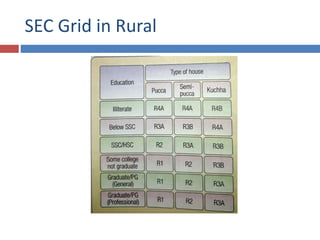
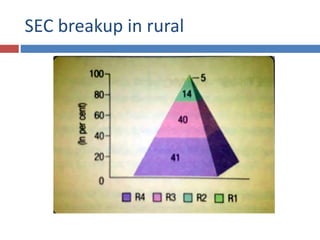
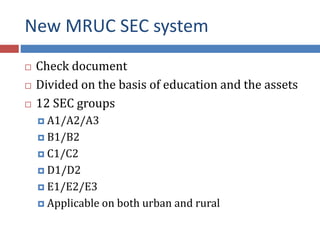
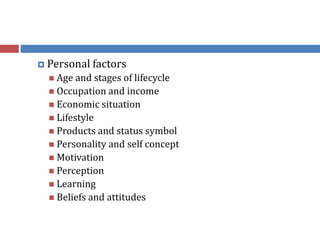
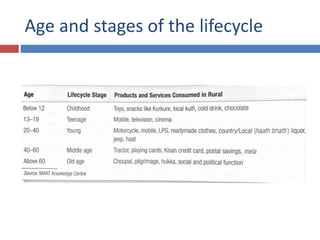
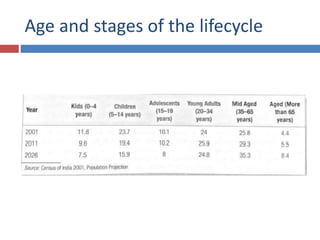
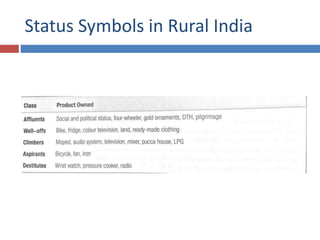
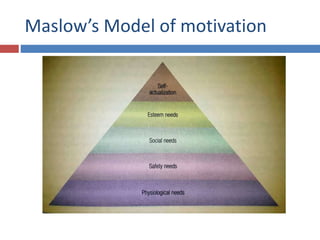
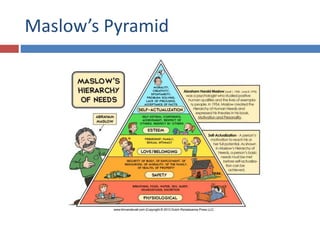
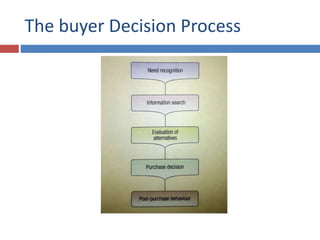
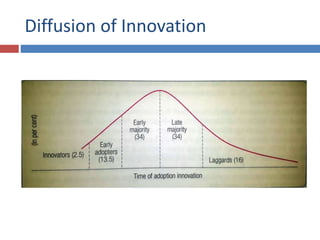
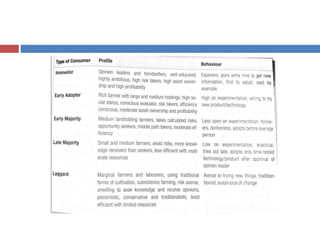
The document discusses factors that influence consumer behavior in rural markets. It outlines cultural, social, personal and psychological factors. Key points include that culture and social norms strongly impact rural consumers. Family and social groups are very influential. Rural consumers tend to be less adventurous and rely more on personal sources for information than commercial sources. Market segmentation models like SEC are used to classify and target different rural consumer groups. Opinion leaders play an important role in rural areas for product adoption.