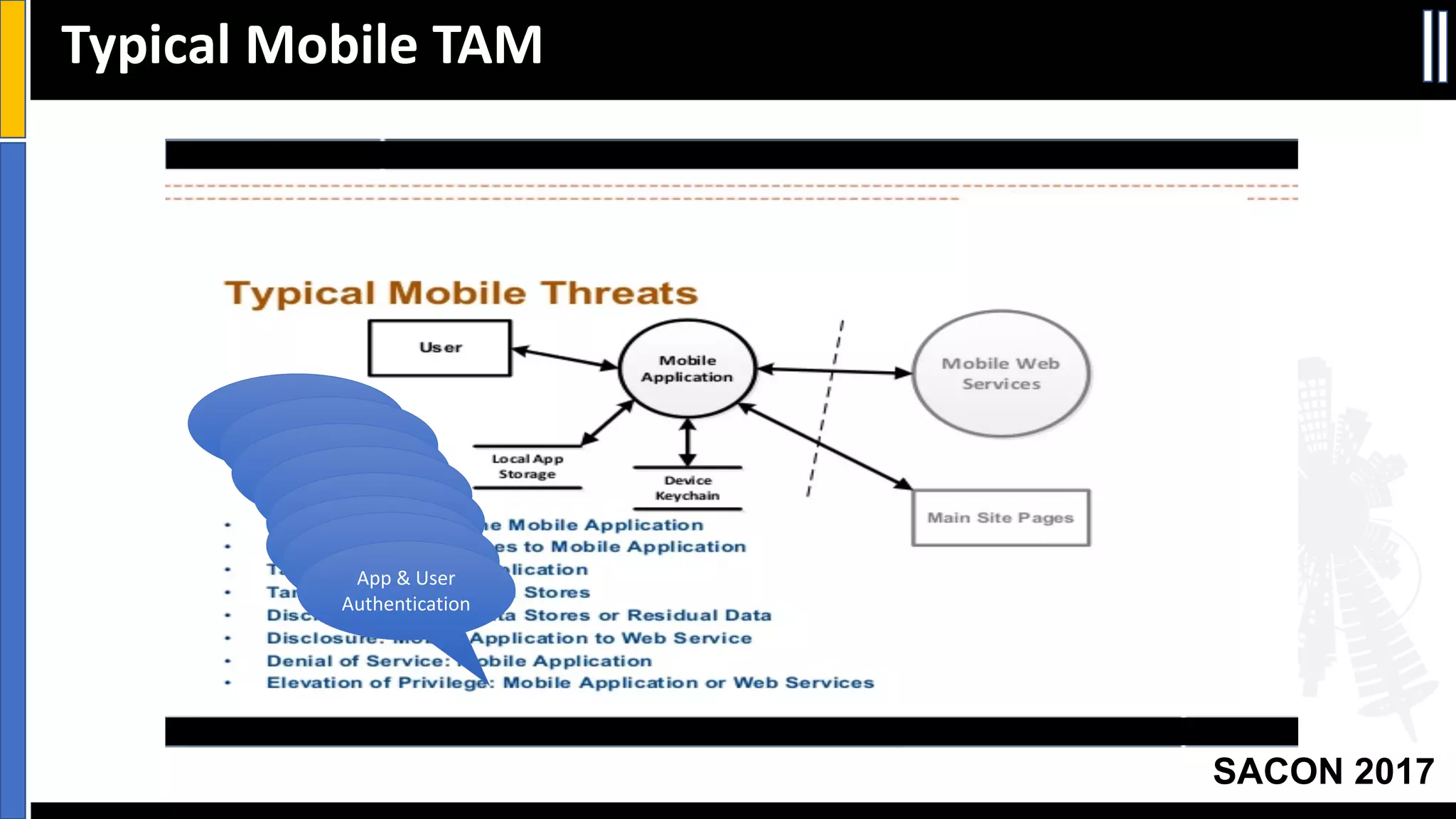
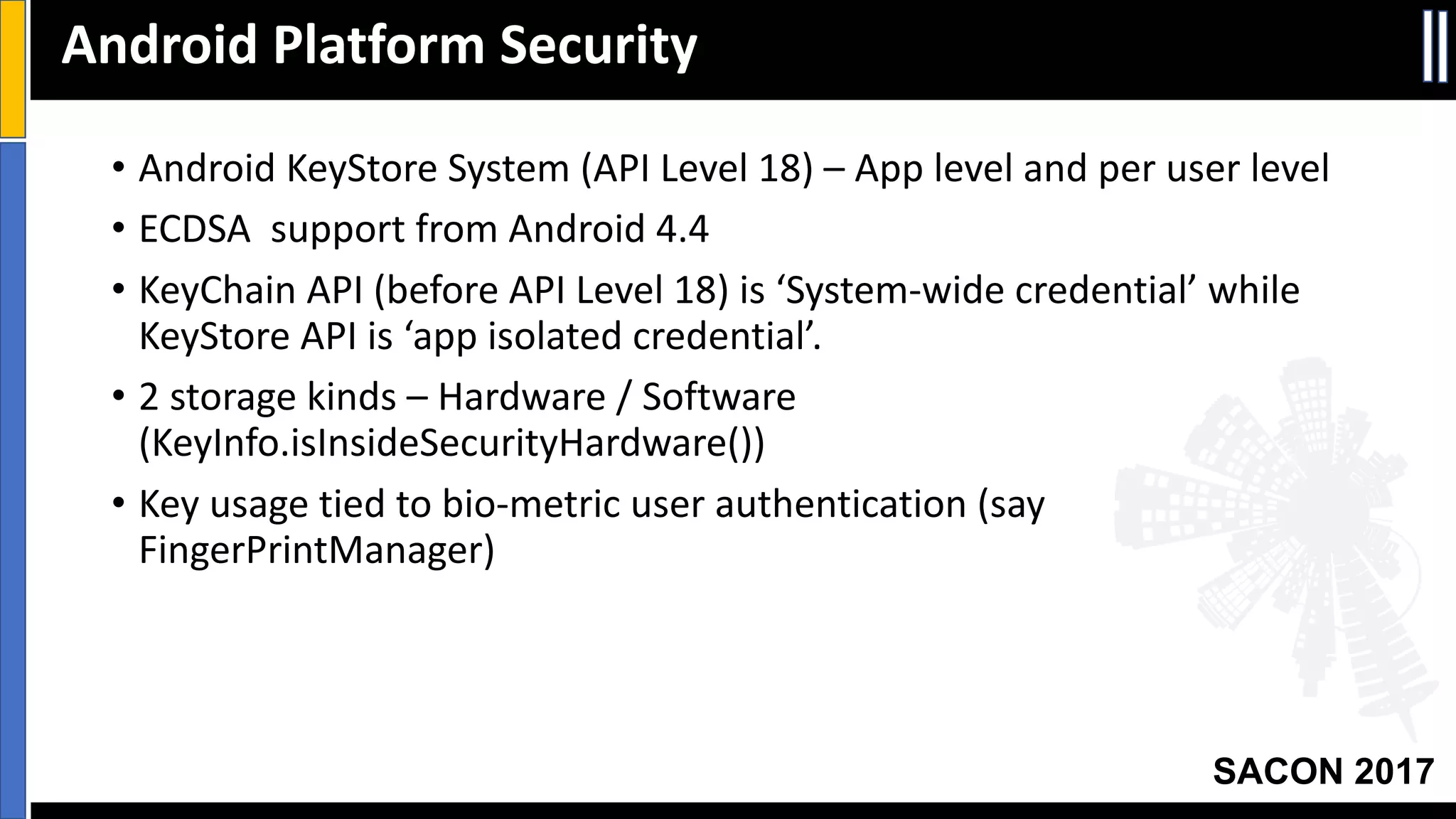
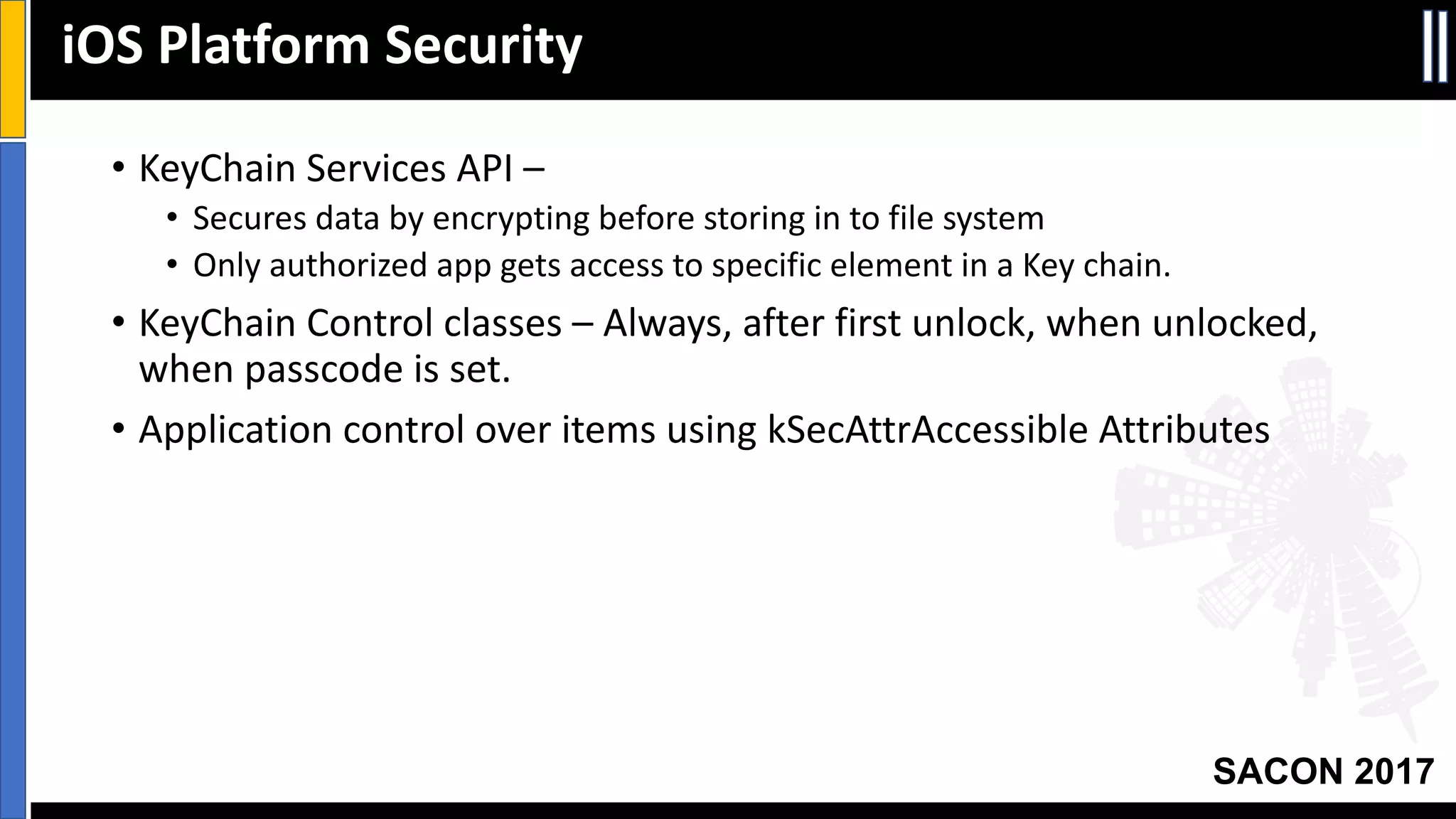
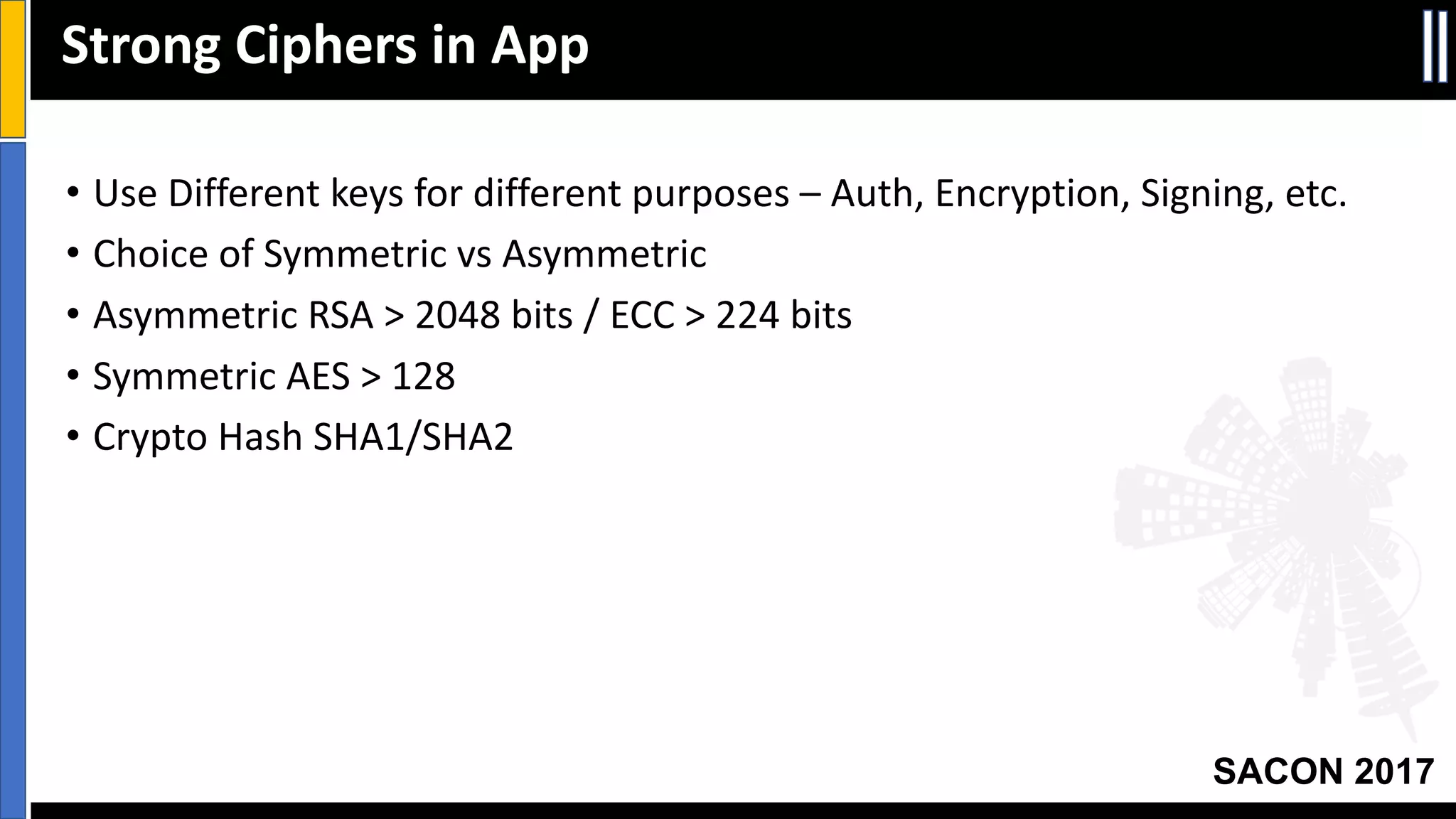
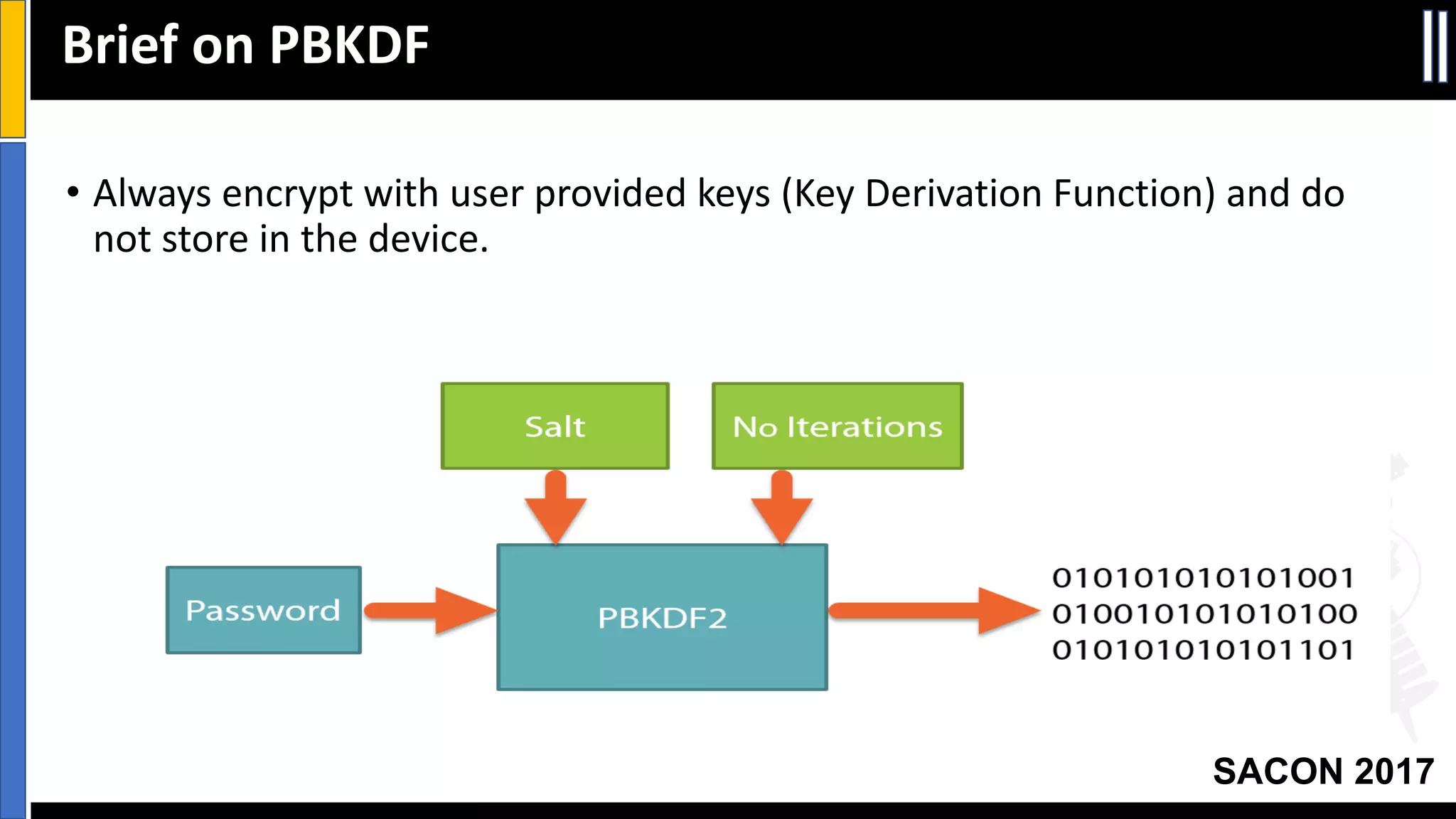
