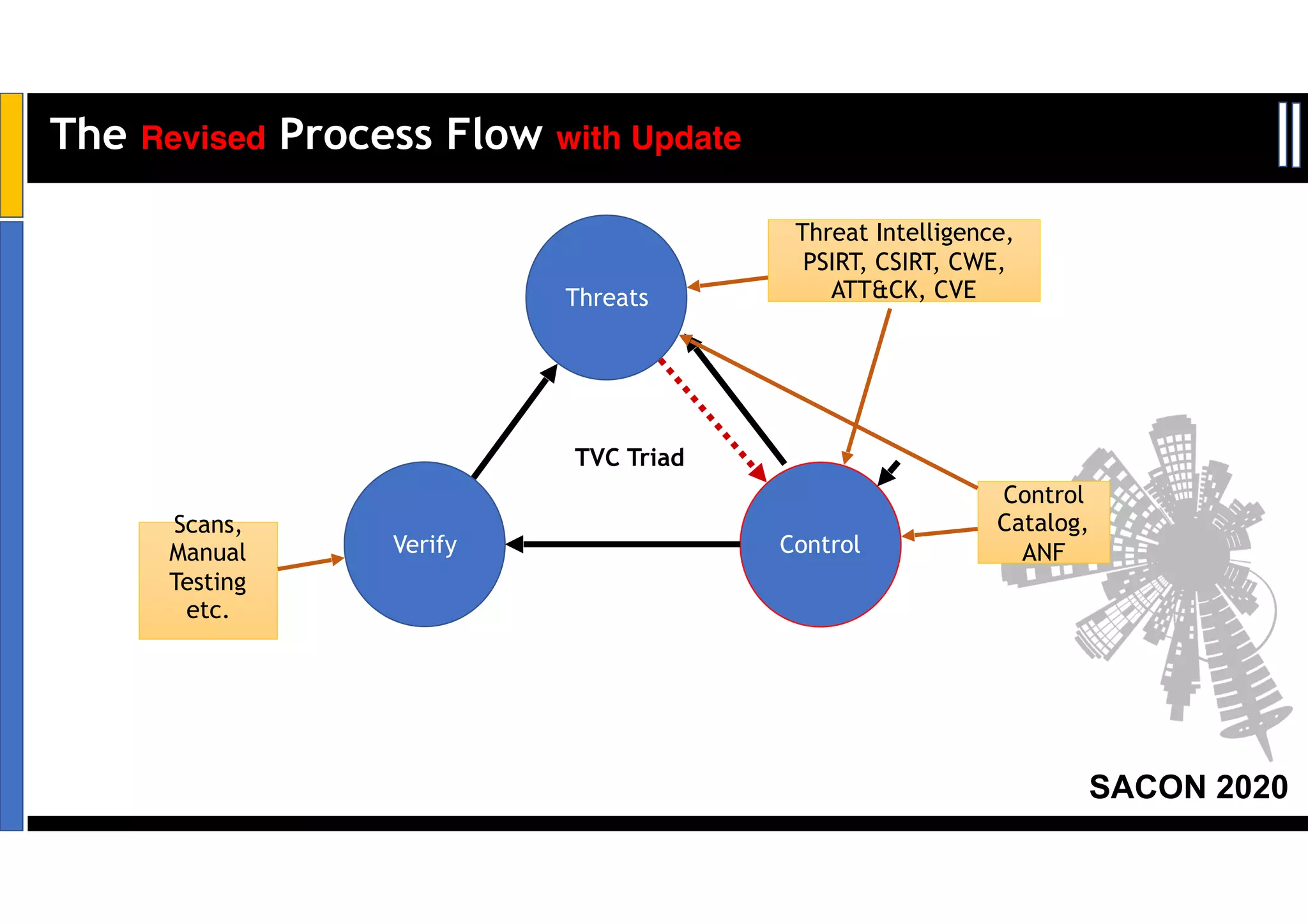
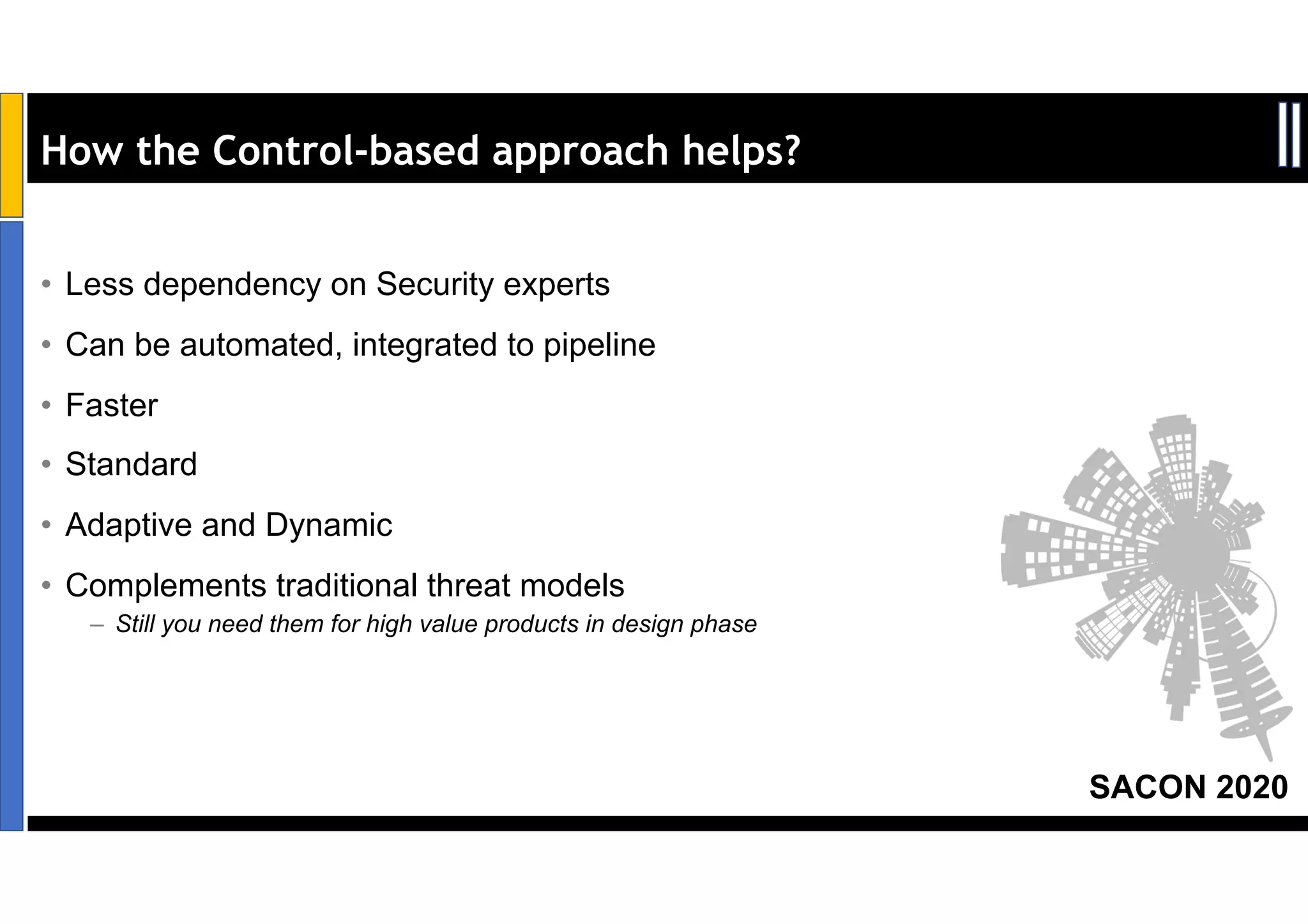
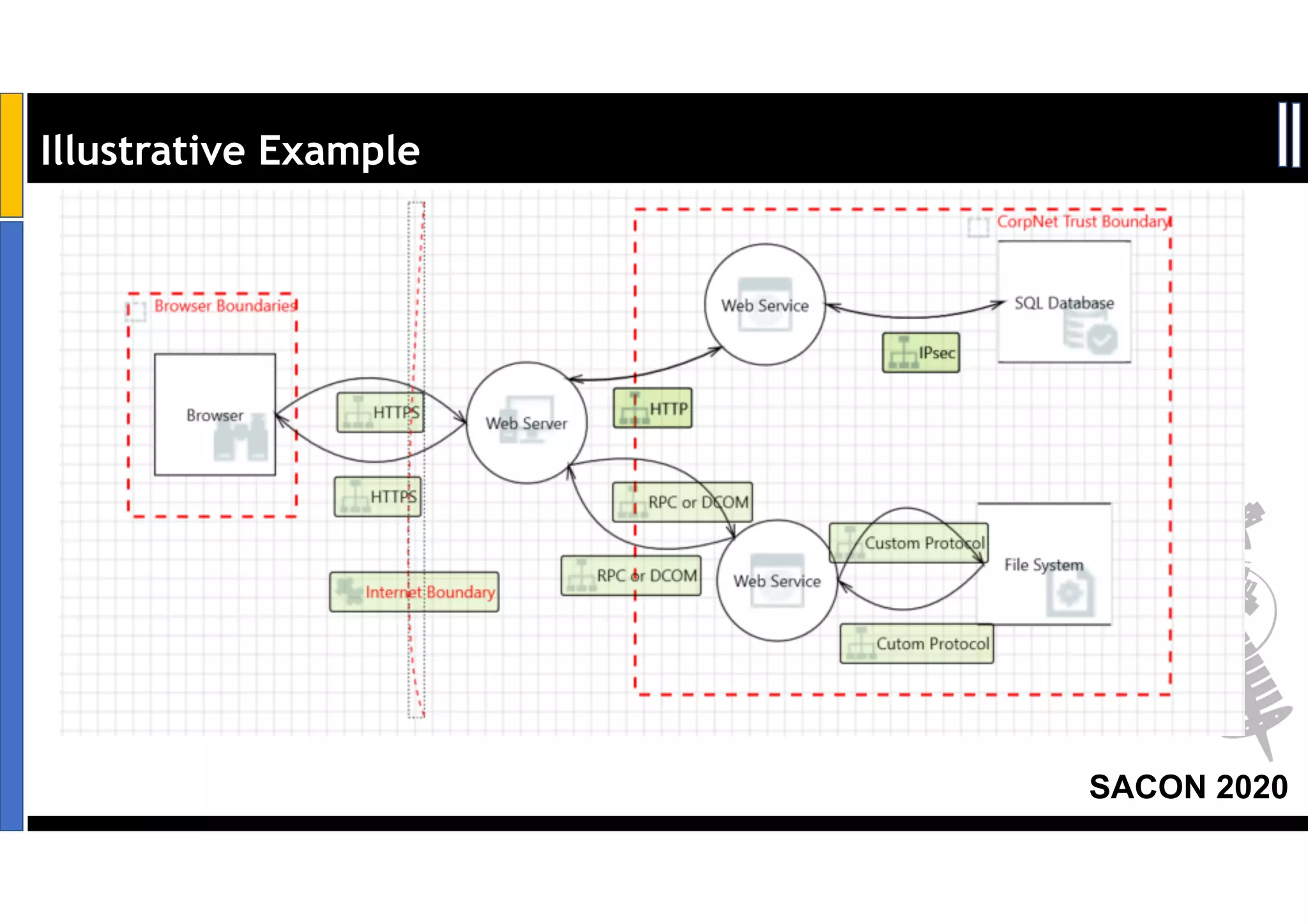
