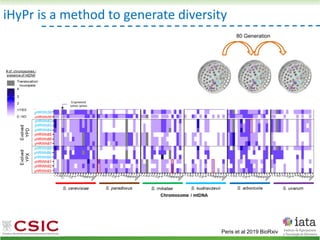
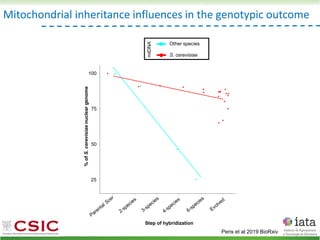
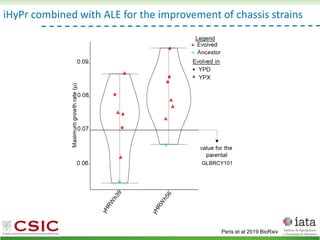
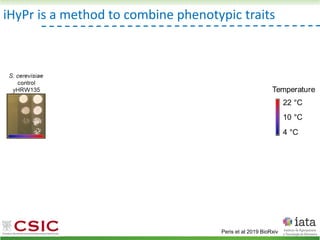
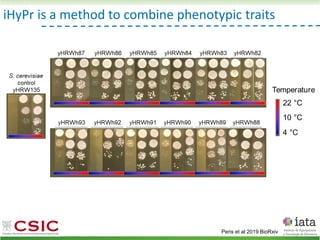
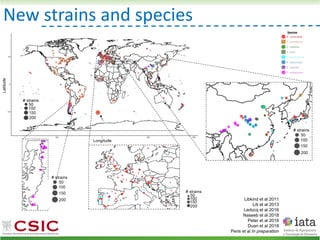
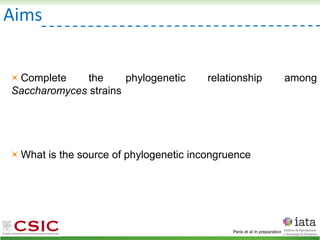
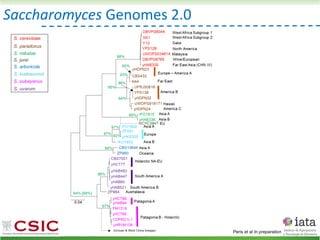
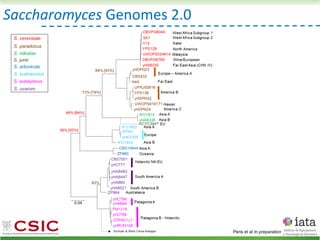
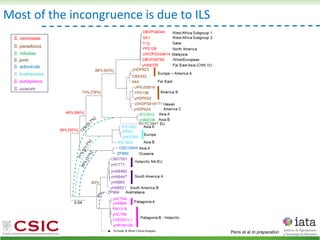
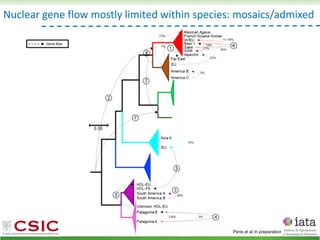
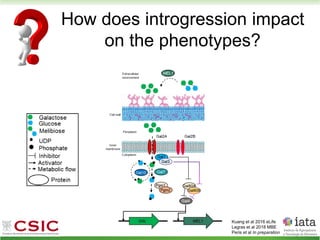
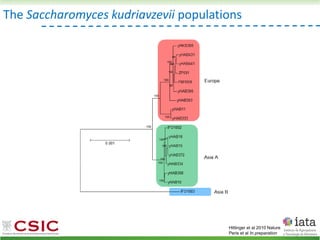
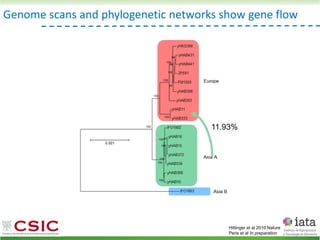
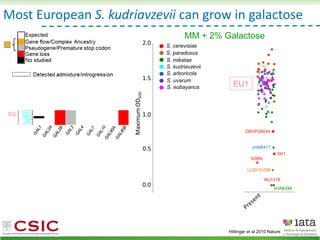
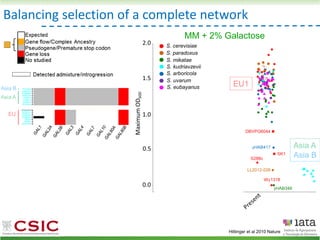
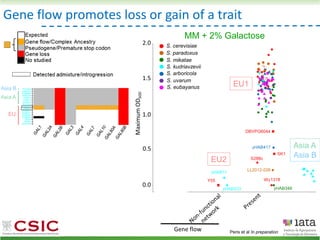
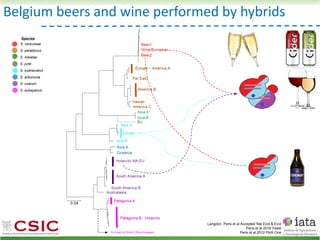
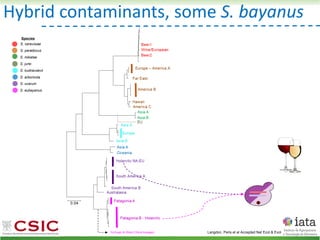
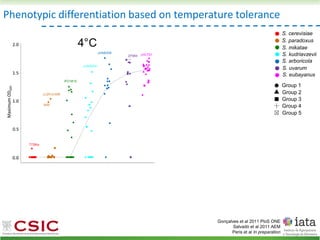
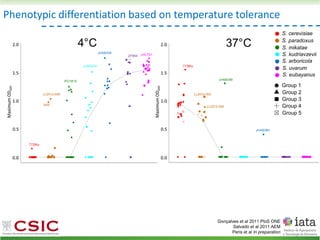
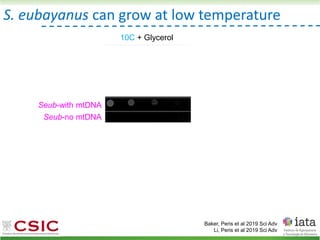
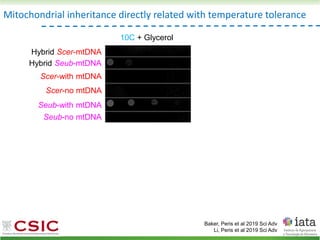
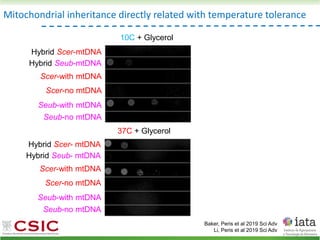
This document summarizes research on reticulate evolution in yeasts and its industrial applications. Reticulate evolution refers to evolution occurring through hybridization and introgression rather than strictly vertical descent. The document discusses how hybridization has contributed to the diversification and domestication of yeasts like Saccharomyces cerevisiae. It also explores how mining genomic diversity through hybridization could enable new industrial applications, such as developing yeast strains capable of growth at lower temperatures or utilizing additional carbon sources.

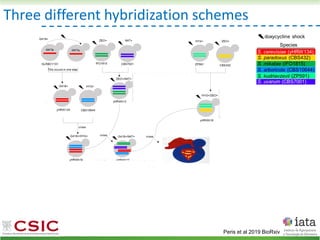
