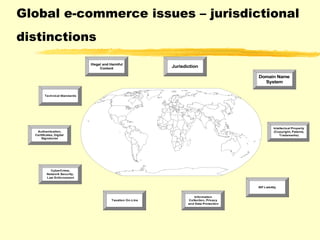
The document discusses several issues related to e-commerce and ICANN's jurisdiction. It notes that e-commerce occurs above the infrastructure layer and can involve various online business and information activities. It also discusses why emerging legal and regulatory frameworks are important as they impact online operations and the continued development of e-commerce. Several specific issues are examined, including authentication, privacy/data protection, copyright, content regulation, and cybercrime. The document concludes that many industries, opportunities, and consumers are impacted and challenges exist to avoid inconsistent laws and policies while balancing technical realities.







![Data Protection [Privacy] Protection of individuals with regard to the processing of personal data and on the free movement of such data. Personal data ranges from name, address, other. Collection, use and transmission of personally identifiable data – Collection on websites, customers, users, employees. Use for purposes other than intended Transferred by company, customers, or others to another party our third country.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s719a-1226683014407695-8/85/S719a-9-320.jpg)