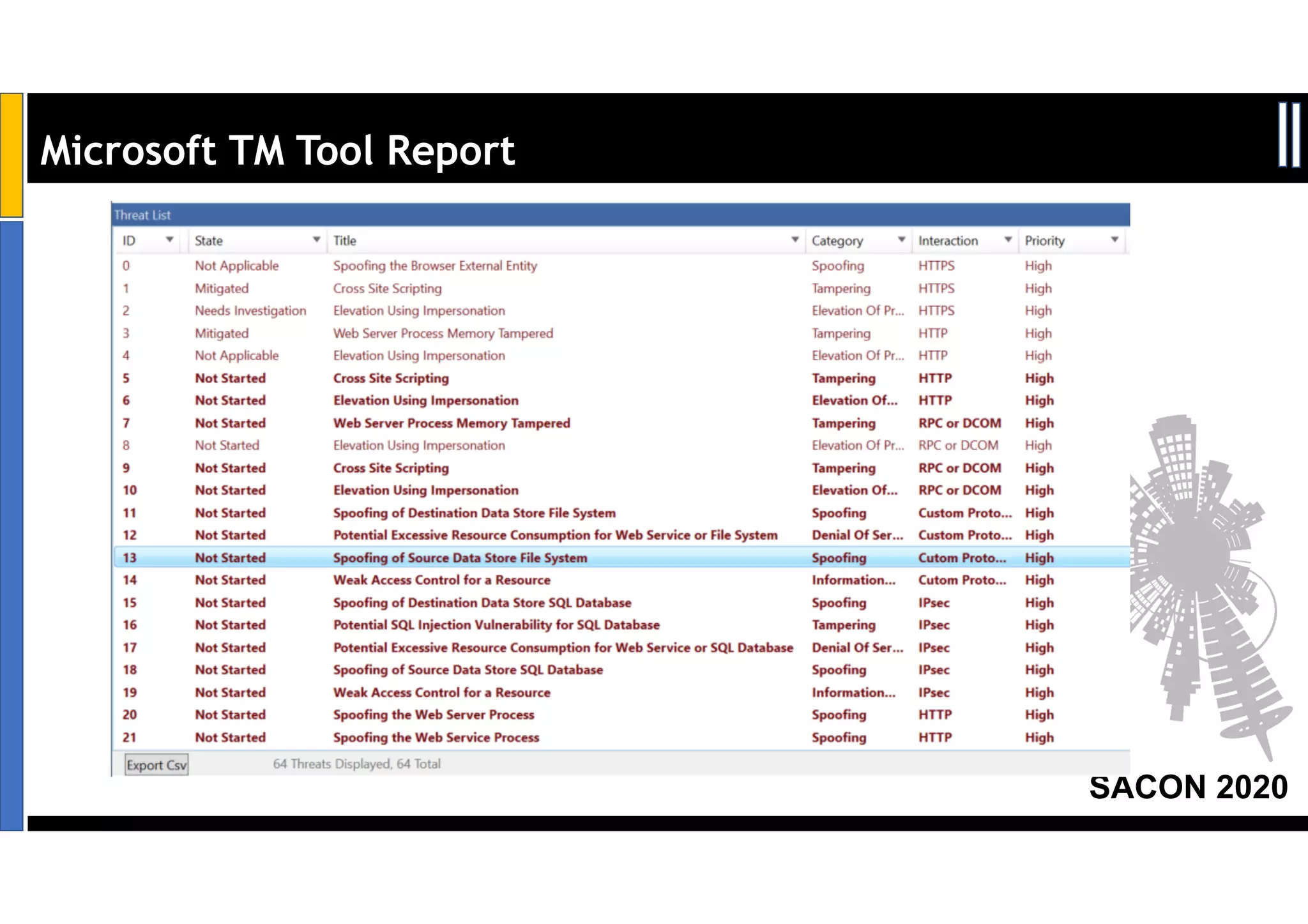
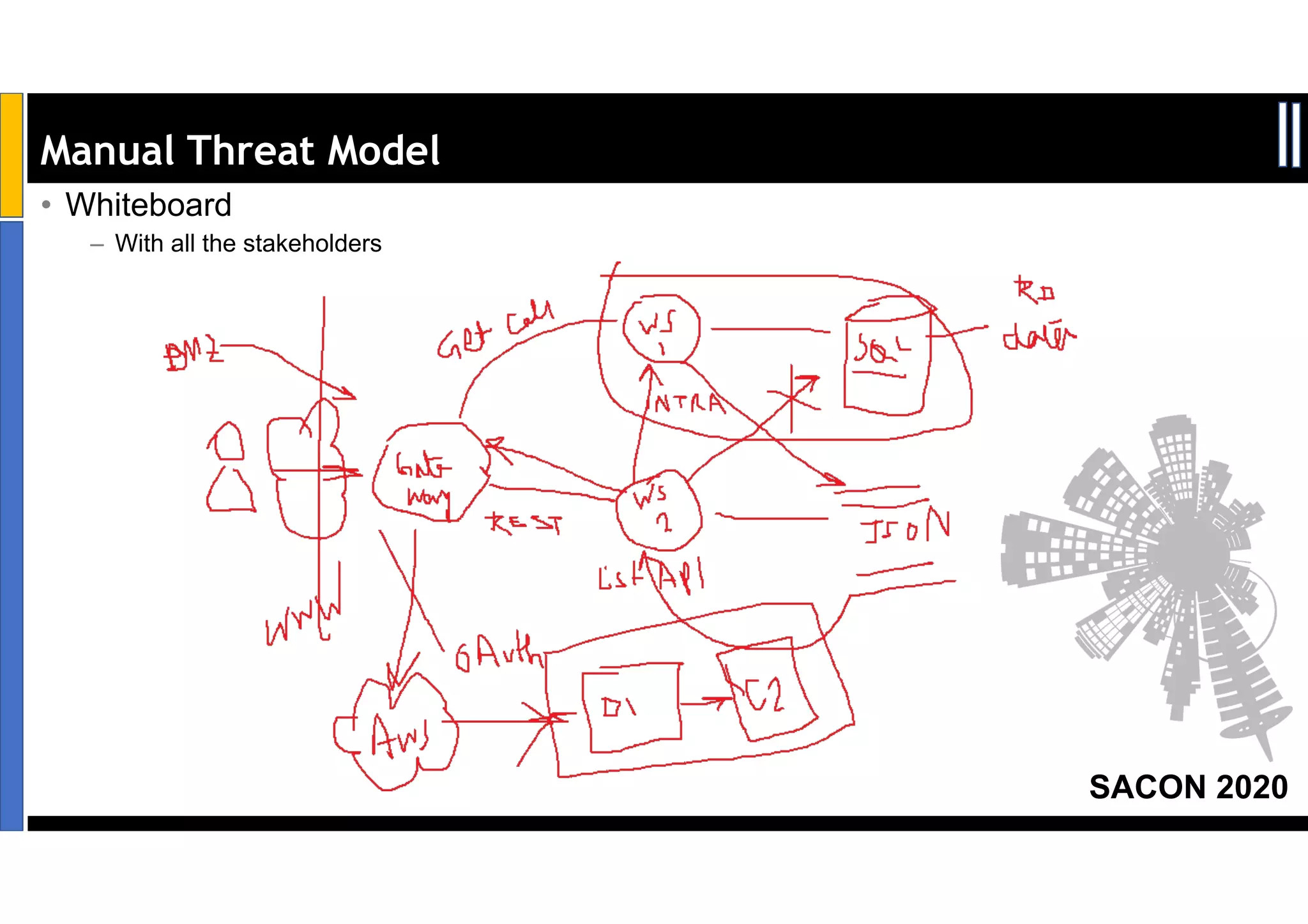
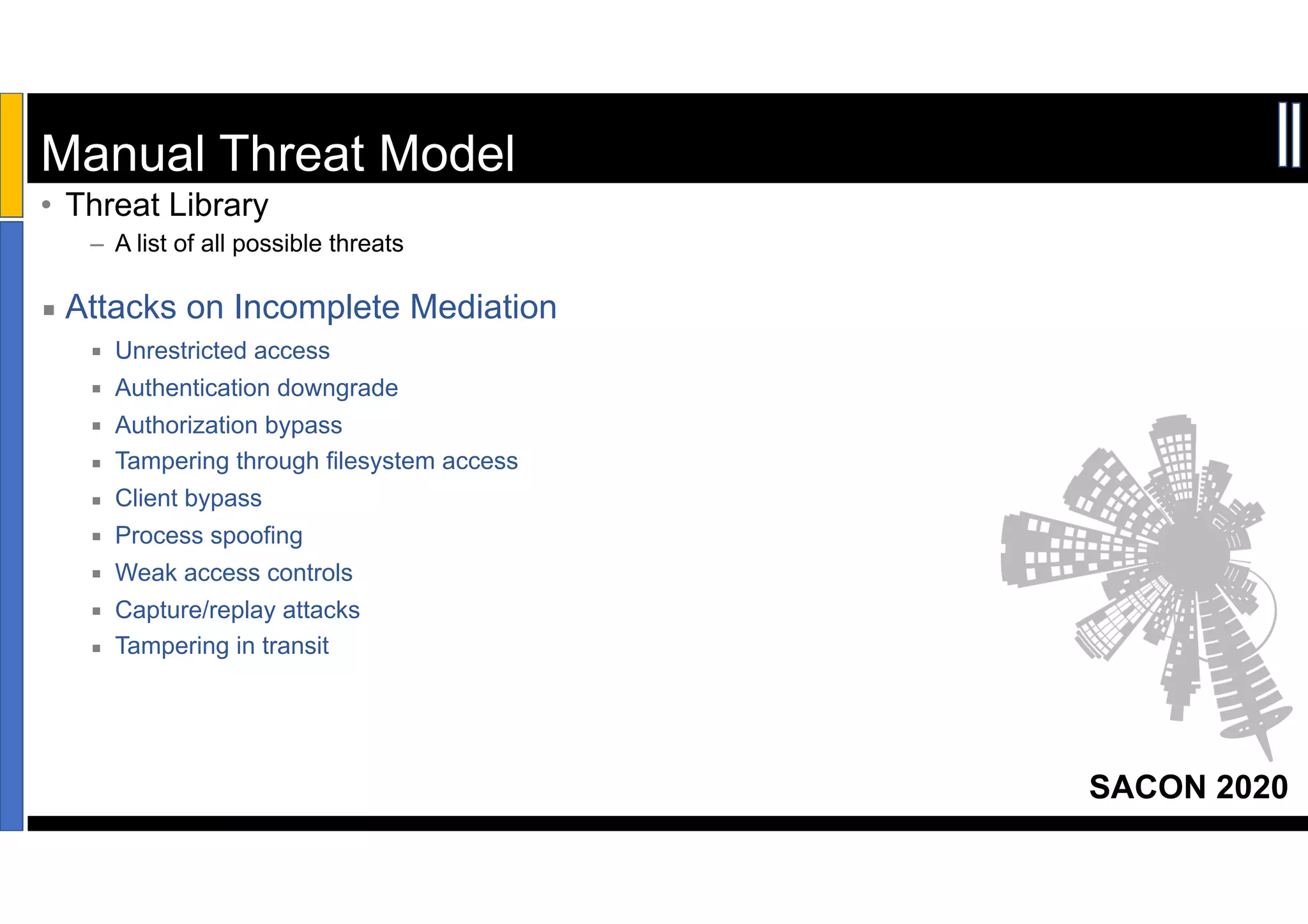