![HyPr: frequent mating
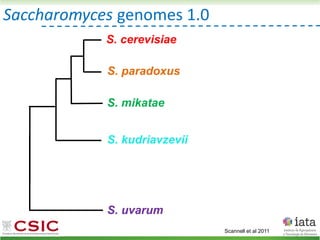
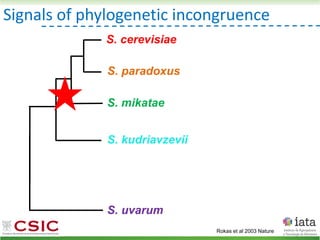
Alexander, Peris et al 2016
HyPr (Hybrid Production) plasmid
doxycycline
shock
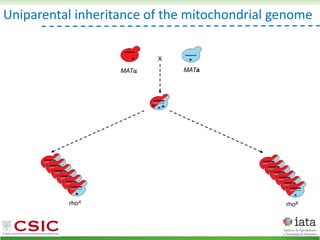
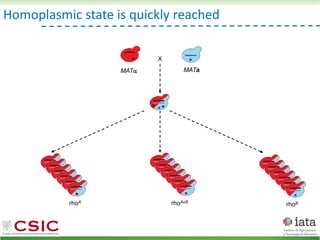
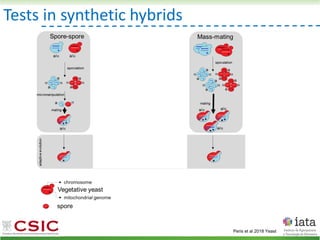
Vegetative yeast
mitochondrial genome
chromosome
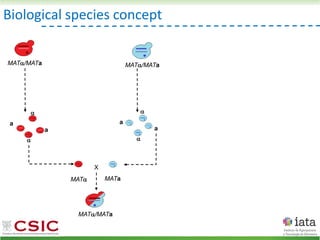
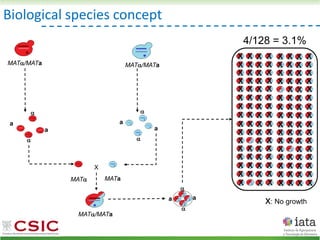
diploid
a/ a/
[pHMK34-HygMX]
[pHCT2-NatMX]
x
a/a /
a/a//
a/a//
Selection in media
with NAT+HYG
Remove selection for HYG
Check loss of NAT plasmid
>4G
Pre-culture
with NAT
Pre-culture
with HYG](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embocompgenomicsdpv2-220831142846-401857a5/85/Reticulate-evolution-in-yeasts-and-its-industrial-applications-42-320.jpg)


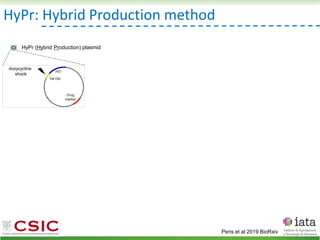
![iHyPr: iterative Hybrid Production method
Peris et al 2019 BioRxiv
HyPr (Hybrid Production) plasmid
doxycycline
shock
Vegetative yeast
mitochondrial genome
chromosome
diploid
a/ a/
[pHMK34-HygMX]
[pHCT2-NatMX]
x
a/a /
a/a//
Selection in media
with NAT+HYG
Pre-culture
with HYG
Pre-culture
with NAT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embocompgenomicsdpv2-220831142846-401857a5/85/Reticulate-evolution-in-yeasts-and-its-industrial-applications-55-320.jpg)
![iHyPr: iterative Hybrid Production method
Peris et al 2019 BioRxiv
HyPr (Hybrid Production) plasmid
doxycycline
shock
Vegetative yeast
mitochondrial genome
chromosome
diploid
Pre-culture
with ZEO
Pre-culture
with HYG
a/ a/
[pHMK34-HygMX]
[pHCT2-NatMX]
x
a/a /
a/a//
a/a/a/a
Selection in media
with NAT+HYG
>4G
a/
/