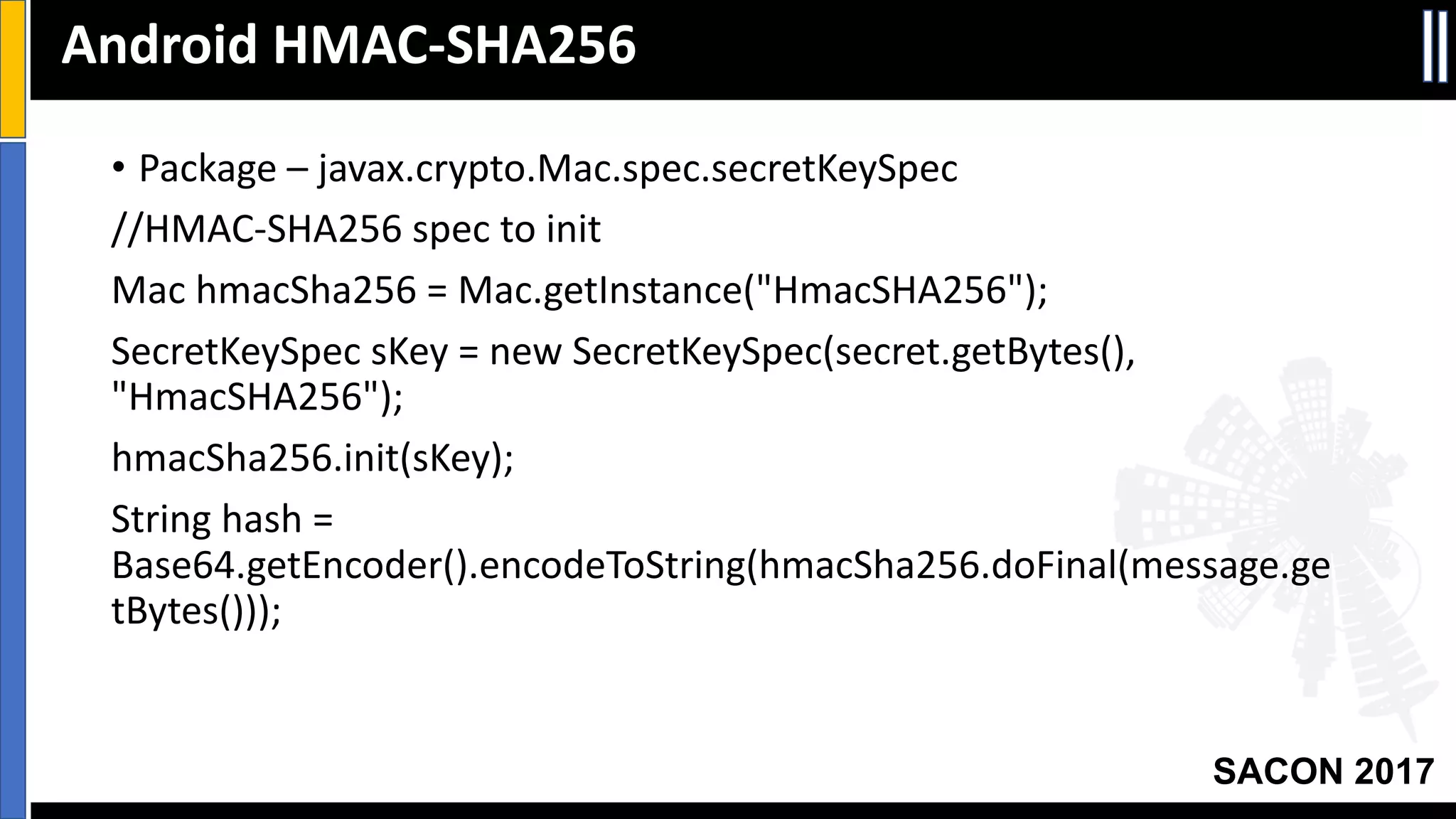
The document outlines best practices for mobile app security including data protection, authentication, and app protection on Android and iOS platforms. It discusses challenges around encrypting data at rest and in transit, authenticating users and devices, and protecting apps from tampering. It provides examples of implementing cryptography, hashing, certificate pinning and PRNG on both platforms. The presentation recommends focusing on security early in development and rigorous code reviews of sensitive areas.















![Your Slide Title
SACON 2017
/* Init SecureRandom
Code snippet as part of Non Deterministic salt generation
*/
…
SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom();
byte[] salt = new byte[saltLength];
random.nextBytes(salt);
…
PRNG Android](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mobileappsecurityv1-171113125901/75/SACON-Mobile-App-Security-Srinath-Venkataramani-23-2048.jpg)