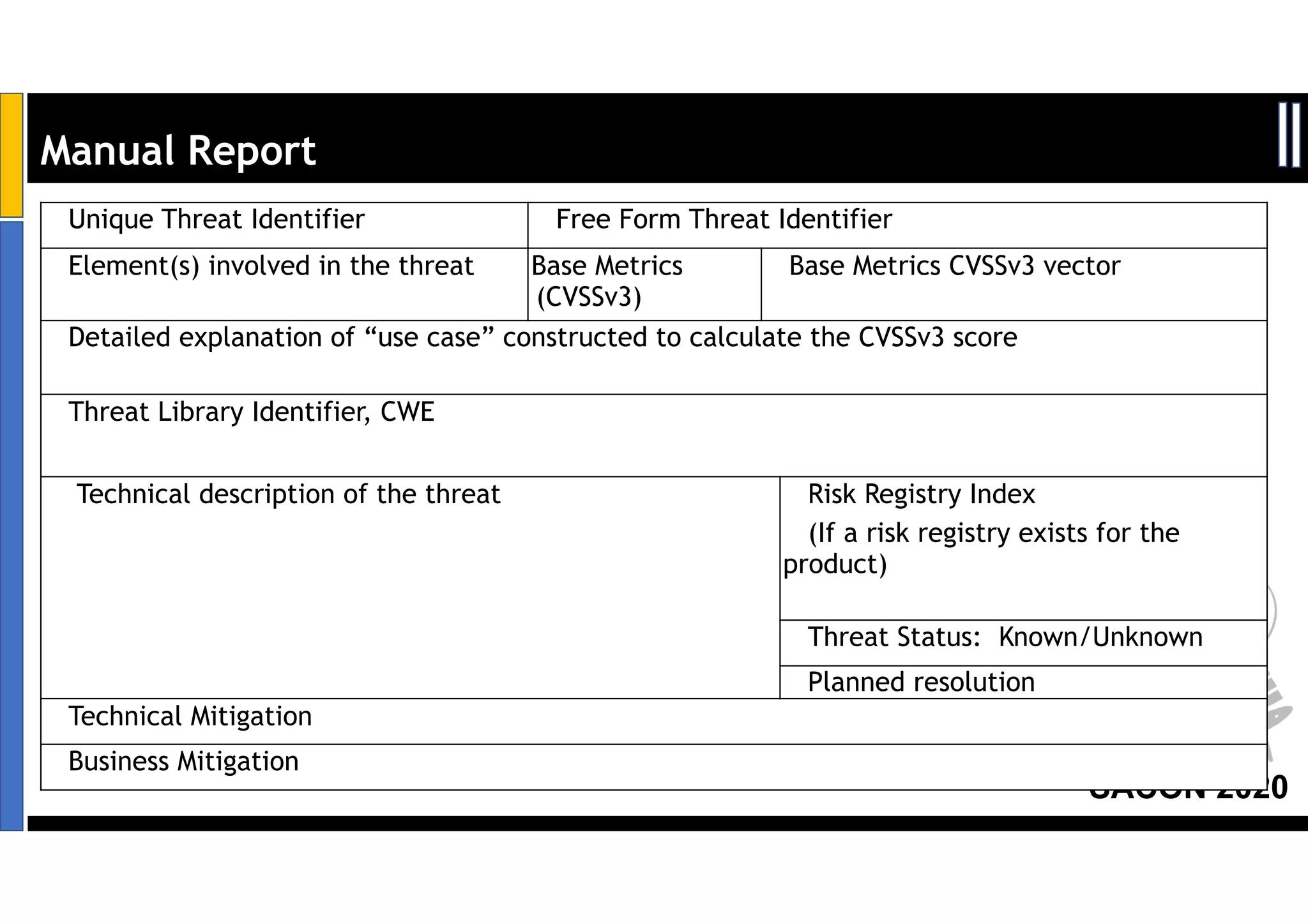
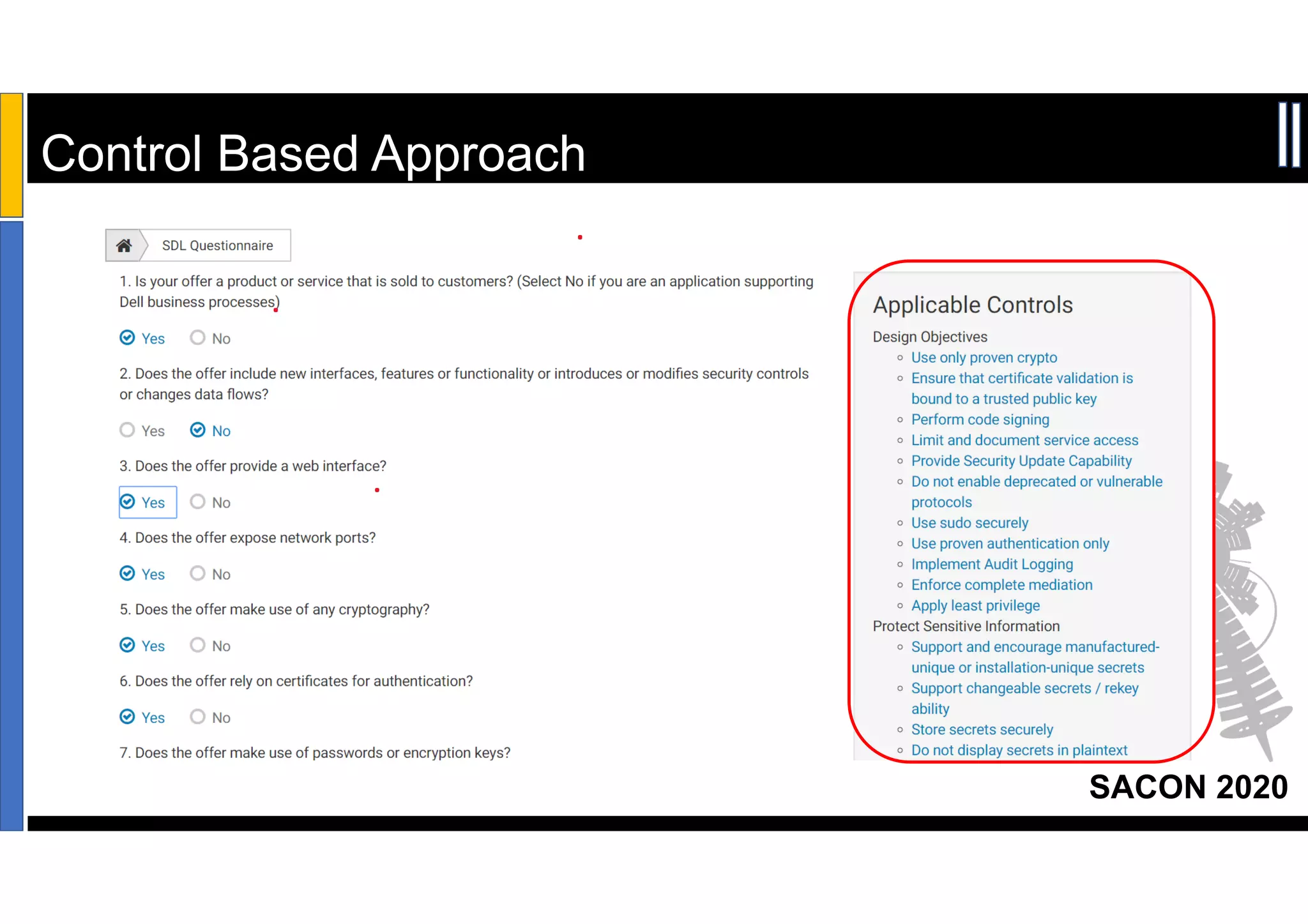
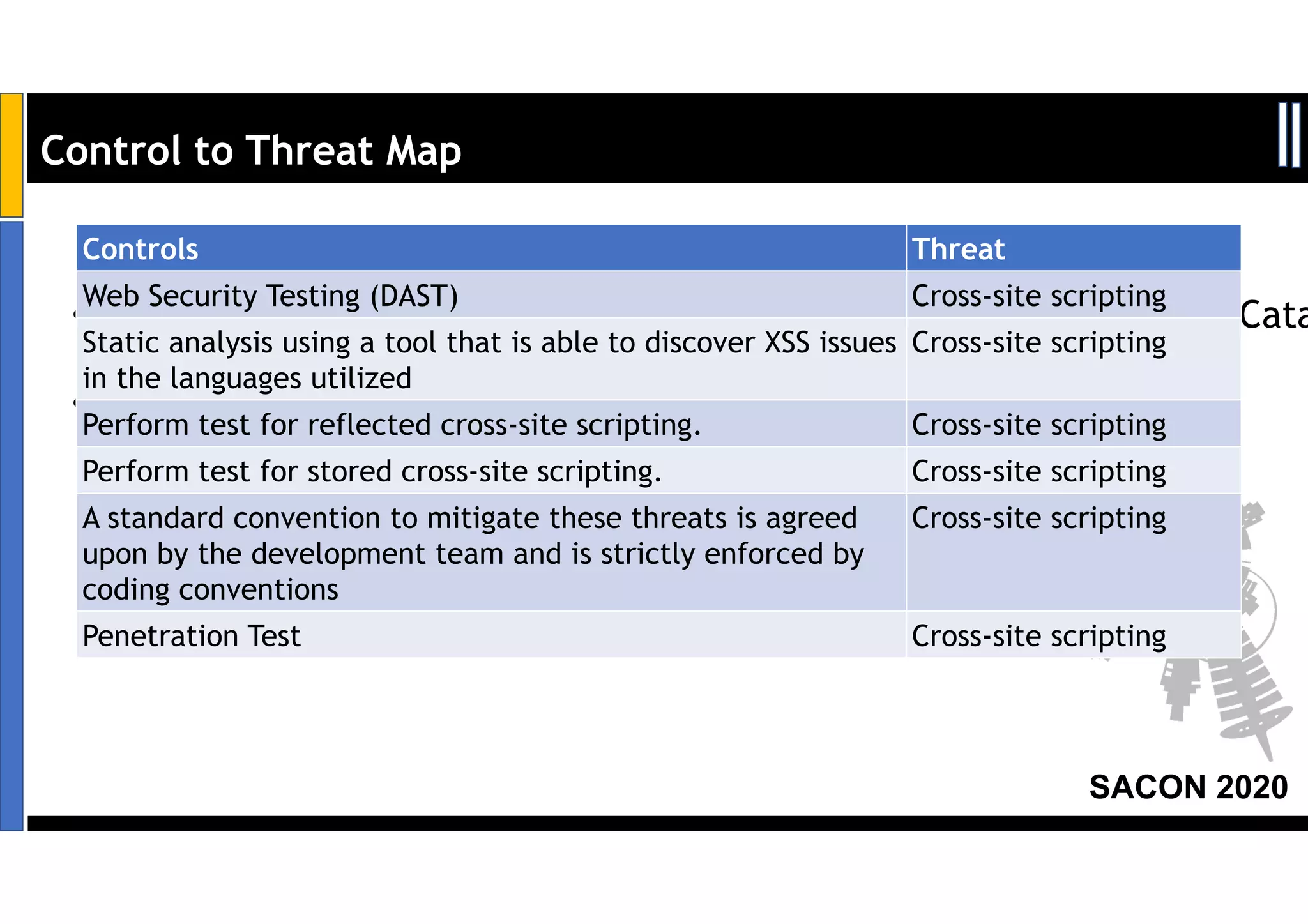
Dr. Soumyo Maity and Lokesh Balu from Dell Technologies presented a new control-based approach to threat modeling at SACON 2020 in Bangalore, India. Their approach maps threats identified through traditional techniques like STRIDE directly to security controls. This makes threat modeling more scalable, developer-centric, and integrated with the software development lifecycle. A case study demonstrated how identifying threats based on failed security controls can complement traditional threat modeling. The control-based approach was presented as an effective way to address challenges of complexity, resources, and agility in modern software development.