[pHRW32-ZeoMX]
x
Pre-culture
with HYG
Pre-culture
with NAT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embocompgenomicsdpv2-220831142846-401857a5/85/Reticulate-evolution-in-yeasts-and-its-industrial-applications-56-320.jpg)
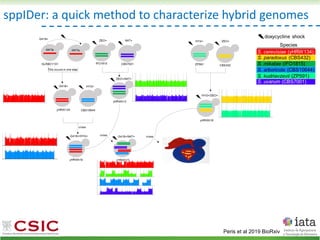
![iHyPr: iterative Hybrid Production method
Peris et al 2019 BioRxiv
HyPr (Hybrid Production) plasmid
doxycycline
shock
Vegetative yeast
mitochondrial genome
chromosome
diploid
>4G
Pre-culture
with ZEO
Pre-culture
with HYG
a/ a/
[pHMK34-HygMX]
[pHCT2-NatMX]
x
a/a /
a/a//
a/a/a/a
Selection in media
with NAT+HYG
>4G
a/
/
[pHRW32-ZeoMX]
x
a/a/a/a//
Selection in media
with HYG+ZEO
Pre-culture
with HYG
Pre-culture
with NAT
Pre-culture
with ZEO
a/a/a/a/a/a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embocompgenomicsdpv2-220831142846-401857a5/85/Reticulate-evolution-in-yeasts-and-its-industrial-applications-57-320.jpg)
![iHyPr: iterative Hybrid Production method
Peris et al 2019 BioRxiv
HyPr (Hybrid Production) plasmid
doxycycline
shock
Vegetative yeast
mitochondrial genome
chromosome
diploid
Pre-culture
with G418
>4G >4G
Pre-culture
with ZEO
Pre-culture
with HYG
a/ a/
[pHMK34-HygMX]
[pHCT2-NatMX]
x
a/a /
a/a//
a/a/a/a
Selection in media
with NAT+HYG
>4G
a/
/
[pHRW32-ZeoMX]
x
a/a/a/a//
Selection in media
with HYG+ZEO
Pre-culture
with HYG
Pre-culture
with NAT
x
a/a////
Reutilization of
NAT plasmid
Selection in media
with NAT+G418
Pre-culture
with ZEO
a/a/a/a/a/a
/////](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embocompgenomicsdpv2-220831142846-401857a5/85/Reticulate-evolution-in-yeasts-and-its-industrial-applications-58-320.jpg)