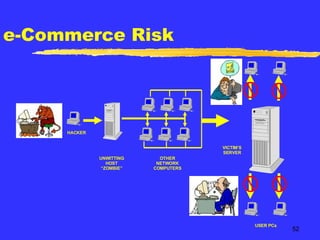
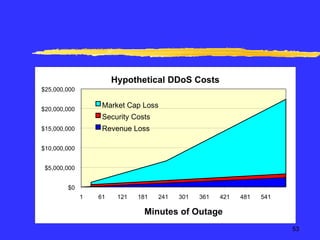
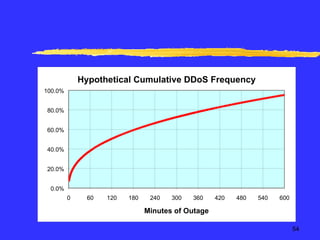
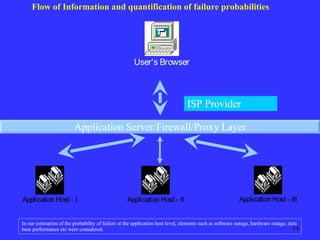
The document discusses quantifying the risks of an e-commerce website for an insurance company. It describes modeling different risk scenarios like hardware failures, software issues, hacking or denial of service attacks. The modeling was done using stochastic testing and Monte Carlo simulations to estimate potential losses. This allowed the company to better understand the risks and pricing of insuring an e-commerce site.










































![e-Commerce Risk Ingram Micro Inc. vs. American Guarantee & Liability Insurance Company “ Restricting the policy’s language to that proposed by American [i.e.that contained in the policy] would be archaic .”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecommerce2-1226683146789375-8/85/Ecommerce-2-44-320.jpg)